|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Kittel C., Knight W., Ruderman M. Ч Berkeley physics course 1. Mechanics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Phase 204 206Ч207
Phase angle, driven oscillator 222 226Ч231 235
Photon 366
Photon deflection by sun 12Ч13 404Ч405
Physical laws 5Ч7
Piazzi, G. 170
Pions 337Ч339 383Ч385
Planck's constant 300 366
Plane, equation of 36
Planets, angular momentum of 195Ч197 240
Planets, discovery of 10 170Ч171
Planets, orbits of 288Ч289
Planets, orbits of Kepler's laws 190 286Ч288
Planets, periods 288Ч289
Pluto, discovery of 10
Point of contact 249
Polar coordinates 54
Position vector 40Ч41
Positron 292 382
Positronium 292
Potential 160Ч161
Potential difference 160Ч161 164
Potential electrostatic 158Ч161 164Ч166
potential energy 137Ч143 148Ч152 155Ч166 270Ч277
Potential energy electrostatic 160 164Ч167
Potential energy in electric field 158Ч159 164
Potential energy of harmonic oscillator 204 206
Potential energy, effective centrifugal 193Ч194 198Ч199 295
Potential energy, inverse-first-power law of 158Ч159 271
Potential gravitational 158Ч159 161Ч164 270Ч274
Pound, R.V. 402
Power 167
Power absorption, harmonic oscillator 222 230Ч231 235
Power dissipation, harmonic oscillator 218Ч221
Precession of gyroscope 263
Precession of gyroscope of perihelion of Mercury 13 405Ч406
Pressure, radiation 366Ч367
Principal axes 258Ч261
Products of inertia 257
Projectile 63Ч65 163Ч164
Projection 34 47
Proper length 329
Proper time 333Ч339 352
Proton 69 73Ч74 80 164Ч165 387
Proton in crossed electric and magnetic fields 130Ч131
Proton scattering by heavy nucleus 191
Pseudoforce 112
Psychology of invention 303
Pythagorean Theorem 8 9 206
Quality factor (Q) 220Ч221
Quantum mechanics, laws of 6 145
RADIANS 15 52
Radians per second 45
Radiation pressure 366Ч368
Radius of earth 4
Radius of electron 278Ч279
Radius of universe 4 320
Random energy, heat 150 155
Random flight 51
RANGE 65
Rebka, G.A., Jr. 402
Recessional red shift 318Ч320
Recessional velocity of galaxy 345
Recoilless emission 371Ч372
Red shift gravitational 402Ч404
Red shift recessional 318Ч320 see
Reduced mass 289Ч293
Reference frames 102Ч131
Reference frames Galilean 106 109Ч110 115Ч122
Reference frames inertial 102Ч110
Reference frames noninertial 112Ч115
Reference frames rotating 113 127Ч130
Reference frames, accelerated 102Ч104 111Ч115
Reference frames, center of mass 122 178 382
Reference frames, transformations of 115Ч120 326Ч329
Refractive medium 300
Relativistic acceleration 376Ч382
Relativistic cyclotron 381
Relativistic dynamics 350Ч392
Relativistic energy 355Ч368
Relativistic mass 355
Relativistic momentum 350Ч355
Relativity, general theory of 13 398Ч407
Relativity, Special Theory of 5 116 118 326Ч406
Relaxation time 215 224
Resistance 212
Resisting force 232
Resonance 222 228 235
Rest mass 355
Rest mass, energy 358
Restitution coefficient 198
Restoring force, linear 149
Reversible pendulum 265
Right-hand-thread rule 37Ч38
Right-handed coordinate system 38
Rigid bodies 240Ч266
Rigid bodies, equations of motion 240Ч241
Rigid bodies, particles in 240
Rigid bodies, two-particle rotator 255Ч256 260
RNA 4
Rocket 199 see
Roemer, O. 301Ч302
Roll, P.G. 66 400
Rolling without slipping 249Ч251
Rotating bucket 110Ч111
Rotating coordinate systems 102Ч108 113 127Ч130 259
Rotating mirrors 305Ч306
Rotation about fixed axes 255
Rotation finite 33
Rotation of galaxies 323
Rotation of rigid body 240Ч266
Rotation, kinetic energy of 241 243 250
Rotational invariance 191Ч192
Sachs, M. 339
Sadeh, D. 341
Satellites in orbit 66Ч67 168
Satellites, angular momentum of 197
Satellites, deceleration of 183
Satellites, period of 66Ч67
Satellites, speed of 183
scalar 29
Scalar field 47
Scalar product 33Ч37 48
Scalar triple product 39
Scalar, multiplication by 31
Scattering, angle 180Ч182
Schiff, L.I. 404
Schwarzschild, K. 11
Sea, on earth 295
Second, definition 61
Self-energy 275Ч277
Semi-major, semi-minor axes of ellipse 284
Series expansion 53
Serpukov (accelerator) 19 381
Shapiro, I.I. 405
SI units electrical 68
SI units mechanical 62
simple harmonic motion 202Ч223 253Ч254 293
simple pendulum 204Ч206
Simultaneity 330Ч332
Sines, law of 39Ч40
Sirius, B. 15
Skin depth 307
Solar constant 371
Solar energy 279 364Ч365
Solar system, angular momentum 195Ч196
| Solid sphere, potential energy of point mass 274Ч275
Sommerfield, A. 240
Sound, Doppler shift 317 346
Space vehicle 183Ч184
Space, properties of 8Ч10 13 14 108 326
Speed of light, (c) 72 300Ч322 326Ч327
Speed of light, (c), ultimate 320Ч321
Sphere, gravitational self-energy 275Ч277
Spherical excess 10
spherical polar coordinates 54
Spherical shell, potential energy in field of 271Ч274
Spherical triangle 8Ч9 15
Spin 189
Spinning top 240 261Ч263
Spring 149 202Ч204
Spring constant 149 204 233
Stable equilibrium 212
Starlight, aberration of 302Ч305
Stars binary 295
Stars novae 277 323
Stars rotation 323
Stars variable 323
Statcoulomb 68 73
Static equilibrium 279
Statistical mechanics 5
Statvolt 70 74 161 164Ч165
Steady state, harmonic oscillator 221 226
Stellar energy 277 364Ч365
Stellar parallax 322
Stilwell, G.R. 343
Stokes' Law 215
Sun energy 277 364Ч365
Sun photon deflection 12 404Ч405
Sunlight 367
Superposition 202 222
Superposition principle 222
Supersonic plane 129
Symmetry 136 258
Synchronization 334Ч336
Synchrotron 392Ч394
Taylor expansion 53
Taylor, J.H. 331
Tension in string 85 249
Tensor 28
terminal velocity 216Ч217 232Ч233
Tesla, N. 71
Tesla, unit 71
Tests of general relativity 405
Tetherball 198
Thermal energy 150
Thermal expansion 225
Third harmonic 226
Threshold energy 376 382Ч387
Threshold energy of antiproton 387
Time derivative 42Ч45
Time dilation 333Ч339
Time, proper 333Ч339
Top, spinning 261Ч263
torque 40 50 174 185Ч189 240Ч266
Torque about center of mass 252
Torque due to gravity 187Ч188
Torque internal 186Ч187
Torque rotating 256 260Ч261
Torricelli, E. 310
Transformation Galilean 116Ч122
Transformation Lorentz 326Ч346
Transformation of force 368
Transformation of momentum and energy 359Ч360 367
Transformation of rate of change of momentum 368Ч369
Transverse Doppler effect 344
Transverse electric field 344
Transverse momentum components 178Ч179
Trigonometrical parallax 11
Triple product of vectors 39
Turning points 157 206
Twin paradox 339
Two-body problem 289Ч293
Ultimate speed 320Ч321
Ultracentrifuge 102Ч104
Unit vector 29 34Ч35 42Ч43 48
Unit vector, derivatives of 43
Unit, astronomical 288
UNITS 61Ч62 67Ч72
Universal gravitation 65Ч67
Universe, age of 15 319Ч320
Universe, mass of 4
Universe, radius of 4 320
Uranus 170 288Ч289
Van de Graaff accelerator 320
Variable mass systems 182Ч185
Variable stars 323
Vector field 47
Vector(s) 28Ч49 55
Vector(s) components 34Ч35 49
Vector(s) derivatives 40Ч46 131Ч132
Vector(s) identities 55
Vector(s) magnitude 34
Vector(s) notation 28Ч29
Vector(s) position 40Ч41
Vector(s) products, triple 39
Vector(s) scalar product 33Ч37 48Ч49
Vector(s) subtraction 31
Vector(s) triple product, scalar 39
Vector(s) unit 29 35 42Ч43 48
Vector(s), acceleration 44Ч46
Vector(s), addition 31 49
Vector(s), vector product 37Ч40 71 76
Veksler, V. 392
Velocity 28 40 42Ч44 49 50 83Ч86 89
Velocity absolute and relative 115Ч116
Velocity addition see "Velocity transformation"
Velocity angular 45 52 241
Velocity escape 161Ч162 295
Velocity in rotating system 127Ч129
Velocity in viscous medium 215
Velocity of earth 310Ч317
Velocity of light 300Ч322
Velocity selector 130
Velocity terminal 216Ч217 232Ч233
Velocity transformation nonrelativistic 118Ч119
Velocity transformation relativistic 339Ч342
Venus (planet) 405
Vibrational frequencies 293
viscosity 215 224
Volt 70 72 160Ч161
Volume change 345
Volume of parallelopiped 39
Volume rate of sweeping out 36
Waterfall, energy conversion 150
Watt 167
Weber, J. 407
Weber, W.E. 71
Webers/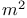 71 71
Weightlessness 114 407
Weisskopf, V.F. 330
Wheeler, J.A. 331
White dwarf star 403
Work 50 137 140 145Ч147 152Ч155
Work and relativistic energy 355
Work around closed path 152Ч155
Work rate of doing 36
Work, dimensions of 141
Work, units of 139
Zeeman effect 38
Zeeman, P. 38
Zero of potential energy 140Ч141 149 155 158Ч159
Zero rest mass 363 365Ч368
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте