|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Allen A. — Probability, statistics, and queueing theory with computer science applications |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Median 459
Memory less property see "Markov property"
Method of moments estimation see "Estimators"
mips 467
MODE 459
Moment generating function (z-transform) 67—69
Moment of a random variable 44—45
Moment, sample 436
Montmort's problem 93
MSE (mean squared error, also called residual mean square) 567
MTTF (mean time to failure) 218
MTTR (mean time to repair) 217
Muir, John 459
Multiclass models, closed 410—414
Multiclass models, mixed 415—417
Multiclass models, open 409—410
Multiplication principle 21
Multiplication rule 25
Multiplication rule, general 25
Myriad 395
Namath, Joe 504
Nonparametric tests 539—545
Normal random variables see "Continuous probability distributions"
Norton, Peter 465 466
Null hypothesis 484
o(h) 202—203
Odds 19—20
Odds, against 19
Odds, for 19
One-sided inequality see "Inequalities"
Outlier 459 580
Parker, Dorothy 335
Parzen, Emanuel 225 229 230 231
Pasteur, Louis 485
Pattern recognition 457
Percentile value 124 460
Permutation 20
pmf see "Probability mass function"
Pogo 501
Poincare's Formula 81
Poisson arrival pattern 254—255
Poisson process 204—208
Poisson random variables see "Discrete probability distributions"
Poker 88—90
Pollaczek — Khintchine formula 307
Pollaczek — Khintchine transformation 309
Pollaczek's formula see "Pollaczek — Khintchine formula"
polling 23 64—65
Polya, George 474
Population 249 254 430
Power of a test 489
Predicted (fitted) value 566
Predicted (fitted) value, interval estimate of 578—579
Predictor variable 557
Predictor variable, selection of 600—606
Priority queueing system 325—336
Priority queueing system, HOL (head-of-the-line priority queueing system) 328
Priority queueing system, M/G/1 326—331
Priority queueing system, M/G/1 processor-sharing (PS) 331—334
Priority queueing system, multiserver 334—335
Priority queueing system, preemptive-resume 328
probability 15—16 see
Probability density function see "Density function"
Probability distribution function see "Distribution function"
Probability distributions see "Continuous probability distributions" "Discrete
Probability mass function (pmf) 36
Probability measures 15—20
Probability measures, axioms of a probability measure 16
Probability theory 9—86
Probability theory, basic concepts 10
Probability theory, event see "Event"
Probability theory, sample space 10
Probability, posterior 29
Probability, prior 29
Proportion, true, of population 447
Pure-birth process 211
Pure-death process 211
Queue discipline 256
Queue discipline, BIFO 325
Queue discipline, FCFS 256 325
Queue discipline, FISH 325
Queue discipline, LCFS 256 325
Queue discipline, WINO 325
Queueing network, BCMP 400—417
Queueing network, closed 378
Queueing network, finite population 381—382
Queueing network, finite processor-sharing 385—386
Queueing network, Jackson 378 386—400
Queueing network, machine repair 382—385
Queueing network, open machine repair 397—399
Queueing network, product form 378
Queueing network, separable (same as product form) 378
Queueing systems, birth-and-death process 261—301
Queueing systems, describing a 251—261
Queueing systems, embedded Markov chain 301—324
Queueing systems, multiserver 256
Queueing systems, networks of queues 325—336
Queueing systems, priority 325—326
Queueing systems, single-server 256
Queueing systems, steady-state 253
Queueing theory 247—342
Queueing theory, approximations 336 340—342
Queueing theory, arrival pattern 254—255
Queueing theory, bounds 337 338—340
Random arrival pattern see "Poisson arrival pattern"
Random variables 34—40
| Random variables, dependent 50
Random variables, jointly distributed 46—60
Random variables, moment of 44
Random variables, parameters of 40—46
Random, experiment 10
Random, sample 430
Random, walk 226
Realization, (sample path) 200—201
Regression, estimation of parameters 558—567
Regression, multiple linear 588—610
Regression, nonlinear 584—587
Regression, polynomial 604—610
Regression, simple linear 557—584
Regression, through the origin 5813—584
Reisser, Martin 386 391
Renewal process 234—238
Renewal process, Poisson 236—237
Reproductive property 59
Residual 564
Residual, standardized 579
Residual, studentized 580
Roosevelt, Theodore 431 547
Runyon, Damon 458
Sample spaces 10
Sampling theorem 432
Saturated 380
Saturation number 385
Scatter diagram 558 559
server 249
Server, utilization,  258 258
Service demand 379
Service discipline see "Queueing discipline"
Service time 255
Shelley, Percy Bysshe 208
Sign test 540—544
Significance, level of 486
Significant 490
Skewed 461—462
skewness 461
Skewness, coefficient of 461
Snedecor and Cochran 459 461 576
Squared coefficient of variation, 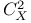 45 255 460 45 255 460
SSE (error sum of squares) 536 566 569 594
SSR (regression sum of squares) 570 571 594
SST (sum of squares for treatment) 534
SST (total sum of squares) 569 594
Standard deviation, sample 431
Standard error 433
Standard error of regression 568
standard error of the estimate 568
Standard statistical model 559 590
State space (for stochastic process), continuous parameter 200
State space (for stochastic process), discrete parameter 200
State space (for stochastic process), probability distribution of 228
State space (for stochastic process), transition probability 220
State, absorbing 217
State, equilibrium 229
State, recurrent 226—227
State, recurrent nonnull (positive recurrent) 227—228
State, recurrent null 226—227
State, steady 229
State, transient 226
Stem-and-leaf plot 456—458
Stochastic process 199—200
Stochastic process, index set 200
Student's t random variables see "Continuous probability distributions"
Sturges' rule 451
Takacs recurrence theorem 310
Teller, Edward 555
Test, sensitivity 30
Test, specificity 30
Tests of means 489—501
Tests of means, one-sample 491—494
Tests of means, two-sample 494—501
Tests of proportions (Bernoulli test), one-sample 506—510
Tests of proportions (Bernoulli test), two-sample 510—514
Tests of variance 501—506
Tests of variance, one-sample 502—504
Tests of variance, two-sample 504—506
Think time 381
Thomas, Lewis 9
Thoreau, Henry David 34
Thurber, James 510
Transform methods 67—76 164—177
Transition probability matrix 222
Tucker, Sophie 67
Twain, Mark 164 506 544
Type I, II, III, and IV errors 488—489
Unbiased 433
Uncorrelated 51
Uniform random variables, continuous see "Continuous probability distributions"
Uniform random variables, discrete see "Discrete probability distributions"
Uniformly most powerful test 490
Variance 42 51—52
Variance, sample 431
Venn diagram 13
Weak law of large numbers 84—85
Whitt, Ward 151—152
Workload 378
Workload, batch 378—379
Workload, terminal 378
Workload, transaction 378—379
Yates' adjustment see "Continuity correction"
Yates' correction see "Continuity correction"
Youden, W.J. 135
z-transform see "Generating function"
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте