|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Dym H., McKean H.P. Ч Fourier Series and Integrals |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Addition formula 249Ч251 262 269Ч270 279
Affine transformation 263
Akhiezer, N.I. 14 29 80 194 196
Algebra see "Convolution algebra"
Almost everywhere (a.e.) 10
Analytic functions 144Ч156
Anderson, W.N., Jr. 221
Annihilator 28
Antisymmetric function 134
Approximate identity 105
Arithmetic sequence, distribution of 54Ч56
Arthurs, E. 131
Associated Bessel function 268Ч269
Associated conical function 279
Associated Legendre polynomial 253Ч254
Auslander, L. 273
Axis 229Ч232
Bachman, P. 223
Band-limited function 121Ч132
Basis in a Hilbert space 24 26 80 170 255 270 see "Span" "Unit-perpendicular
Basis of eigenfunctions (of Sturm Ч Liouville operator) 73
Basis of Haar functions 27Ч28
Basis of Hermite functions 98
Basis of Laguerre functions 153 165
Basis of Legendre polynomials 36 246Ч247
Basis of prolate spheroidal wave functions 123
Basis of sampling functions 131
Basis of trigonometric functions 30 57 60 81
Basis of Walsh functions 272
Basis theorem, for finite commutative groups 215Ч217
Basis, of skew matrix 231
Bateman, H. 106
Bellman, R. 54 225
Berberian, S.K. 29
bernoulli 2
Bessel equation 133
Bessel functions 132Ч133 143 266Ч267
Bessel inequality 25 27
Bessel transform 132Ч133 267Ч268
Beurling, A. 169
Birkhoff, G. 74 80 203
Bochner, S. 282
Boemer, H. 228 256
Borel measurable set 7
Borel Ч Cantelli lemma 11 19
Cantor set 8
Caratheodory, C. 273
Carleman, T. 169 282
Carleson, L. 34
Carslaw, H.S. 43 44 282
Case, K.M. 184
Cauchy formula 148Ч151 167
Cauchy theorem 145Ч148
Cauchy Ч Riemann equations 148
Central limit theorem 114Ч116 142
Central subgroup 274
Chandrasekhar, S. 142
Chandrasekharan, K. 141 222 282
Character of group 205Ч206 210 218Ч220 222 223 226Ч227 229 232 241 249
Character of representation 258Ч260
ChebyshevТs inequality 11 19
Class function 258
Closed curve 145
Closed subspace 28
Colatitude 233 239
compact function x 21 37
complete 13 16 37
Conical functions 277
Conjugacy class 258
Convergence in 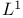 37 38 37 38
Convergence in 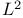 16 18 16 18
Convergence, pointwise a.e. 16Ч18
Convolution algebras 41Ч43 87Ч88 103 212Ч213 237Ч239 262 264 277
Coppel, W.A. 2 282
Copson, E.T. 144
Corner 145
Coset 204Ч205
Coset, double 233 262 263 275
Coset, group of 214Ч215 220
Coset, space of 232Ч233 262 263 275
Cosine integral 92Ч93 132 134 262Ч263
Cosine series 60
Courant, R. ix 49 74 131 196
Crimmins, T. 221
de Branges, L. 194
de Hoffman, F. 184
de la Vallee-Poussin, C. 5
De Moivre 115
Dense 13 21 30 34
Descent, method of 136Ч137
Dimension, of Hilbert space 22 26
DiniТs test 40 105
Direct product, of groups 215
Directed curve 145
Dirichlet 2 105
Dirichlet kernel 31Ч35 40 41 45 260
Divergence theorem 147Ч148
Doetsch, G. 213
Domain 144
Dominated Convergence Theorem 10
Double coset 233 262 263 275
Dual group 206 207 210 218Ч222
Duren, P. 169 194
DТAlembert 1
dТAlembert, formula of 2 71 109 139
Edwards, R.E. 42 43 282
Eigenfunctions (eigenvalues) of Fourier transform 97Ч98
Eigenfunctions (eigenvalues) of integral operators 123Ч126 130Ч131
Eigenfunctions (eigenvalues) of Laplacian 242Ч245 247 251Ч252 265Ч266 268Ч269 270 277 279
Eigenfunctions (eigenvalues) of ordinary differential operators 56Ч60 72Ч80 99 208 211
Eigenvalues see Eigenfunctions"
Energy of string 72
Entire function 154
Erdoes 196
Ergodic 54
Euclidean motion group 261Ч273
Euler 2
Euler Ч Maclaurin summation formula 112Ч114
Exponential type 155 158
Factor group 214Ч215 220
FatouТs Lemma 10 19
Fejer kernel 35 38 41
Fejer theorem 34Ч36 49 55
Fejer, L. 34 103 106
Feller, W. 53 84 115 187 196
Feynman, R. x
Filter 170Ч176
Finicky proof 41
Flanders, M. 61
Ford, G.W. 54
Fourier Bessel transform 132Ч133 267Ч268
Fourier coefficient 23 26 39
Fourier cosine integral 92Ч93 132 134 262Ч263
Fourier cosine series 60
Fourier integral 86Ч105 132Ч134 160Ч161 209Ч212
Fourier integral as a rotation 97Ч98
Fourier integral, application of 106Ч116 134Ч143
Fourier integral, growth of 116Ч121 156Ч160
Fourier inversion formula 88 90 94 103 112 132Ч133
Fourier series 30Ч46 81Ч85 206Ч209
Fourier series on finite commutative groups 217Ч219
Fourier series on rotation group 256 261
Fourier series, application of 46Ч72 82Ч84
Fourier sine integral 92Ч93 134 263
Fourier sine series 57
Fourier Ч Legendre series 245Ч249
Fourier Ч Mehler transform 278
Fourier, J. 2 282
Fredholm alternative 60
Frobenius 4 227
| FubiniТs Theorem 12 41 102
Fundamental solution, of heat equation 64
Fundamental theorem of algebra 154
Gain 170 172
Gauss 215 222 223
Gauss kernel 104 108 111Ч112
Gauss lattice point formula 140
Gaussian sum 223Ч226
Gelfand, I.M. 229 256 261 281
Gibbs phenomenon 43Ч46
Gibbs, J.N. 43
Ginibre, J. 222
Glazman, I.M. 14 29
Goldberg, R.R. 282
Graev, M.I. 261 281
GrafТs addition formula 269Ч270
Gram Ч Schmidt recipe 25 26 153 247
Green function 58 59 60 64 67 72 80
Group interpretation of classical Fourier analysis 206Ч212
Group, central subgroup of 274
Group, direct product of 215
Group, dual 206 207 210 218Ч222
Group, factor 214Ч215 220
Group, finite commutative 214Ч217
Group, introduction to 203Ч206
Group, orthogonal 228Ч229
Group, permutation 134 204Ч206
Group, representations 227 255Ч261
Group, representations of rigid motions of Euclidean line 262
Group, representations of rigid motions of Euclidean plane 261 263
Group, representations of rigid motions of hyperbolic plane 273Ч274
Group, rotation 228Ч236
Group, special orthogonal 229Ч236
Group, stability 275
Haar functions 27Ч28
Hammermesh, M. 256
Hardy function applications 194Ч196
Hardy function spaces 161Ч176 187Ч194
Hardy, G.H. 3 22 282
Hardy, theorem of 156Ч158
Heat equation 60Ч70 82 107Ч109
Heaviside 213
HeisenbergТs inequality 100 116Ч121 122 156
Heitler, W. 119 251
Helgason, S. 281
Helson, H. 169 194
Hermite function 98Ч101 157 211
Hewitt, E. 5 282
Hilbert space 13Ч15 22 26 29 37
Hilbert transform 93
Hilbert, D. 49 74 131
Hobson, E.W. 2 282
Hoffman, K. 169 194
Homogeneous function 254
Homogeneous polynomial 253 255
Homomorphism, convolution algebra 185 208Ч209 211Ч213 214 239Ч241 249 262 264 273
Homomorphism, group-to-group 204Ч205
Hopf Ч Wiener factorization 176Ч184
Hopf, E. 177 184
Horwitz, H. 221
Hurwitz 49
Hyperbolic distance 274
Hyperbolic plane 273Ч281
Ideal 41
Ikehara, S. 196
Images, Lord KelvinТs method of 66 67 68 108
Improper integral 95Ч96 97 150 151
Indicator functionЧx 9
Infinitely often (i.o.) 11 19
Ingham, A.E. 196
Inner functions (filters) 172 193Ч194
Inner product 13 14 16 22 27 29 218Ч219
Integral function 154
Integration on (other continuous) groups 234Ч236 260 262 264 276
Integration, advantage of Lebesgue theory of 16
Integration, introduction to Lebesgue theory of 5Ч12
Invariant subspace 207Ч208 210Ч211 253
Inverse Fourier transform (formula) 88 90 94 103 112 132Ч133
Irreducible-representation 227
Isomorphic groups 205 207 210 219 220
Isomorphic Hilbert spaces 22 26
Isomorphism between groups 204 207 210 218
Isomorphism between Hilbert spaces 30 272Ч273
Isoperimetric problem 49Ч51
Ito, K. 221
JacobiТs identity 52Ч54 65Ч66 67 85 112
JensenТs Inequality 168 192Ч193
John, F. ix 137
Kac, M. 106 211
Katznelson, Y. 282
Kelvin, Lord (method of images) 66 67 68 108
Kingman, J.F.C. 187
Kolmogorov, A.N. 34
Lagrange 2
Laguerre functions 153 165
Landau, H.J. 122 130
Landsberg Ч Schaar identity 225Ч226
Laplace 115
Laplace operator 134 242Ч247 251Ч253 255 265Ч266 268Ч271 276Ч279
Laplace transform 213
Lardy, L.J. 213
Latitude 233
Lattice, dual 84
Lattice, GaussТ formula 40
Lattice, MinkowksiТs theorem 140Ч141
Lattice, nonstandard 84
Lattice, random walk on 82Ч84
Lattice, standard 81
Lebesgue 2
Lebesgue integration 5Ч12 16
Lebesgue measurable 7
Leblanc, N. 273
Lee, Y.W. 172
Legendre operator 74
Legendre polynomials 26 242 245Ч249
Legendre symbol 223
Levinson, N. 144 196
LiouvilleТs theorem 154 158
Littlewood 3
Local convergence, of Fourier series 39Ч40
Local-global duality 31 93 106 116
Loomis, L. 282
Ludwig, D. 137
MacLane, S. 203
Maximal invariant subspace 208
Maximum principle for analytic functions 155
Maximum principle for solutions of heat equation 64Ч65
Maxwell equation 256
Maxwell poles 254Ч255
Maxwell, J.C. 254
McKean, H.P. 222
Measurable function 9Ч10 12
Measurable set 7Ч8 12
Measure 7 8 11 12
Mehler transform 278
Mellin transform 103
MercerТs theorem 131
Michaelson, A. 44
MilneТs equation (problem) 176Ч178 181Ч184
Minimal invariant subspaces 208 253
Minimal type 158
MinkowskiТs theorem in the geometry of numbers 140Ч143
MinkowskiТs triangle inequality 16
Minlos, R. 229 256
Moebius function 214 226
Moebius inversion formula 214
Momentum 118
Monotone Convergence Theorem 10 83
MoreraТs theorem 150 152
Mueller, C. 253 256
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте