|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gorenstein D., Lyons R., Solomon R. Ч Classification of the Finite Simple Groups (Vol. 1) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Peterfalvi, T. 48Ч49 96 107 138
Phan, K.-W. 35 71
Presentation 31Ч35
Presentation of classical groups 35
Presentation of symmetric groups 32 36 68Ч70
Presentation, Steinberg presentation of groups of Lie type 32 33 36 51 118
Presentation, Steinberg presentation of groups of Lie type, a la Curtis Ч Tits 34 67 70
Presentation, Steinberg presentation of groups of Lie type, a la Gilman Ч Griess 35 67 71
Pumpup 22 127
Pumpup as 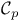 , , 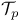 , or , or 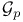 -group 103 114 -group 103 114
Pumpup, diagonal, proper, trivial, or vertical 22 127
Quasisimple group 16 53 81
Quasithin 5 37 41 43 60Ч61 82 105 114Ч116
Recognition of simple groups 31Ч35
Recognition of simple groups, alternating groups 32
Recognition of simple groups, groups of Lie type 32Ч35 42 49 137Ч138
Recognition of simple groups, recognition of symmetric groups 68Ч70
Recognition of simple groups, sporadic groups 35
Ree groups 3 10 49 50
Ree, R. 10
Rowley, P. 37
Schreier property 21 24 29
Schreier, O. 21
Schur multiplier 18 45 48 139
Schur, I. 17
Scott, L. 18
Section 12
Seitz, G. 48
Sibley, D. 48
Signalizer functor 29Ч30 124ff.
Signalizer functor method 29Ч30 36Ч38 41 60 64Ч65 104Ч105 116 118 120 128Ч129
Signalizer functor, closed 124
Signalizer functor, closure 30 124
Signalizer functor, complete 124
Signalizer functor, k-balanced, weakly k-balanced 124Ч126
Signalizer functor, solvable 124
Signalizer functor, trivial 124 128
Simple groups, table of 8Ч10
Simplicity criteria 29Ч31
Sims, C. 39 45
Sims, C., conjecture 74
Smith, F. 41
Smith, S. 41
Solomon, R. 35 39 53
Sporadic groups 3 6 9 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, as 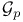 -group 103 -group 103
Sporadic groups, as target group 77 87
Sporadic groups, background properties of 44Ч48 50
Sporadic groups, existence and uniqueness of 46Ч47 50 72
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Baby Monster 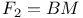 11 38 87 100 11 38 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Conway groups  , ,  , , 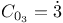 11 38 42 72 87 100 11 38 42 72 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Fischer 3-transposition groups 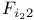 , , 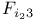 , , 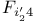 11 38 87 100 11 38 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Fischer Ч Griess Monster  3 11 38 42 47 61 72 87 100 3 11 38 42 47 61 72 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Harada Ч Norton 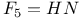 11 67Ч68 87 100 11 67Ч68 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Held 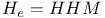 11 87 100 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Higman Ч Sims HS 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Janko 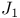 , , 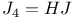 , , 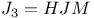 , , 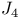 3 11 87 100 3 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Lyons Ч Sims Ly 11 45 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Mathieu  , , 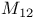 , , 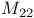 , , 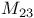 , , 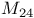 11 42 46 72 87 100 11 42 46 72 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, McLaughlin Mc 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, OТNan-Sims O'N 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Rudvalis Ru 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Suzuki Suz 11 87 100
Sporadic groups, individual groups, Thompson 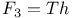 11 87 100 11 87 100
Standard form problems 38
Steinberg, R. 3 7 10 17 45 47 48
Stellmacher, B. 37 50
Strongly  -embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ -embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ
Strongly closed subgroup 61
Strongly embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ
Strongly p-embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ
Stroth, G. 5 37 38 43 53 98Ч99 107 130
Subterminal pair 64Ч66
Suzuki groups 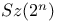 3 10 3 10
Suzuki, M. 10 38 46 47 49
Symmetric group 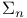 6 6
Symplectic pair 117
Symplectic pair, faithful, of 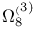 -type, trivial 117 -type, trivial 117
Symplectic type 2-group 116
Tanaka, Y. 37
Target group (G*) 27 54Ч55 86Ч87
Target group (G*) in  89 89
Target group (G*) of Lie type 76Ч77
Target group (G*) of Lie type,  , ,  , , 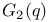 , , 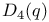 , ,  , q odd 61Ч63 , q odd 61Ч63
Target group (G*) of Lie type, of large Lie rank 63Ч68 71 76
Target group (G*) of Lie type, of Lie rank 1 77 110Ч113
Target group (G*) of Lie type, of small Lie rank 77 110Ч116
Target group (G*), 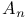 , ,  63Ч68 76Ч77 63Ч68 76Ч77
Target group (G*), 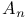 , ,  , , 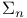 68Ч70 68Ч70
Target group (G*), 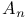 , , 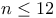 77 111Ч112 114Ч116 77 111Ч112 114Ч116
Target group (G*), quasithin 77
Target group (G*), sporadic 77 87
Target group (G*), sporadic, large sporadic 116Ч117
Target group (G*), the 8 families 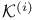 ( (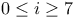 ) 86 ) 86
Theorem 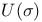 5 86 92 106Ч108 129 131 5 86 92 106Ч108 129 131
Theorem 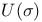 , Corollary , Corollary 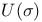 92 92
Theorem 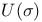 , stages 1Ч3 98Ч99 , stages 1Ч3 98Ч99
Theorem PS 92
Theorem SA 89 97
Theorem SE 89Ч90
Theorem SE, stages 1Ч2 95Ч96
Theorem SF 89
Theorem SZ 88Ч89
Theorem TS 92 114
Theorem U(2) 89 97 106
Theorems  , ,  , ,  92 92
Theorems,  - - 104Ч106 104Ч106
Theorems, Alperin Ч Brauer Ч Gorenstein Ч Walter classification of groups of 2-rank 2 39 41
Theorems, Alperin Ч Goldschmidt conjugation theorem 97 122
| Theorems, Aschbacher classical involution theorem 41Ч43
Theorems, Aschbacher proper 2-generated core theorem 89
Theorems, Aschbacher uniqueness case theorem 43 92
Theorems, Aschbacher Ч Bender Ч Suzuki strongly Z-embedded subgroup theorem 88
Theorems, Aschbacher Ч Gilman component theorem 39 40 52 75
Theorems, Aschbacher Ч Gilman component theorem, generalized to odd primes 75Ч76
Theorems, Baumann Ч Glauberman Ч Niles theorem 50 130Ч131
Theorems, Baumann Ч Glauberman Ч Niles theorem, revision of 50
Theorems, Bender F*-theorem 17 138
Theorems, Bender uniqueness theorem 123
Theorems, Bender Ч Suzuki strongly embedded subgroup theorem 30Ч31 33 36 38 52
Theorems, Bender Ч Suzuki strongly embedded subgroup theorem for 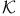 -proper groups 75 -proper groups 75
Theorems, Bender Ч Thompson signalizer lemma 116
Theorems, Brauer Ч Suzuki quaternion theorem 52
Theorems, Burnside 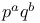 -theorem 30 -theorem 30
Theorems, classification theorem 6 79
Theorems, classification theorem, comparison of new and old proofs 41Ч44 55 63 72 74Ч76 98
Theorems, classification theorem, four-part division 58Ч59
Theorems, classification theorem, main logic 106
Theorems, classification theorem, stages of the proof 61 106Ч121
Theorems, Curtis Ч Tits theorem 35 63 67 113 115
Theorems, Curtis Ч Tits theorem, variations for classical groups 35 63 113 115
Theorems, Feit Ч Thompson theorem see УOdd Order TheoremФ
Theorems, Fong Ч Seitz classification of split (B, N)-pairs of rank 2 63 138
Theorems, Gilman Ч Griess recognition theorem for groups of Lie type 35 67 71
Theorems, Glauberman Z*-theorem 30 31 36 38 43 48 79 122 135
Theorems, Glauberman ZJ-theorem 26 38
Theorems, global C(G, ?)-theorem 38 53
Theorems, Goldschmidt strongly closed abelian 2-subgroup theorem 43 89
Theorems, Gorenstein Ч Harada sectional 2-rank at most 4 theorem 39 42 43
Theorems, Gorenstein Ч Walter dihedral Sylow 2-subgroup classification 50 74
Theorems, Gorenstein Ч Walter dihedral Sylow 2-subgroup classification, revision by Bender and Glauberman 50 74
Theorems, Hall Ч Higman theorem B 26
Theorems, HoltТs Theorem 89
Theorems, Jordan Ч Holder theorem 12ff
Theorems, local C(X, T)-theorem 50 96Ч97 129Ч131
Theorems, Mason quasithin theorem 37 41
Theorems, odd order theorem 30 31 36 38Ч39 48 79 104 134 135
Theorems, odd order theorem, revision of 48 74 123
Theorems, p-component uniqueness theorems 30Ч31 38 53 65 90Ч92 118
Theorems, Schur Ч Zassenhaus theorem 24
Theorems, signalizer functor theorems 49 124
Theorems, Solomon maximal 2-component theorem 39
Theorems, theorem  104 104
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч4 106Ч108 , stages 1Ч4 106Ч108
Theorems, theorem  104 104
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч4 110Ч113 , stages 1Ч4 110Ч113
Theorems, theorem  104 104
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч3 113 , stages 1Ч3 113
Theorems, theorem  105 105
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч4 114Ч116 , stages 1Ч4 114Ч116
Theorems, theorem  105 105
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч4 116Ч118 , stages 1Ч4 116Ч118
Theorems, theorem  106 106
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч2 118 , stages 1Ч2 118
Theorems, theorem  106 106
Theorems, Theorem  , stages 1Ч5 118Ч121 , stages 1Ч5 118Ч121
Theorems, Theorem M(S) 5 90 99 129
Theorems, Theorem M(S), stages 1Ч3 97Ч98
Theorems, Thompson 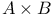 -lemma 21 -lemma 21
Theorems, Thompson dihedral lemma 134
Theorems, Thompson factorization theorem 26 130
Theorems, Thompson N-group classification theorem 38Ч40 43
Theorems, Thompson order formula 114 136
Theorems, Thompson replacement theorem 26 130
Theorems, Thompson transfer lemma 55 104 122 128
Theorems, Three subgroup lemma 17
Theorems, Timmesfeld root involution theorem 42Ч43
Theorems, Tits classification of spherical buildings of rank at least 3 73
Theorems, Walter classification of groups with abelian Sylow 2-subgroups 74
Theorems, Walter classification of groups with abelian Sylow 2-subgroups, revision by Bender 74
Thompson subgroup 26 130
Thompson, J.G. 37 39Ч40 43 48 49 107Ч108 130
Tightly embedded subgroup 39 43
Timmesfeld, F.G. 37 39 40
Tits system see У(B N)-pairФ
Tits, J. 10 25 34 137
TRANSFER 29 31 74 107
Triality 10
Ulmost strongly p-embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ
Ulternating group 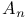 6 32 36 6 32 36
Ulternating group 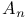 as as 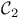 , , 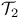 , or , or 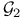 -group 103 -group 103
Uniqueness case 5 38 43 53
Uniqueness grid 79 83 84 87Ч89
Uniqueness subgroups, 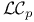 -uniqueness subgroup 94 -uniqueness subgroup 94
Uniqueness subgroups, 2-uniqueness subgroup 82 87Ч89
Uniqueness subgroups, near component 2-local uniqueness subgroup 97
Uniqueness subgroups, p-component preuniqueness subgroup 90Ч93
Uniqueness subgroups, p-component preuniqueness subgroup of strongly closed type 93
Uniqueness subgroups, p-component preuniqueness subgroup, controlling rank 1 or 2 fusion 91Ч92
Uniqueness subgroups, p-component preuniqueness subgroup, standard 91Ч92
Uniqueness subgroups, p-component preuniqueness subgroup, wreathed 93
Uniqueness subgroups, p-uniqueness subgroup, p odd 52Ч53 82
Uniqueness subgroups, p-uniqueness subgroup, p odd, strong p-uniqueness subgroup 52Ч53 58 63 68 82Ч83 92Ч96 99 106
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly embedded subgroup 30Ч31 75 82 87Ч89 95Ч96
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly p-embedded subgroup 31 82 91Ч92
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly p-embedded subgroupm almost strongly p-embedded subgroup 91Ч94
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly p-embedded subgroupm almost strongly p-embedded subgroup, almost p-constrained 93
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly p-embedded subgroupm almost strongly p-embedded subgroup, of strongly closed type 93
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly p-embedded subgroupm almost strongly p-embedded subgroup, wreathed 93
Uniqueness subgroups, strongly Z-embedded subgroup 87Ч89 96
Uniqueness subgroups, weakly Z-embedded subgroup 89
Uniqueness subgroups, {2, p}-uniqueness subgroup 53 98Ч99
Walter, J.H. 29 38Ч39 124 126 127
Ward, H. 49
Weak closure method 43
Weakly Z-embedded subgroup see УUniqueness subgroupsФ
Wong, W. 35
Yoshida, T. 29
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



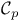 ,
, 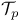 , or
, or 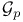 -group
-group 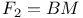
 ,
,  ,
, 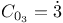
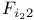 ,
, 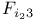 ,
, 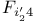

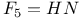
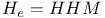
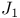 ,
, 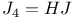 ,
, 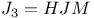 ,
, 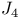
 ,
, 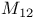 ,
, 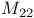 ,
, 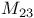 ,
, 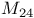
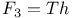
 -embedded subgroup
-embedded subgroup 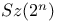
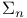
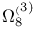 -type, trivial
-type, trivial 
 ,
,  ,
, 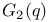 ,
, 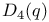 ,
,  , q odd
, q odd 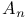 ,
, 
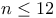
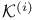 (
(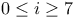 )
) 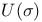
 ,
,  ,
, 
 -
-
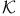 -proper groups
-proper groups 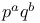 -theorem
-theorem 




 -lemma
-lemma 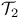 , or
, or 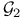 -group
-group 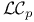 -uniqueness subgroup
-uniqueness subgroup