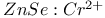јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Powell R. Ч Physics of Solid State Laser Materials (Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics Series)
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Physics of Solid State Laser Materials (Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics Series)јвтор: Powell R. јннотаци€: This graduate-level text presents the fundamental physics of solid-state lasers, including the basis of laser action and the optical and electronic properties of laser materials. After an overview of the topic, the first part begins with a review of quantum mechanics and solid-state physics, spectroscopy, and crystal field theory; it then treats the quantum theory of radiation, the emission and absorption of radiation, and nonlinear optics; concluding with discussions of lattice vibrations and ion-ion interactions, and their effects on optical properties and laser action. The second part treats specific solid-state laser materials, the prototypical ruby and Nd-YAG systems being treated in greatest detail; and the book concludes with a discussion of novel and non-standard materials. Some knowledge of quantum mechanics and solid-state physics is assumed, but the discussion is as self-contained as possible, making this an excellent reference, as well as useful for independent study.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1998 оличество страниц: 437ƒобавлена в каталог: 22.12.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
285Ч287 286 287 286 287 382 407Ч408 273 287Ч288 271Ч272 290Ч292 215Ч270 261 263 232 261 245Ч251 258Ч259 261Ч263 216Ч224 224Ч229 264Ч265 263 226 261 264Ч265 233Ч237 233Ч237 233 237Ч253 232 233 254Ч270 271 282Ч285 382 340 372Ч377 289Ч290 408Ч411 340 364Ч371 376 364 369Ч371 364Ч368 343Ч344 341Ч342 344 376 350 287Ч288 287Ч288 287 287Ч288 287Ч288 289Ч290 290 290 290 289 272 282 286 294Ч360 341Ч345 348Ч350 309Ч319 317 299 340 295Ч299 349Ч353 318 359Ч363 341 298 314 296Ч301 300Ч301 341 275 289Ч290 414 382Ч383 147Ч156 148 149Ч153 149Ч153 153Ч155 145Ч156 271Ч272 276Ч282 410 382 340 365Ч368 371Ч372 376 365Ч368 340 371Ч372 376 382Ч384 272 282 288Ч289 282Ч286 284Ч285 285 283 285 285 284Ч285 285 285 285 372Ч375 341Ч342 347Ч348 347Ч348 328Ч329 290Ч292 291 291 291 291 291 Absorption, coefficient 5 104 Absorption, cross section 6 104 108 113Ч115 Absorption, excited state 24 26 111 115 Absorption, photon 3Ч7 25Ч26 93Ч94 104 Absorption, transition probability 4 Absorption, transition rate 4 93Ч94 Absorption, two-photon 110Ч115 Accepting modes of vibration 165 Acceptor ion 182 Activation energy 157Ч159 195 203 Activator ion 182 Active ion distribution 29Ч30 175Ч177 181Ч182 191Ч192 196 205 259 276 285 343Ч344 352 ADP 393 Alexandrite 254Ч261 Alexandrite, absorption spectrum 255Ч257 262 Alexandrite, energy levels 256 Alexandrite, energy transfer 258Ч260 Alexandrite, exchange coupled pairs 258Ч259 Alexandrite, fluorescence lifetime 256Ч258 Alexandrite, fluorescence spectrum 256Ч259 262 Alexandrite, N-lines 258Ч259 Alexandrite, quantum efficiency 260 Alexandrite, R-lines 256 Alexandrite, site occupancy 255 Alexandrite, stimulated emission cross section 260 Alexandrite, vibronic laser 260 Allowed transition 94Ч98 Amplification 7 Angular momentum, coupling 37Ч49 177Ч182 Angular momentum, electron 33Ч49 171 Angular momentum, LS coupling 37Ч42 96Ч98 Angular momentum, Quantum number 34Ч38 Angular momentum, raising and lowering operators 35 Angular momentum, Russell Ч Saunders coupling 37Ч42 96Ч98 Annihilation operator, phonon 120Ч122 Annihilation operator, photon 87Ч88 Antiferromagnetic coupling 179Ч182 Atomic polarizability 108 113 261 263Ч267 328Ч329 329 342 352 Avalanche absorption 344 Back transfer 204 Banana 393 Basis 53 BBO 393 Beer Ч Lambert law 5 104 BEL: Nd 341 Bohr magneton 42 Boltzmann distribution 131 159 162 165 180Ч181 Borate 261 Born approximation 201 Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation 160 169Ч174 Bose Ч Einstein distribution function 130 Branching ratio 315 325 341Ч342 353 Branching ratio, R-parameter 341 Branching ratio, x-parameter 341 Cavity dumping 22 Cavity quality factor 20 CHARACTER 52Ч54 Chromium 215Ч271 282Ч285 290Ч292 Chrysoberyl 255 class 51Ч53 Clausius Ч Mossatti relationship 108 Clebsch Ч Gordan coefficients 38Ч41 56Ч57 72Ч75 227Ч229 303 Coherence factor 194 Collision broadening 103 Color center lasers 407Ч411 Colquiriite 265 Concentration quenching 176 202Ч203 245 334 336 347Ч350 355Ч357 Condon approximation 60Ч62 Configuration mixing 240 310Ч319 Configurational coordinate diagram 157Ч160 249 250 280Ч281 Corundum 237 Coulomb gauge 85 88 Coulomb integral 46Ч48 81 219 230Ч231 Coulomb interaction 32Ч33 36 41 177 Creation operator, phonon 120Ч122 Creation operator, photon 87Ч88 Critical concentration 189 Critical interaction distance 189 Crystal field strength 58Ч59 77Ч80 121Ч122 159 160 232 261 267Ч268 271Ч275 285 301Ч309 Crystal field strength, operator equivalents 302 306Ч309 Crystal field strength, Racah algebra 302 Crystal field strength, tensor operators 301 Crystal field theory 57Ч59 Crystal growth 27Ч28 343Ч344 Debye model 130 135Ч136 142 146Ч147 194 Density of states, phonon 129Ч130 142 Density of states, phonon, Debye cutoff frequency 130 142 147 Density of states, phonon, Debye temperature 142Ч147 156 Density of states, photon 93Ч94 Diagonal sum rule 44 Dieke diagram 340 Diffusion model 199Ч203 Diffusion model, diffusion coefficient 199 202Ч203 213 Diffusion model, diffusion length 199 213 Diffusion model, mean-free-path 203 213 Dipole moment operator 95 Direct transitions 127Ч132 143 147 Donor ion 182 Doppler broadening 103 Dye lasers 411Ч412 ED-2: Nd 351Ч353 Effective Bohr radius 190 Effective cross section 19Ч20 Effective phonon mode 134 Efficiency 7 12 14Ч16 18 Efficiency, pump efficiency 12 19 Efficiency, quantum efficiency 7 106 Efficiency, slope efficiency 16 Einstein coefficients 94 100 104Ч105 188 315 Electromagnetic multipole-multipole interaction 184Ч185 Electron configuration 66Ч69 Electron-phonon coupling 121Ч122 127 154 156Ч160 169Ч170 269 363 Electron-phonon coupling, anharmonic electron-phonon coupling 156-157 Electron-phonon coupling, strong electron-phonon coupling 156Ч174 Electron-phonon coupling, weak electron-phonon coupling 127Ч147 Electron-phonon interaction 121Ч122 158Ч160 169Ч171 Emerald 261Ч262 Emission, photon 4 11 Emission, photon, effective cross section 19Ч20 Emission, photon, emission cross section 6 19Ч20 104Ч105 Emission, photon, emission intensity 105Ч107 Emission, photon, emission lifetime see "Lifetime" Emission, photon, emission transition probability 7 315 Emission, photon, fluorescence emission 105 Emission, photon, spontaneous emission 4 7 26 Emission, photon, spontaneous emission rate 93Ч95 Emission, photon, stimulated emission 6 19Ч20 Emission, photon, stimulated emission rate 13 93Ч94 103Ч105 Energy gap law 134 168 195 331Ч332 359Ч363 Energy migration 176Ч177 Energy migration, diffusion theory 198Ч203 Energy migration, hopping model 196Ч198 Energy migration, Kenkre model 365Ч368 Energy migration, Monte Carlo simulation 202 Energy migration, random walk 196Ч198 Energy transfer 25 175 333Ч336 345Ч348 364Ч371 Energy transfer rate 188Ч192 Energy transfer rate, diffusion limited energy transfer rate 201 Energy transfer rate, diffusion model 199Ч200 Energy transfer rate, electric dipole-dipole interaction 188Ч191 Energy transfer rate, electric dipole-quadrupole interaction 189 Energy transfer rate, electric quadrupole-quadrupole interaction 189 Energy transfer rate, exchange interaction 189Ч190 Energy transfer rate, multistep random walk 196Ч199 Energy transfer rate, phenomenological energy transfer rate parameter 206Ч209 Energy transfer rate, phonon-assisted energy transfer 192Ч195 Energy transfer rate, trap limited energy transfer rate 201 Energy transfer, coherent energy transfer 203 213 Energy transfer, phonon-assisted energy transfer 192Ч195 Energy transfer, radiative energy transfer 175 5.31 Energy transfer, resonant energy transfer 182Ч192 Energy transfer, strong coupling 175 Energy transfer, weak coupling 175 Energy, pulse 21 Exchange integral 46Ч48 81 219 230Ч231 exchange interaction 175 177Ч182 184 189Ч190 245Ч250 Excited state absorption (ESA) 111 115 251 261 263 285 287 289 323 326Ч327 343 357 Exciton 176Ч177 Exciton, diffusion 199Ч203 212Ч213 Exciton, Frenkel 176 Exciton, localized 196 Exciton, mean-free-path 203 212 Exciton, migration 196Ч213 Exciton, random walk 196Ч198 Exciton, self-trapped 203 Exciton, trapping 196 Exciton, Wannier 177 f-number 6 99Ч100 105 FAP: Nd 341 Fermi Ч Dirac statistics 33 Fermi's golden rule 92Ч93 129 162 183 Ferromagnetic coupling 179Ч181 Fiber lasers 414Ч415 Findley Ч Clay analysis 15Ч16 Fluorescence emission 105Ч107 207Ч209 Fluorescence linenarrowing 210Ч211 354Ч357 Foerster Ч Dexter energy transfer process 183 Forbidden transition 96Ч98 Forced electric dipole transition 235 309Ч319 Forsterite 282 Four-level system 8Ч17 18 Frank Ч Condon overlap 157Ч158 165 250 Gain 8 14Ч16 Gain, cavity roundtrip gain 8 Gain, saturated gain 13 Gain, small signal gain 8 13Ч17 GFG 261 269Ч270 GGG 261Ч262 GGG: Nd 341 Glass: Nd 349Ч353 Glass: Nd, branching ratios 353Ч354 Glass: Nd, effective linewidth 353 Glass: Nd, emission cross section 353 Glass: Nd, fluorescence linenarrowing 354Ч357 Glass: Nd, Judd Ч Ofelt parameters 353 Glass: Nd, radiative lifetime 353 Group 51 Group of the wavevector 149 Group, basis 53 Group, character 52Ч54
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



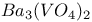 : Mn
: Mn 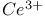
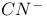
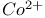
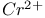
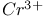
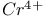
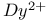
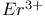 lasers
lasers 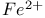
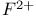
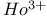 lasers
lasers 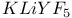 : Nd
: Nd 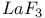 : Nd
: Nd 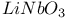 : Nd
: Nd 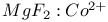
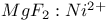
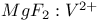
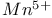
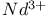
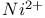
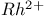
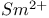
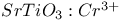
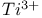
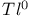
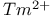
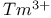
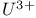
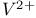
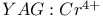
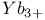 lasers
lasers 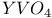 : Nd
: Nd 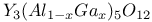 : Nd
: Nd