|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| HarrisR. Ч Nonclassical physics: beyond Newton's view |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Linear differential equation 183 300 594
Liquid Drop model 481Ч484
London force 428
Lorentz transformation 9Ч13 44 45 47 551Ч553
Lyman series 269
M-theory 543
Macrostate 344
magic numbers 481 484 485
Magnetic confinement 504 506Ч507
Magnetic dipole moment, intrinsic 291
Magnetic dipole moment, orbital 292 293
Magnetic monopole 539
magnetic quantum number see "Quantum number"
Majority carrier 446
Mass number 469 476 477 498 501
Mass, gravitational versus inertial 51Ч53
Mass-kinetic energy conversion 41
Massless particles 42
Matter wave 96
Maxwell speed distribution 362Ч363
Mediating particle 514
Meissner effect 454
Meson 523
Metallic hydrogen 460
Metastable state 278 331 386Ч388
Michelson Ч Morley experiment 3 547Ч547
Microstate 344
Minority carrier 446 450
Moderator 500
Molecular energy levels 415
Momentum operator see "Operator"
Momentum, relativistic 34Ч36
Momentum-position uncertainty 122
MOSFET 451 466
MRI see "Nuclear magnetic resonance"
Multiwire proportional counter 528
Muon 8
N-type semiconductor 444
Nanotube 460
Natural abundance see "Isotopes"
Neutrino 59 60 68 490 498 531
Neutrino oscillations 61 541Ч542
Neutron number 469
Neutron star 59 375 407
Noble gas 309
Normal core 454
Normalization 146 153 155 161 173 178Ч179 234 239 256Ч257
Nuclear binding 471Ч484
Nuclear composition 469
Nuclear density 471
Nuclear fission see "Fission"
Nuclear fusion see "Fusion"
Nuclear magnetic resonance 485Ч487
Nuclear mass 482
Nuclear potential energy 473 474 475 484 503
Nuclear radius 470Ч471
Nuclear reactors 37 500Ч501 503Ч505
Nuclear spin 474 476
Nuclear spin-orbit interaction 485
Nucleon 469
Observable 163Ч164 180
Occupation number 356
Ohm's law 434
One-electron atom see "Hydrogenlike atom"
Operator, 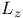 244Ч245 575Ч577 244Ч245 575Ч577
Operator, angular momentum 248 575Ч577
Operator, definition 163
Operator, energy 164 181 183 296
Operator, kinetic energy 164 233 254 296 575Ч579
Operator, momentum 164 569
Operator, position 163 164 181
Operator, rotational energy 578
Optical pumping see "Pumping"
Orbital angular momentum see "Angular momentum"
Orbital magnetic dipole moment see "Magnetic dipole moment"
Orbital quantum number see "Quantum number"
Orbits: circular versus elliptic 259
p-n junction 447
P-type semiconductor 445
Pair annihilation 82 84 94 502
Pair production 83Ч85
Pairing effect 485
Parent nucleus 210 487
Parity 275 536
Parity, intrinsic 523 536
Particle accelerators 42 527
Particle detectors 528
Particle-wave duality see "Wave-particle duality"
Paschen Ч Back effect 327
Penetration depth 171 204 208
Penetration of classical forbidden region see "Classically forbidden region"
Periodic table 308 311Ч312
phase velocity 216Ч222
Phonon 392 434
Phonon, gas 393Ч396
photoelectric effect 72Ч75
Photon 43
Photon absorption 270 271Ч272
Photon emission 184 267Ч272 484Ч485 492
Photon energy 72
Photon gas 378Ч381
Photon momentum 78
Photon spin 295
Pi bond 414
Planck length 545
Planck's blackbody radiation law 381 392 556Ч564
Planck's constant 72 119 198
Plane wave 108
Point defect 434
Polar angle 241
Polar covalent bond 415
Population inversion 385Ч388
Positron 83 490 501
Positron emission 490
Potential barrier 199
Potential energy, diatomic molecule 172
potential step 194
Potential well, comparison: finite & infinite 169Ч170
Potential well, finite 167Ч171
Potential well, infinite 150Ч159 164Ч166 169Ч170 484
principal quantum number see "Quantum number"
Principle of equivalence 53
Probabilities, reflection and transmission 196Ч199 200Ч201 203Ч204 205Ч209 211Ч212
Probability amplitude 102
probability density 98 110 111 123 146 156 160 234
Probability, statistical 353 558
Proper length, time 14
Proton decay 539
Proton-proton fusion cycle 501
Pulsar 59
Pumping, current injection 452
Pumping, electric discharge 385Ч388
Pumping, optical 385Ч388
Q-value 487
QND 134
Quantization 155
Quantization, angular momentum 244Ч251 287Ч294 295 318Ч320 485
Quantization, bound states 177Ч179 193
Quantization, energy 155 156 169 170 172 177Ч179
Quantum cascade laser 399
Quantum chromodynamics 522
Quantum computing 185Ч186 333
Quantum corral 159Ч160
Quantum dot 185
Quantum electrodynamics 269
Quantum gas 371Ч375
Quantum logic gate 333
Quantum number, magnetic 249
Quantum number, orbital 249
Quantum number, origin of 235
| Quantum number, principal 254
Quantum number, spin 293
Quantum-nondemolition 134
Quark confinement 520
Quark content 520
Quark, nature of 520Ч521
Quasicrystal 101 461
Qubit 333
Radial antinodes and energy 259 265
Radial probability 264Ч267
Radial wave function 254 257
Radioactive dating 495Ч497
Radioactive identification, tracing, tagging 492
Radioactivity 487Ч492
Raman scattering 91
Rare earths 312
Reaction, chemical 36 308Ч310 469
Reaction, nuclear 36 469 497Ч505
Reactor see "Nuclear reactor"
Real part of complex quantity 111 592
Recombination, electron-hole 447
Red shift, gravitational 53Ч56
Reduced mass 240 285 420 586
Reflection probability see "Probabilities reflection
Relativistic acceleration transformation 70
Relativistic quantum mechanics 106 292 294 321Ч322 516Ч518
Reverse bias 448 449
Rotational energy, molecular 389 391 418Ч425 584Ч587
Rydberg constant 267
Saturation in nucleus 475
Scanning tunneling microscope 214Ч215 230
Schroedinger equation in spherical polar coordinates 242
Schroedinger equation, free particle 108
Schroedinger equation, N-particle 312
Schroedinger equation, one dimension 143
Schroedinger equation, three dimensions 233
Schroedinger equation, time-independent 145 234
Schwartzchild radius 59 69
Scintillation counter 528
Screening of atomic electrons 307 309 314
Second law of motion 224Ч225
Second law of thermodynamics 346 349 352
Selection rule 275 295 421
Self-consistent field approach 315
Semi-empirical binding energy formula 481Ч484
Semiconductor 437
Semiconductor laser see "Diode laser"
Separation of variables 144 235Ч236 243 247 296Ч297
Shell (electron orbit) 307
Shell model of nucleus 484Ч485
Sigma bond 412 414
Simple harmonic oscillator see "Harmonic oscillator"
Simultaneity 5Ч6 7Ч8 13Ч14 19 554
Single-atom laser 398
Single-electron transistor 225
Singlet state 303Ч304 328Ч331
Slater determinant 305 337
Smoothness 146Ч147 167Ч168 177Ч178 196 200 203 205
Sodium doublet 338
Solar neutrino problem 542
Solid, types of (covalent, ionic, metallic, molecular) 426Ч428
Soliton 91 226
Space-time, warping of 55Ч58
Spatial state 294
Specific heat 176 388Ч397
Specific heat of a gas 389Ч391
Specific heat of a solid 391Ч397
Spectra, multielectron 328Ч331
Spectral content 125 130
Spectral energy density 557Ч564
Spectral line 267 269 421Ч425
Spectral line broadening 67 141 285
Spectroscopic notation 258
Spectroscopy, (e,2e) technique 135
Speed of light: absolute limiting speed 47Ч51
Spherical harmonics 258
spherical polar coordinates 240Ч242
Spin 291Ч295
Spin crisis 541
Spin dependence of strong force 473 474
Spin of fermions, bosons 304
spin quantum number see "Quantum number"
Spin state 294
Spin-orbit interaction 315Ч318 319Ч322
Spontaneous emission 382 383Ч388
Spontaneous fission 492 498
Spontaneous symmetry breaking 525
Squeezed light 134
Squids 225
Stability, atomic 308Ч312
Stability, nuclear 469 473Ч481 484 487
Standard deviation 114 162 165
Standard model 519
standing waves 156 169 179Ч180 237
Stationary state 144Ч145 194 234 274
Stefan Ч Boltzmann law 380 405 564
Stellar collapse 58Ч59
Stern Ч Gerlach experiment 290Ч293
Stimulated absorption 383
Stimulated emission 383 388
Stirling's approximation 348 403
STM see "Scanning tunneling microscope"
Stopping potential 74
Strangeness 524
String theory see "M-theory"
Strong force 472Ч475 477Ч478 520Ч522
Strong force, residual 472 524
Strong nuclear force see "Strong force"
Subshell 307
Superconductivity 452Ч459
Superconductor, fulleride 461
Superconductor, heavy-fermion 461Ч462
Superconductor, high 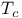 458Ч459 458Ч459
Superconductor, Type-I and Type-II 454Ч458
Superfluidity 377Ч378 398
Superfluidity, helium-3 398
Superstring theory see "MЧtheory"
Supersymmetry 543
Synchrotron 527
Synchrotron radiation 91
Temperature, definition of 347
tetrahedral bonding 416Ч418
Thermal neutron 500
Thermionic emission 213
Thermodynamic system 342 580
Time dilation 6 14
Time operator 164
Time reversal 537
Time-independent Schroedinger equation see "Schroedinger equation"
Time-reversal asymmetry 350
Time-reversal invariance 350
Total angular momentum 318Ч322 323 329
Total energy 34
Total spin 318 328Ч332
transistor 441 450Ч451
Transition elements 310
Transition rate 276Ч278
Transmission probability see "Probabilities reflection
Transmission resonance 201 207
triplet state 303Ч304 328Ч331
Tunnel diode 213 449 466
Tunnel junction 225
Tunneling 204Ч209
Tunneling, alpha-decay, as example 209Ч212
Tunneling, time required for 225
Twin paradox 22Ч26
Ultra-cold neutrons 135
Ultraviolet catastrophe 72 557
Uncertainty 113Ч114 161
Uncertainty principle 90 113Ч121 122 129Ч130 157 166 171 249
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте