|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Recktenwald D. (ed.), Radbruch A. (ed.) — Cell Separation Methods and Applications |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) 62
Ada see Adenosine deaminase
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) 77(figure)
Adeno-associated virus (AAV), plasmids 75
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) 81
Adhesion molecules 73 (table) 285
AIDS see Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Albumin 190
Analysis, residual cell. 188 198
Anemia, aplastic 290
Anemia, refractory 290
Antibody, fiuorochrome-conjugated 66 79
Antibody, fluorescein-conjugated 67 126
Antibody, OKT3 138
Antibody, phyccerjthrin-conjugated 66 122 126
Antibody, use in cell sorting 1 5 61 62 63 67 80 88 90 96 103 104 106 115 133—146 154 160 161 175—176 177 179 184 186 188 198 210 225 230 238 243 258 261 278
Antigen, use in cell sorting 1 65 68
Apoptosis 249 259—260
Avidin, columns 11 (table) 88—89 89
B cells 2 7 8 (figure) 34 51 163 164 272 273 274
B cells, depletion of 34
Bags, gas—permeable 69
Basic principles of 44—46
Beads, anti—immunoglobulin 183 188 191
Beads, avidin 91 92 156 161 179 210
Beads, coating protocols 189
Beads, Dynal 176 177 181 210 232
Beads, fluorochrome 156
Beads, hapten 156 164
Beads, incubating protocols 191
Beads, latex 220 221 221
Beads, magnetic 154 155 220 221 229
Beads, polyacrylamide 88 89 90 91
Beads, streptavidin 188 228
Biohazard 248 265
Biotin 228
Biotin columns 88—89 89 156 162
Blood, cord 88 98 117 284 284
Blood, murine 2
Bone marrow cells 19 52 69 70 75 90 246 258 261 284
Bone marrow cells, mononuclear cells of 63 65 66 67 68 74
Bone marrow cells, transplantation of 52—53 62 80—81 94 95 104 108 111 114 121 146 166 261 285
Bone marrow cells, vertebral, use of 114—117 118 119
Borohydride reduction 156
Calcium 239
Cancer 82 289
Cancer, breast 94 95 96 98 170 182 186 289
Cancer, lung 289
Cancer, neuroblastoma 182
Cancer, ovarian 72
Cancer, small-cell lung 182
Catcher tube sorting 248—249 248
Cell cycle, separation of cells according to 51 258
Cell selection, negative 133 158 159—160 162 181 182 200
Cell selection, positive 133 158 159—160 162—166 181 182 200 201
Cell selection, two-step 200—201
Cell selectors, Ceprate SC 87—101
Cell selectors, MacroCELLector 62—63 78
Cell selectors, RPR CELLector 62—66
Cell separation, direct 191
Cell separation, direct versus indirect 183—186 184 185
Cell separation, indirect 187 (figure) 191
Cell separation, using flow cytometry for 237—265
Cell sorting, efficacy of 252—254
Cell sorting, protocols 2—10 11 20 63
Cell sorting, punty of 252—254
cell types also see specific names
Cell types, 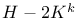 273 274 274 276 277 273 274 274 276 277
Cell types, CD15 115 117
Cell types, CD19 99 164 165 222 224 284
Cell types, CD2 96
Cell types, CD20 27
Cell types, CD25 272
Cell types, CD3 51 (figure) 64 161 165 169 187
Cell types, CD34 16 19 20—24 25 28 29 30 34 48 50 52 53 63 64 66 67 68 70 75 77 91 94 98—99 103 115 117 169 170 171 183 190 258 279 283—290
Cell types, CD38 64 67 68
Cell types, CD4 64 66 81 99 112 126 162 273 275 276 278
Cell types, CD45 25 (figure) 30 162
Cell types, CD5 64 66 71 80 161 164 170
Cell types, CD56 99
Cell types, CD8 64 66 67 72 74 76 78 80 81 126 272
Cell types, gene—modified 77—78 261
Cell types, MOLT-4 107
Cell volume, electronic measurement of 245
Cenirifugation 24 25 27 28 52
Centrifugal elutriation 43—54
CFU see Colony—forming units
Chambers, types used in 47
Chemotherapy 290
Chimerism 113
Chromatography 159
Chromium-release assay 26 74 142
Chromosomes 226—229 238 262
Chymopapain 195
Clinical use 48 52 78 80—82 87 104 210 233 263 283—290
Closed systems 48
Cobalt 155
COBE 2991 27
Colony-forming units/cells (CFU/C) 19 24 34 283
Complement 9 10 11 176 201
Computer-assisted (CACE) 50
Cotton wool 5 6 11
Cryopreservation 289 290
Cyanogen bromide 157
Cytokeratin 166 167
Cytokines see Specific names
Cytostatic drugs 52
Dendritic cells 51 53 82 103 104 126 162 163
Density gradient material, characteristics of 17
Density—adjusted cell sorting (DACS) 29—34
DETACHaBEAD 195
Diaminohexane 157
Dimethylsulfoxide (DSMO) 29 93 114
Diphtheria toxin 134
Dispase 195
DNA, analysis 126 228 239 249
DNA, transfection 271—279
DSMO see Dimethylsulfoxide
Dyspnea 29
Electromagnets 216—217
Electronic gate dissemination 2
Elutriation 106
Endocrine cells 225
Eosin 145
Eosinophils 126
Epithelial cells 51 225 226
Erythrocytes 2 3 50 115 117 162 164 223 224 264
Erythrocytes, lysis of 2
Erythroid burst-forming cells (E—BFC) 70
Erythropoietin (EPO) 290
Ex vivo expansion 98 289 290
FACS see Fluorescence-activated cell sorting
Fc receptor 157 160 181
Ficoll 1 2 3 4 4 11 15 24 25 107 109 111 117 142 259
Flow cytometry 67 145 153 222 225 237—265 241 272 274
Flow cytometry, multiparameter 239—245 244
Flow cytometry, one-parameter 50 286
Flow cytometry, two-parameter 50 67 116
Fluidic-switching sorting 249—250 249
Fluorescence cell sorting (FACS) 1 2 15 33 158 159 163 165 167 170
Fluorochromes 237 238—239
Forward scatter 240 242 245
Gastrin cells 224—225
Gaucher’s disease 98
Gene, CAT 75 273
Gene, env 72
Gene, gagpol 11
Gene, mdr 273
Gene, nef 72
Gene, rev 81
| Gene, therapy 81 98 104 166 277 279 289
Gene, tk 278
Gene, transduction 63
Gene, transfer 75
Glutaraldehyde 225
Glycophorin 109 117 120 162
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) 26 27 28 52 81 96 99 103 288—289
Graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) 26 288—289
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming cell (GM-CFC) 70 95 95 96
Granuloses 3 109 223
GVHD see Graft-versus-host disease
GVL see Graft-versus-leukemia
Hematopoietic progenitor cells 18 19 20—23 25 27 29 50
Hemoglobinuria 29
Heparin 143
Hepatocytes 51
High-density particles, separation using 103—129
HIV see Human immunodeficiency virus
Human immunodeficiency virus 98
Human immunodeficiency virus, gene 72 74 75
Human immunodeficiency virus, infection 248
IFN see Interferon
IL see Interleukin
Immunoabsorption 258
Immunoaffinity 134
Immunoglobulin, presence of 67
Immunomagnetic techniques 134 135 139 153—171 175—201 209—233 258 273 275
Immunomagnetic techniques, continuous 211—233
Immunotherapy 53 81 88 101
Immunotoxin 176 201
Integrins 285
Interferon (IFN),  61 61
Interferon (IFN),  53 61 53 61
Interleukin (IL), -2 61 73 76 81 272
Interleukin (IL), -3 75 99 285
Interleukin (IL), -6 75 99
Internet 238
Investigational device exemption (IDE) 140
Investigational new drug (IND) 140
Iron 155
Iron, dextran 155—156 156 159
Iron, oxide 210
Isothiocyanate 157 165 170 273 277
Keratinocytes 51
Kupffer cells 51
L-leucine methyl ester 1
Laser 239—240 240 242 242 247
Laser, tweezers 246
Lectin 62
Leukemia 285—286
Leukemia, acute lymphocytic (ALL) 81 286
Leukemia, acute myelogenous (AML) 81 286
Leukemia, chronic myelogenous (CML) 81 286
Leukocytes 2 53 162 190 285
Lipofection 81
Lipopolysaccharide 270
Liposomes 75
Liver transplantation 113
Long-term culture-initiating cell (LTCIC) 283
Lymphocytes 1 18 47 50 51 100 103 109 126 139 222 224 225 243 245 258 279
Lymphoma 124—125 135 182
Macrophages 2 8 190
Macs see Magnetic cell sorting
Magnetic cell separation 192—195
Magnetic cell sorting (MACS) 1 2 153—171 272 274 274 275 276
Magnetic filter 211 224
Major histocompatibility class (MHC) I 273
Major histocompatibility class (MHC) II 10 276 278
Markers, activation 73 (table)
Markers, other 73 (table)
Markers, surface 271—279
Medium, Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle (DMEM) 63 75
Melanoma-associated antigens 53
Methacrylate 155
Methylcellulose 15
Metrizamide 15
MHC see Major histocompatiblity class
Monocles 1 18 43 50 57 53 162 163 223
Mpl ligand 285 290
Myelocytes 70
N-acetyl galactosamine 63
N-hydroxy-succinimide 157
Natural killer (NK) cells 1 18 26 27 29 162 163
Nen’e growth factor receptor 78
Neodymium-iron-boran magnets 180
Neutrophils 70
Neutrophils, recovery of, after transplantation 34 94 290
NHL see Non-Hodgkir’s lymphoma
Nickel 104 105 106 107 107 108
Nitrocellulose filters 259
NK cells see natural killer cells
Non-Hodgkiris lymphoma 19
Nuclei, separation of 250
Nylon wool 2 8 11 190
O-sialoglycoprotease 191
Optical scanning 212 220 229 237 242
Osteoblasts 18
Pancreatic islets 249 262—263
Panning 1 5 7 8 11 134 272 275
Parasites 249
PBMC see Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
PBPC see Peripheral blood progenitor cells
peg see Polyethylene glycol
Percoll 3 (table) 17—18 19 24 45
Perfusion system 212
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) 3 5 50 62 64 66 72 76 161 162 163 165 167
Peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC) 63—64 87 90 284
Peroxisomes 230 231
Phagocytosis 190 191
Phycoerythrin 222 273
Phytohemagglutinin 65 74 76 81
Plasma membrane 239 245 250
Platelets 28 (figure) 64 111 115 223
Platelets, recovery of 34 94
Poisson statistics 252—253
Polyacrylamide 88
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 17
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) 106 124 125 135 145 198 249 259
Polysaccharide 155
Polystyrene, immunoaffinity devices 61—82 176—201 210
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) 17
Prion 279
Promyelocytes 70
Pulmonary edema 29
PVP see Polyvinylpyrrolidone
QBENDl0 283
Rare cells 210 213 224 249 264 211 275
Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rHuG-CSF) 19 20 23 27 28 30 34 50 52 94 94 97 97 117 120 284 289
Recombinant human granulocyte—macrophage colony—stimulating factor (rHuGM-CSF) 51 52 53 289
Recombinant human interleukin (rHuIL) -1 53 69
Recombinant human interleukin (rHuIL) -11 290
Recombinant human interleukin (rHuIL) -2 65
Recombinant human interleukin (rHuIL) -3 69 289 290
Recombinant human interleukin (rHuIL) -7 72
Recombinant human stem cell factor (rHuSCF) 69
Recovery of cells 257
Red blood cell see Erythrocytes
Reducing sample size by 48
Renal cell carcinoma 81
Renal cell carcinoma, cell line 61
RHuG-CSF see Recombinant human granulocyte colony-Renal cell carcinomastinrulating factor
RHuGM-CSF see Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor
RHuIL see Recombinant human interleukin
RHuSCF see Recombinant human stem cell factor
Ricin 134
RNA 239
Rosette 1 11 179—180 181 192 193 195 211 275
Samarium-cobalt magnets 180
SBA see Soybean agglutinin
Sephadex G-10 11 (table)
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте