|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Kittel C., Knight W., Ruderman M. Ч Berkeley physics course 1. Mechanics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Form invariance of physical laws 119
Form invariant 47
Foucault pendulum 109
Foucault rotating mirror 305Ч306
Frames of reference 102Ч124 313Ч314
Frames of reference, Galilean 116Ч123
Frames of reference, inertial 102Ч110 309Ч312
Frames of reference, relativistic 326Ч344 350Ч353
Free fall 113 147
frequency 5 46 202Ч222
Frequency angular 46 207Ч208
Frequency cyclotron 77 381
Frequency driving 226Ч230
Frequency fundamental 226
Frequency harmonic 225Ч226
Friction 86Ч89 154Ч155 214Ч215 250Ч252
Friction, coefficient of 87 266
fundamental frequency 226
Fundamental length 279
G 63Ч65
g, centrifugal correction to 105Ч106
g, values of 106
Galaxy (ies) 107
Galaxy (ies), diameter 194
Galaxy (ies), gravitational energy 276
Galaxy (ies), mass 195
Galaxy (ies), motion in 295
Galaxy (ies), rotation 323
Galaxy (ies), shape 193Ч195
Galaxy (ies), velocity 318Ч319
Galilean frames of reference 116Ч123
Galilean invariance 102 115Ч122 174
Galilean transformation 116Ч122
Galilean transformation, failure of 309 313 326Ч327
Galileo Galilei 108Ч109
Galle, J.G. 170
Gamma rays 371Ч372 382Ч385
Gamma rays, recoil from 371Ч372
Gauss, C.F 9 170
Gauss, unit of magnetic field 71 73
Gaussian units 67Ч70
Genetics, DNA molecule in 6
Geodimeter 309
Geometry 7Ч14
Gibbs, J.W. 15 29
Gram, definition 62
Gravitational attraction 5 65Ч67 270Ч292
Gravitational energy 275
Gravitational energy of galaxy 276
Gravitational energy of sphere 276Ч277
Gravitational energy of stars 294
Gravitational energy of sun 277
Gravitational field 60 63 104
Gravitational field, uniform 63Ч65 154
Gravitational length 402
Gravitational mass 66 398Ч403
Gravitational mass of photons 400Ч403
Gravitational potential 158Ч163 271Ч279
Gravitational red shift 402Ч405
Gravitational self-energy 275Ч277
Gravitational waves 407
Greenstein, J.L. 407
Ground speed 128
Guidance, inertial 240
Gyrofrequency 77 80 381
Gyroradius 78 80 81 381
Gyroscope 240 261Ч263
Gyroscopic stabilization 263
Hadamard, J. 303
Hamiltonian 145
Harmonic frequency 225Ч226
Harmonic motion about equilibrium 212
harmonic oscillator 157 202Ч236 293
Harmonic oscillator, damped 217Ч221 226Ч231 233Ч234
Harmonic oscillator, driven 221Ч222 226Ч231 234Ч236
Harmonic oscillator, energy 204Ч206 213Ч214 218Ч220
Harmonic oscillator, power absorption 230Ч231
Harmonic oscillator, power dissipation 218Ч220
Havens, W.W., Jr. 337
Hayes, T.L. 22
HCL (hydrogen chloride) 293Ч294
Heat 155
Heaviside, O. 29
Helium 364Ч365
Helium-filled balloon 103
Helix 78
Hertz (unit) 5 208
HF (hydrogen fluoride) 293Ч294
Hole through earth 294
Hooke's law 149
Horsepower 167
Hydrogen atom 363
Hydrogen chloride 293Ч294
Hydrogen flouride 293Ч294
Hydrogen, burning of 364Ч365
Hyperbola 54
Impulse 138
Impulse approximation 405
Inclined plane 87 249
Inductance 202 210Ч212
Inelastic collision 83Ч84 120Ч122 360Ч361
Inertia see "Moment of inertia"
Inertial mass 66 398Ч400
Inertial reference frames 102Ч120 185 309Ч312
Initial conditions 94
Integral, line 145
Interferometer 312Ч316
Internal excitation 121
Internal forces 174Ч175 186Ч187 240
Internal torques 186Ч187 240
International System of units, SI units 68Ч72 159Ч161
Invariance 13 51 136
Invariance Galilean 119Ч122
Invariance Lorentz 328
Invariance of velocity of light (c) 317
Invariance rotational 14 191Ч192
Invariance translational 14
Invariants 46Ч47 50 328 357Ч358
Inverse Compton effect 389 391
Inverse-square-law force 66 158Ч160 270Ч292
Io, eclipses of 301
Ionization energy 197
Ions, high-speed 96Ч97
Isotropy of space 326
Ives, H.E. 343
Joule 139
Jupiter, eclipses of Io by 301 322
Kepler problem 280Ч284
Kepler's laws 190 286Ч289
Kerr cell 307Ч309
Kilogram, definition 62
kinetic energy 76 85 120Ч124 137Ч167 283Ч284
Kinetic energy of harmonic oscillator 213Ч214
Kinetic energy of rotation 241Ч263
Kinetic energy relativistic 320Ч321 355Ч357
Kinetic energy, dimensions of 141
Kinetic energy, random 155
Klein, F. 240
Krotkov, R. 66 400
Laboratory frame of reference 180Ч181 383Ч387
Ladder, forces on 197
Lagrangian 145
Larmor, J. 328
Law(s) Hooke's 149
Law(s) of classical mechanics 5
Law(s) of cosines 35
Law(s) of electrodynamics 6
Law(s) of physics 5Ч7 326
Law(s) of quantum mechanics 6
Law(s) of sines 38Ч39 see "Newton's "Newton's
| Lawrence, E.O. 95Ч99
LC circuit 209Ч212
LCR circuit 212
Length in Galilean transformation 116Ч118
Length, contraction parallel to relative velocity 329Ч332
Length, perpendicular to relative velocity 332Ч333
Leverrier, U.J.J. 171
Life 4
Lifetime of particles 336Ч339
Lift force 129
Light year 4 12 15
Light, curved path of 12Ч13 404Ч405
Light, speed of 72 300Ч322 326Ч327
Lilliequist, Carl 12
Line integral 145
Linear equation 218
Linear momentum, conservation of 14 82Ч85 120Ч124 174Ч181 350Ч355
Linear response 202 222
Linear restoring force 149Ч150
Livingston, M.S. 95Ч99
Loar, H.H. 337
Local Group 107
Longitudinal acceleration 73Ч74 376Ч378
Longitudinal Doppler effect 342Ч344
Loop the loop 169
Lorentz force 72 154
Lorentz invariant 328 352 357
Lorentz transformation 136 326Ч343 350Ч369
Lorentz Ч FitzGerald contraction 330
Mach's principle 111
Magnetic field 70Ч72 76Ч78 81Ч82 97 154 380Ч382
Magnetic field and electric, crossed 130Ч131
Magnetic focusing 81
Magnetic force 40 70Ч72 76Ч78 81Ч82 380Ч382
Magnitude of vector 28 29 35 46Ч47
MARS 23 24
Mass 58 60 62
Mass gravitational 66 398Ч403
Mass inertial 66 398Ч401
Mass of earth 4
Mass of electron 72
Mass of photon 400Ч405 572
Mass of Sun 4
Mass on spring 202Ч204
Mass reduced 290Ч293
Mass relativistic 355
Mass rest 355 357 358
Mass spectrometer 169
Mass, units of 62
Mass-energy conversions 362Ч365 372
Mass-energy equivalence 357Ч359 362Ч365 372
Mathematical notes 51Ч53 93Ч94 231Ч236
Maxwell, J.C. 310
McDonald, D.F. 301
McMillan, E.M. 392Ч395
McVitties, G.C. 319
Mechanics, classical 5
Mercury, orbit of 12Ч13 405Ч406
Mesons  344Ч345 344Ч345
Mesons  337 337
Mesons 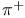 337 337
Mesons 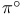 , photo production 383Ч385 , photo production 383Ч385
Meter stick (length) 118
Meter, definition 62
Michelson Ч Morley experiments 312Ч317 326
Michelson, A.A. 306 312 322
Milky Way 107
Molecules, vibration of 293Ч294
Moment of force see "Torque"
Moment of inertia 242Ч246 257
Moment of inertia of disk 245
Moment of inertia of plate 246
Moment of inertia of ring 244
Moment of inertia of rod 245
Moment of inertia of sphere 246
Moment of inertia of triangle 264
Momentum linear 58 83 174Ч181
Momentum of photon 366
Momentum relativistic 350Ч355 376Ч382
Momentum selector 81
Momentum total, for particle system 174
Momentum transverse 178
Momentum, conservation of 59 82Ч85 120Ч124 174 350Ч355
Momentum-energy transformation 359Ч360
Morley, E.W. 312
Mossbauer effect 372
Moving clocks 333
Mulligan, J.F. 301
Neptune, angular momentum of 195Ч196
Neptune, discovery of 10 170Ч171
Neutrino 326 337 344 365
Neutron decay 370
Neutron-proton force 271
New particles 376 385Ч387
Newkirk, Gordon 12
Newton (unit) 58
Newton pendulum 399 408
Newton rotating bucket example 110Ч111
Newton's laws of motion 13 58Ч60 102 398
Newtons law of gravitation 65Ч67
Noninertial frame 111Ч115
Nonrelativistic dynamics 58
novae 321
Nuclear reactions 362Ч365
Nuclei, binding energy 363Ч365
One-body problem (from two-body problem) 289Ч294
Orbits circular 44Ч46 66Ч67 284Ч286
Orbits equation and eccentricity 279Ч289
Orbits of planets 288
Origin of elements 365
Orthogonal axes 34 38
Oscillator 202Ч236
Oscillator anharmonic 224Ч226
Oscillator critically damped 234
Oscillator damped 217Ч221 226Ч231
Oscillator driven 221Ч222 226Ч231 234Ч236
Oscillator overdamped 234
parabola 54 64 283 286
Parallax 11
Parallax stellar 322
Parallel-axis theorem 242Ч247
Parallelogram law of addition 31
Parallelogram, area of 39
Parallelopiped, volume of 39 50
Parsec 15 288 289
Partial derivatives 156Ч157
Particles in rigid body 240Ч241
Particles interacting 174Ч175
Particles with zero rest mass 365Ч368
Particles, acceleration of 45
Particles, collision of see "Collision"
Particles, lifetime of 337Ч339
Particles, orbits of 279Ч292
Particles, velocity of 42
path integral 153
Pendulum 204Ч206
Pendulum compound 253
Pendulum Foucault 114Ч115
Pendulum large amplitude 226
Pendulum Newton 399 408
Pendulum nonlinear effects 224Ч226
Pendulum reversible 265
Perihelion of Mercury, precession 13 405Ч406
Period 46
Period oscillator 204Ч212
Period planets 288Ч289
Period satellite 67
Perpendicular axis theorem 244
Perpetual motion device 136
Perturbation 225
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте





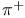
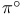 , photo production
, photo production