јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hopcroft J.E., Ullman J.D. Ч Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computation
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computationјвторы: Hopcroft J.E., Ullman J.D. јннотаци€: It has been more than 20 years since this classic book on formal languages, automata theory, and computational complexity was first published. With this long-awaited revision, the authors continue to present the theory in a concise and straightforward manner, now with an eye out for the practical applications. They have revised this book to make it more accessible to today's students, including the addition of more material on writing proofs, more figures and pictures to convey ideas, side-boxes to highlight other interesting material, and a less formal writing style. Exercises at the end of each chapter, including some new, easier exercises, help readers confirm and enhance their understanding of the material.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1979 оличество страниц: 426ƒобавлена в каталог: 15.12.2013ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
282 see Limited erasing 390Ч393 248Ч260 267Ч268 see Item 260Ч264 207 320Ч324 362Ч365 320Ч324 362Ч365 Aanderaa, S. O. 319 Abstract family of languages 277Ч280 Accepting state see Final state AckermannТs function 175 Ackley, S. I. 46 54 Adelman, L. 375Ч376 AFL see Abstract family of languages Aho, A. V. 54 75 106 124 227 268 284 394 Algol 268 Algorithm 146Ч147 Alphabet 2 Ambiguous grammar 87 200 255 Ancestor 4 Arbib, M. A. 54 ARC 2 Arden, D. N. 54 Asymmetry 7 atom 355 Auxiliary pushdown automaton 377Ч381 385 393 Axiomatic complexity 312Ч314 Axt, P. 319 Backus Ч Naur form 78 Backus, J. W. 106 Baker, B. S. 216 Baker, T. 376 Bar Ч Hillel, Y. 76 145 216 Beeri, C. 269 394 Berman, L. 375 Bird, M. 76 284 BLANK 148 Blattner, M. 395 Blum, M. 319 BlumТs axioms 313 BlumТs speed-up theorem 308Ч310 Boasson, L. 145 Book, R. V. 216 319 375 Boolean expression 324Ч325 Borodin, A. 319 BorodinТs gap theorem 306Ч307 Borosh, I. 374 Brainerd, W. S. 176 Bruno, J. L. 374 Bruss, A. R. 375 Brzozowski, J. A. 54 Bullen, R. H., Jr 54 Canonical order 168Ч169 Cantor, D. C. 106 216 Cardoza, E. 376 Cartesian product 5 Celoni, J. R. 319 CFG/CFL see Context free grammar/language Chandler, W. J. 284 Chandra, A. K. 376 Checking off symbols 155Ч156 Chomsky hierarchy 217Ч232 Chomsky normal form 92Ч94 Chomsky, N. 106 123 145 216 232 Christofides, N. 375 Chromatic number problem 341 369 Church, A. 176 ChurchТs hypothesis 147 166 Circuit value problem 370 Clique cover problem 365 Clique problem 365 369 Closure see Kleene closure Closure properties 59Ч63 130Ч136 230 233 235Ч247 270Ч284 365 392 Closure, of a relation 8 Co- 341Ч342 Cobham, A. 374 Cocke, J. 145 (see also CYK algorithm) Code generation problem 367 Coffman, E. G. 374 Cole, S. N. 269 Compiler 122Ч123 Complementation 59 135 179Ч180 204 235Ч239 279 281 342 392 Complete problem 323Ч354 Complexity class 288 Computable function 9Ч10 Computation, of a Turing machine 201Ч202 211Ч212 Computational complexity 285Ч376 Concatenation 1Ч2 28 59 131 230Ч231 246 266 278 280 Configuration 379 (see also Instantaneous description) Congruence relation 74 Conjunctive normal form 325 328 Constable, R. L. 319 Containment problem 203 Containment property 189 Containment, of sets 5 Context-free grammar/language 9 77Ч145 115Ч120 189 203Ч206 228 246Ч247 270 281 395 Context-sensitive grammar/language 223Ч228 270 346Ч347 390 393 Conway, J. H. 54 Cook, S. A. 124 176 306 319 350 374Ч375 394 Corasick, M. J. 54 Countable set 6 Counter machine 123 171Ч173 Cremers, A. 284 Crossing sequence 38 314Ч315 318 CSG/CSL see Context-sensitive grammar/language Cudia, D. F. 216 CYCLE 72 142Ч144 281 CYK algorithm 139Ч141 Davis, M. 176 dead state 236 Decidable problem 178 (see also Undecidable problem) Decision properties 63Ч65 137Ч141 230 247 281 393 395 DeRemer, F. L. 268 Derivation 80 84Ч87 220 389 Derivation tree 82Ч87 Descendant 4 Deterministic CSL 229 Deterministic finite automaton 19 (see also Finite automaton) Deterministic language see Deterministic pushdown automaton Deterministic pushdown automaton 112Ч113 121 233Ч269 281 DFA see Deterministic finite automaton Diagonalization 182Ч183 364 Digraph see Directed graph Directed graph 2 (see also Transition diagram) Distinguishable states 68Ч69 Domain 6 dspace see Space complexity DTIME see Time complexity Dyck language 142 Earley, J. 145 EDGE 2 Effective closure 59 205 Effective procedure see Algorithm Emptiness problem 63Ч64 137 189 281 348Ч349 Empty set 28 Empty stack, acceptance by 112 114Ч115 254 Empty string 1Ч2 28 Encoding, of a Turing machine 181Ч182 Endmarker 51 166 377 381 Enumeration 167Ч170 189 228 Epsilon Ч CLOSURE 25 Epsilon-free GSM 272 Epsilon-free GSM mapping 272 274 280 Epsilon-free homomorphism 270 278 280 Epsilon-free regular set 271 Epsilon-move 24Ч27 239 264 Epsilon-production 90Ч92 Equivalence class 7 11Ч12 66Ч67 Equivalence problem 64Ч65 281 Equivalence relation 7 65Ч66 Equivalent states 68 Euclid 8 Even, S. 375 Evey, J. 123Ч124 Exact cover problem 341 367 FA see Finite automaton Family of languages 270 (see also Abstract family of languages. Trio) Father 4 Fermat's conjecture 179 Ferrante, J. 375 FIN 282 Final state 17 110 148 272 Finite automaton 9 13Ч54 67Ч71 250-253 Finite control 17 (see also State) Finite state system 13Ч14 (see also Finite automaton) Finite-turn PDA 143 Finiteness problem 63Ч64 137Ч138 189 370 First-order theory 354 Fischer, M. J. 232 319 375 394 Fischer, P. C. 124 176 267 319 Floyd, R. W. 106 145 216 Formal language see Language Freedman, A. R. 319 Friedman, A. D. 54 Friedman, E. P. 269 Full AFL 280 (see also Abstract family of languages) Full time/space constructibility 297Ч299 Full trio 270Ч277 280 Gabriellian, A. 284 Gap theorem see BorodinТs gap theorem Garey, M. R. 374Ч375 Gathen, J. 374 Generalized sequential machine 272Ч276 (see also GSM mapping Inverse Gill 376 Ginsburg, S. 76 106 124 145 216 232 267 269 284 394 Godel, K. 147 354 371 Gonzalez. T. 375 Graham, R. L. 374 Graham, S. L. 145 Grammar see Context-free grammar Context-sensitive Regular Type Graph 2 Gray, J. N. 124 Greibach normal form 94Ч99 Greibach's theorem 205 393 Greibach. S. A. 106 124 216 232 267 269 284 319 394Ч395 Griffiths, T. V. 284 Gross, M. 106 216 Grzegorczyk, A. 319 GSM see Generalized sequential machine gsm mapping 272Ч274 280 Haines, L. 267 Halting Turing machine 149 215 Hamilton circuit problem 332Ч336 Handle 249 Hardy, G. H. 57 Harrison, M. A. 124 145 394 Hartmanis, J. 76 124 145 176 216 319 375 Hayashi. T. 395 Hell. P. 374 Hennie, F. C. 76 176 319 Herman. G. T. 395 Hibbard. T. N. 232 Hilbert, D. 147 Hogben. L. 8 Homomorphism 60Ч61 132 230Ч231 246 266 270 278 280 283 Honesty theorem 316 Hopcroft, J. E. 75Ч76 124 216 227 267Ч269 284 319 374 394 Huffman, D. A. 54 76 Hunt. H. B., III. 216 374 376 Ibarra. O. H. 124 319 id see Instantaneous description III 148Ч149 Independence of operators 279 282 Indexed language 389Ч391 393 Inductive hypothesis 4 Infinite set 6 Inherent ambiguity 99Ч103 INIT 72 142 280 282 Initial state 17 110 272 Input alphabet 17 110 272 Input symbol 148 Input tape 377 389 Instance, of a problem 177 Instantaneous description 36 Integer linear programming 336Ч340 Interior vertex 4 Interleaving 282 Intersection 5 59 134 204 281 283 Intersection with a regular set 135Ч136 246 270 278 280 283 392 Intractable problems 320Ч376 Invalid computation see Computation Inverse GSM mapping 272 276 280 392 Inverse homomorphism 61 132Ч133 230Ч231 246 270 278 280 283 Inverse substitution 142 Irreflexivity 7 Item 248Ч252 261 Jefferson, D. 375 Johnson, D. S. 374Ч375 Johnson, S. C. 268 Johnson, W. L. 46 54 Jones. N. D. 176 375 Kannan, R. 374 Karp, R. M. 374Ч375 Kasami, T. 145 269 Kernel 368 Kirkpatrick, D. G. 374 Kleene closure 28 59 131 246 266 278 280 Kleene, S. C. 54 176 216 Knuth, D. E. 54 268 Kohavi, Z. 54 Korenjak, A. J. 268Ч269 Kosaraju, S. R. 76 Kozen, D. 376 Kuroda, S. Y. 232 Laaser, W. T. 375 Ladner. R. E. 319 375Ч376 Landweber, L. H. 176 232 Language 2 18 80Ч81 112 149 168 LBA see Linear bounded automaton Left-linear grammar see Regular grammar Left-matching 39 Leftmost derivation 87 Length, of a string 1 Leong, B. 176 Lesk, M. E. 46 54 Levin, L. A. 375 Lewis, J. M. 374 Lewis, P. M., II 106 124 176 269 319 375 Lexical analyzer 9 54 Lien, E. 375 Limited erasing 275 280 Lindenmayer, A. 395 Linear bounded automaton 225Ч226 Linear grammar/language 105 143 214 283Ч284 Linear programming see Integer linear programming Linear speed-up 289Ч291 Lipton, R. J. 376 Literal 325 Logspace reduction 322Ч323 Logspace transducer 322 Logspace-complete problem 347 349Ч350 Lookahead set 261 Loop program 317 Lynch, N. 376 Machtey, M. 176 Mager, G. 394 Maibaum, T. S. E. 395 Manders, K. 375Ч376
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



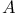 -transducer
-transducer 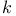 -limited erasing
-limited erasing  -system
-system  (0) grammar
(0) grammar  theorem
theorem