јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Lau J. Ч Low Cost Flip Chip Technologies for DCA, WLCSP, and PBGA Assemblies
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Low Cost Flip Chip Technologies for DCA, WLCSP, and PBGA Assembliesјвтор: Lau J. јннотаци€: One-stop, cutting-edge guide to flip chip technologies. Now you can turn to a single, all-encompassing reference for a practical understanding of the fast-developing field that's taking the electronics industry by storm. Low-Cost Flip Chip Technologies, by John H. Lau, brings you up to speed on the economic, design, materials, process,equipment, quality, manufacturing, and reliability issues related to low cost flip chip technologies. This eye-opening overview tells you what you need to know about applying flip chip technologies to direct chip attach(DCA), flip chip on board (FCOB), wafer level chip scale package (WLCSP), and plastic ball grid array (PBGA) package assemblies. You'll discover flip chip problem-solving methods, and learn how to choose a cost-effective design and reliable, high-yield manufacturing process for your interconnect systems as you explore...
*IC trends and packaging technology updates *Over 12 different wafer-bumping methods...more than 100 lead-free solder alloys *Sequential build up PCB with microvias and via-in-pad *How to select underfill materials *And much, much more!
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2000 оличество страниц: 602ƒобавлена в каталог: 28.04.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Micro dynamic solder pump (MDSP) 61 Micro Via-in-Pad 145Ч146 Microball mounting method 72Ч78 Microhardness 118 Microprocessor, described 4Ч6 Micropunching method 61Ч67 Microscopic moire interferometry 343 Microstripline tracers 467Ч469 469Ч470 Microvia hole (MVH) 135 Microvia/VIP substrates 363Ч367 see on Microvias, advantages 121 Microvias, categories of 122Ч125 Microvias, conductive-ink formed vias 136Ч141 Microvias, forming by conventional mechanical NC drilling 125 Microvias, forming by laser drilling 126Ч132 Microvias, local deformation 384Ч385 Microvias, production in Japan 141Ч145 Millenia electra electrochemical plating system (MEEPS) 7 Mitsubishi, FC-BGA package 519Ч529 Mitsubishi, PC-BGA package 520 523Ч525 Mitsubishi, SBU substrate 523 MLBs (multilayer boards) 128 Modulus, definition 108 Moisture content 234Ч236 Moore's law 7 8Ч9 Moore, Gordon 1 Motorola, FC-PBGA packages 537Ч545 Multibond (black oxide) 128 Multilayer boards (MLBs) 128 MVH (microvia hole) 135 National Center for Manufacturing Sciences (NCMS) 96 NC (numerical controlled) drilling 123 125 NEC Toyama, microvia production 143 Net resistance change 420 Ni-Au bumps 161Ч163 175Ч177 Non-C4 solder-bumped flip chips 186 Non-solder mask defined (NSMD) 336 370 Non-through-hole microvias 121 Nonlinear finite element analysis 241Ч246 531Ч534 Nonuniform heat spreader 494Ч496 Noyce, Robert 1 NSMD (non-solder mask defined) 336 370 NuBGA, design 466Ч474 NuBGA, electrical performance 474Ч478 505Ч507 NuBGA, solder joint reliability 490Ч492 504 NuBGA, standard packages 493Ч494 NuBGA, thermal performance 490Ч492 504 NuBGA, thinner substrate and nonuniform heat spreader 494Ч496 Numbering, of gauge elements 421 Numerical controlled (NC) drilling 123 125 OCC (organic-coated copper) 165Ч170 OLGA (organic land grid array) 511Ч513 Operating voltage 3Ч4 Optoelectronic devices 356Ч359 Organic land grid array (OLGA) 511Ч513 Organic solderability preservatives (OSP) 336 Organic-coated copper (OCC) 165Ч170 Package reliability 518Ч519 Package-level reliability tests 333Ч336 Packaging technology 9Ч11 467 Packaging, definition 2 Parasitic parameters, NuBGA package 474Ч477 passivation 568 patterning 343 PBGA 10 PBGA, packages see "Plastic ball grid array" PBGA, packages, assembly with large PQFP directly on opposite side 452Ч463 PBGA, packages, crack initiation due to thermal expansion mismatch 435Ч437 PBGA, packages, dried 423 PBGA, packages, experimental measurements of pop=corning 417Ч426 PBGA, packages, popcorning by fracture mechanics 434Ч435 PBGA, packages, solder reflow 427Ч434 PC-BGA package 520 523Ч525 PCB see "Printed circuit board" PCB assembly 367Ч370 PCB thickness effect 285Ч290 PECVD (Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) 158Ч159 PERL (Plasma-etched redistribution layers) 233 Pessel solderability test 118 Photo-defining vias 123 132Ч134 Photoimageable dielectrics (PIDs) 132Ч134 Photoimaging method 145 photoresist 343 Photosensitive dielectric layer (AA') 383 385 PI (polyimide) 204 341 Plasma (dry) etching 124 135Ч136 Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) 158Ч159 Plasma-etched redistribution layers (PERL) 233 Plastic ball grid array (PBGA) 10 417Ч463 Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) 10 Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) 10 Plastic quad flat pack (PQFP) 10 12 474 Plated-through-hole (PTH) microvias 121 PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier) 10 Point-to-point system net 478 Poisson's ratio, material properties 244 Poisson's ratio, microvia/VIP substrates and 373 Poisson's ratio, NuBGA and 480 Polyimide (PI) 204 341 Popcorning by fracture mechanics, crack initiation due to thermal expansion mismatch 435Ч437 Popcorning by fracture mechanics, described 434Ч435 Popcorning by fracture mechanics, due to thermal expansion mismatch and pressure 437Ч438 Popcorning, definition 437 Popcorning, experimental measurements of PBGA packages 417Ч426 Porosity 196 Power integrity 466 PPGA (plastic pin grid array) 10 PQFP (plastic quad flat pack) 10 12 474 Pressure control system 58 Printed circuit board (PCB) see "Microvias" Printed circuit board (PCB) of Direct 390Ч396 Printed circuit board (PCB), 346 Printed circuit board (PCB), assembly, choices 95 Printed circuit board (PCB), assembly, of 403Ч414 Printed circuit board (PCB), assembly, of WLCSP 317 322Ч323 Printed circuit board (PCB), comparison of laser methods 130Ч132 Printed circuit board (PCB), design 163Ч164 Printed circuit board (PCB), design rules and process 471 Printed circuit board (PCB), effects of construction on thermal management of FCOB 302Ч303 Printed circuit board (PCB), materials 174Ч175 Printed circuit board (PCB), reliability testing 336Ч339 Printed circuit board (PCB), signal copper content 308Ч309 Printed circuit board (PCB), temperature distribution 306 480Ч486 Printed circuit board (PCB), thermal resistance 309 Programmable VDD/FSS SVC 467Ч469 Programmable VDD/FSS SWA 469Ч470 Propagation delay 397 401 PTH (plated-through-hole) microvias 121 Qualification tests for high-density PCB and substrates 131 Qualification tests, FC-BGA package 528Ч529 Qualification tests, wsCSP 333 Rambus module 347 348 RCC (Resin Coated Copper 127 RCF (Resin Coated Copper 127 Read-only memory (ROM) 5 Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) 5 Reliability stresses 519 Reliability tests, FC-PBGA package 530 Reliability tests, FCOB 179Ч180 240Ч241 Reliability tests, WAVE 350Ч352 Reliability tests, wsCSP 337 Resin Coated Copper 127 Resins for microvia formation 127 Resins, SBL process 341Ч342 RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) 5 Rosette measurements 421 Royce Instruments Model 550 410 568 SAM see "B-SAM image" "C-SAM SBB (stud bump bonding) 157 SBL (stress buffer layer) 339Ч342 SBU (sequential buildup) fabrication technique 121 137 523 SCAM (SNEMA chip attach module) 515Ч517 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) 166 168 Semiconductor Industry Association (SLA) 3 4 Sequential bonded films 223 Sequential buildup (SBU) fabrication technique 121 137 523 SGS-Thompson test chip 301 Shear 410Ч411 Shear fracture surface 331 Shear on interface between underfill and passivation 568 Shear strain distribution, in corner solder joint 327 Shear stress and creep shear strain 328 Shear test of FCOB with filmlike no-flow underfills 252Ч253 Shear test of FCOB with underfills 206Ч210 240 Shockley, William 1 SIA (Semiconductor Industry Association) 3 4 Signal copper content in PCB 308Ч309 Signal integrity 466 Silicon integrated circuit see "Integrated circuits" Silicon nitride 333 Silicon wafers 158Ч163 Simultaneous switch output (SSO) 466 477Ч478 SIR (surface insulation resistance) 172 SLC (Surface Laminar Circuit) 142 223 382 SLC substrates, effects of underfill on deformations 380Ч385 SLT (solid logic technology) 183 Small outline IC (SOIC) 10 SMD (solder mask defined) copper pads 370 Sn-Pb solder 95 111 SNEMA chip attach module (SCAM) 515Ч517 SOIC (small outline IC) 10 Solder alloys 96Ч99 100 Solder ball formation 343 Solder ball generator and integrated stream angular control system 58 Solder ball temperature 489 490 494 Solder bumps on A1 pads without UBM 84Ч88 Solder bumps on PCB method 84 Solder bumps, definition 183 556 Solder bumps, population 308 Solder fatigue failures 338 Solder flow-out 557Ч562 Solder joint reliability of FC-PBGA assemblies 544Ч545 Solder joint reliability of NuBGA package 504 Solder joint reliability of Rambus module 403Ч404 Solder joint reliability of two-sided assembly 403 Solder joint reliability, chip size and 280 Solder joint reliability, omega-CSP 339 Solder joint reliability, underfill voids and 291Ч297 Solder joint reliability, VIP 375Ч379 Solder joint thermal fatigue life prediction 536Ч537 Solder joints 183 556 Solder mask coating 343 Solder mask defined (SMD) copper pads 370 Solder mask, local deformation 383Ч384 Solder reflow 406Ч408 423 427Ч434 456 Solder Reliability Solution (SRS) software 343 Solder-bumped flip chips, assembly process 33Ч34 Solder-bumped flip chips, assembly with cracks (delaminations) 286 Solder-bumped flip chips, compared to wire bonding 28Ч33 Solder-bumped flip chips, cost of materials 35Ч43 Solder-bumped flip chips, development history 183 Solder-bumped flip chips, lead-free solders for 116Ч118 Solder-bumped flip chips, major equipment requirements 34Ч35 Solder-bumped flip chips, microvia-in-pad 146 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, effects of underfill on the deformations of SLC substrates 380Ч385 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, assembly process 367 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, considerations 363Ч364 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, design 365Ч367 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, elastoplastic analysis 370Ч375 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, IC wafer for the 32-pin SRAM device 364Ч365 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, PCB assembly 367Ч370 Solder-bumped flip chips, on microvia/VIP substrates, in a CSP, solder joint reliability 375Ч379 Solid logic technology (SLT) 183 Sonix, TAMI technique 418 554 560Ч562 Split via connection (SVC) 467 468 Split wraparound (SWA) 467 469Ч473 Spray fluxer 556 SRAM see "Static random access memory" SSO (simultaneous switch output) 466 477Ч478 Static random access memory (SRAM) 4Ч6 12 354Ч359 364Ч365 Steady-state creep data 110Ч114 Stencil printing method 50Ч55 332 Storage modulus 194Ч195 204 233 Strain energy release rate 289 294 Strain gauge 419 423 Strain rosette 421 Stress buffer layer (SBL) 339Ч342 Stress-induced strain distributions 385 Stress-strain relations 199Ч200 491 Stud bump bonding (SBB) 157 Substrate technology 514Ч518 Subtractive PCB processes 127 SuperSolder method 69Ч72 73 75 Surface insulation resistance (SIR) 172 Surface Laminar Circuit (SLC) 142 223 382 Surface laminar layer 382Ч383 Surface-mount components 452 Surface-mount technology (SMT) 12 SVC (split via connection) 467 468 SWA (split wraparound) 467 469Ч473 Swiss outline J-leaded (SOJ) 10 Swiss outline package (SOP) 10 TAB (tape automated binding) 13 27 Tacky 78Ч84 TAMI (tomographic acoustic microimaging) 418 554 560Ч562 Tangent delta and 195Ч196 233Ч234 Tape automated bonding (TAB) 13 27 Tape ball grid array (TBGA) 10 Tape carrier package (TCP) 10 12 TCE see "Thermal coefficient of expansion" TCP (tape carrier package) 10 12 TCR (Thermal-Curing Resin) 127 TDR (time domain reflectometer) 392 466 TDT (time domain transmission) 466 Technical University of Berlin 173 TechSearch International 121 Tektronix Digital Sampling Oscilloscope 396 TEM (thermal expansion mismatch) 417 Temperature cycling test 181 462 Temperature distribution, for NuBGA and PCB 480Ч486 496 499 Temperature loading 324Ч326 Temperature time-history responses 535 Temperature-dependent stress-strain 491 Temperature-dependent Young's modulus 491 Temperature-voltage relationship 502 Tensile fractures 202 203 Tessera, Wide Area Vertical Expansion (WAVE) technology 347Ч354 Texas Instruments 1 TGA (thermogravimetric analysis) 100 109Ч110 Thermal boundary conditions 530Ч531 Thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE) of lead-free solders 100 103Ч105 Thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE) of photosensitive material 384 Thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE) of underfill 193Ч194 232 277 Thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE), mismatch 382 Thermal cycling test of FCOB assemblie with liquidlike no-flow underfills 240 Thermal cycling test of FCOB assemblies with ACF 170Ч172 Thermal cycling test, 411Ч413 Thermal cycling test, PBGA package 462Ч463 Thermal expansion coefficient, material properties 244 Thermal expansion coefficient, microvia/VIP substrates and 373 Thermal expansion mismatch (TEM) 417 Thermal fatigue crack initiation life 329 Thermal fatigue data 115Ч116 244 Thermal fatigue life, of corner solder joint 331 Thermal fatigue reliability 264 Thermal management, of FC-PBGA assemblies 538Ч544 Thermal mechanical analysis (TMA) 100 103Ч105 Thermal output, of the gauge 419 420Ч421 Thermal performance, NuBGA 494 Thermal resistance of Mitsubishi's 784-pin FC-BGA assemblies 525Ч527
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



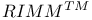
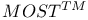 on
on 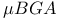 on Rambus modules
on Rambus modules 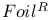 )
) 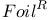 (RCC or RCF)
(RCC or RCF) 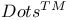 method
method 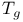
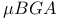 package
package