|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bueche F. Ч Physic Properties of Polymers |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Activation energy 255Ч256
Addition polymer, definition 3
Addition polymer, table 4Ч5
Affine deformation 42 58
Affine deformation, failure for networks 138Ч142 151
Arrhenius plot 90 91
Atactic polymer 318 319
Boltzmann superposition principle 153 173 187
Boltzmann superposition principle, applied to creep-recovery experiment 203
Boyer Ч Beaman rule 110Ч111
Branching, and network formation 9Ч11
Branching, effect on dynamic properties and viscosity 222Ч223
Breakdown of rubber by mechanical means 336Ч341
Breakdown of rubber networks 332Ч333
Brittle temperature 98Ч99 102
Brownian motion and chain dynamics 148
Chain end correction 45 228
Chain end distribution function 16Ч18 30Ч33 55
Chain folding 314Ч315
Cis and trans forms 319Ч320
Complex compliance 155 167
complex modulus 167 168
Compliance, complex 155 167
Compliance, definition of 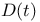 125 125
Compliance, effect of molecular weight heterogeneity 223Ч224
Compliance, loss 156
Compliance, storage 156
Condensation polymer, definition 1Ч2
Condensation polymer, table of 6
Copolymerization, effect on glass temperature 120Ч123
Crazing 269
Creep, compliance for linear chains 208Ч209 214
Creep, compliance for networks 137 140
Creep, entanglement effects 201 ff.
Creep, measurement methods 179Ч183
Creep, of linear polymers 199 ff.
Creep, of networks 125 ff.
Creep, of polymeric glasses 248 ff.
Creep, of SBR samples 180 ff.
Creep, plateau region 200Ч202
Creep-recovery experiment 203
Critical hole size 106
Crosslink density, effect on creep curve 183
Crystal growth and nucleation 306 ff.
Crystal morphology 313Ч317
Crystallinity 295 ff.
Crystallinity, molecular factors affecting 317 320
Crystallite dimensions 296 305Ч307
Damping 158
Degree of polymerization 1
Delta function method 32Ч34
Dielectric dispersion, Debye equations 279Ч280
Dielectric dispersion, for small molecules 278Ч281
Dielectric dispersion, polymers 281Ч286
Dielectric dispersion, relation to jump frequency and friction constant 283
Dielectric loss, alpha and beta loss peaks 285Ч286
Dielectric loss, for polymers 282Ч286
Dielectric loss, for small molecules 280Ч281
Dielectric loss, relation to mechanical loss 286
Dielectric properties 272 ff.
Diffusion constant, for polymers at high temperatures 91
Diffusion constant, for small molecules at high temperatures 90
Diffusion constant, in terms of free volume 97
Diffusion constant, relation to viscosity for polymers 72
Diffusion of polymer molecules and jump frequency 63Ч69
Dipole moments of polymers 274Ч277
Dipole moments of polymers, free rotation model 276
Dipole moments of polymers, polyvinyl chloride types 277
Distribution function, about center of mass 16 19 34Ч35
Distribution function, chain end separation 16Ч18
Distribution function, for chain ends under stress 55
Distribution of relaxation times see Relaxation time spectra
Distribution of retardation times see Retardation time spectra
Doolittle equation 104Ч105
Dynamic compliance for linear molecules 210
Dynamic measurements 178 ff.
Dynamic modulus for linear molecules 210
Dynamic properties of linear polymers 206 ff.
Dynamic properties of linear polymers, effect of branching 222Ч223
Dynamic properties of linear polymers, effect of molecular weight heterogeneity 223Ч224
Dynamic viscosity, definition 167
Dynamic viscosity, frequency dependence 216Ч218
Dynamics of motion for a polymer molecule 129 ff. 148
Dynamics of motion for a polymer molecule, effect of friction 134 ff.
Effective network chains 228
Elasticity, of a chain 37Ч40
Elasticity, of a network 41Ч45 60
Energy loss 157
Energy of activation 90Ч93
Entanglement crosslink 201
Entanglement molecular weight, influence of polymer concentration 73Ч76
Entanglement molecular weight, table 76
Entanglement network 202
Entanglements, effect on diffusion constant 65 69
Entanglements, effect on dynamic behavior 212 ff.
Entanglements, effect on elasticity modulus 51
Entanglements, effect on molecular friction factor 67
Entanglements, in natural rubber 52
Entropy of fusion 300
Excluded volume effect 22
Fiber formation 320Ч322
Fillers, effect on modulus 46Ч49
Fillers, non-reinforcing 47
Fillers, reinforcing 46Ч49
Flaws, effect on strength 225 269
Forced vibration methods 192Ч195
Free vibration methods 187Ч192
Free volume, at glass temperature 115
Free volume, considerations in definition 115
Free volume, cooperative effects 94Ч96
Free volume, definition 105 115
Free volume, hole size distribution 95
Free volume, methods for computing 86Ч87
Free volume, of chain end 114Ч115
Freely orienting chain, definition 15
Freely orienting chain, dimensions of 21
Freely orienting chain, relation to reality 20Ч21
Friction factor see Molecular friction factor and Segmental friction factor
Gel formation 9Ч11
Gel point 11
Glass temperature, as an iso-free volume state 112
Glass temperature, dependence on molecular structure 108Ч110
Glass temperature, effect of copolymerization upon 120Ч123
Glass temperature, effect of diluent on 116Ч118
Glass temperature, effect of molecular weight on 113Ч116
Glass temperature, methods of measurement 97Ч100
Glass temperature, of block and graft copolymers 120Ч121
Glass temperature, rate effects 100
Glass temperature, table of 110
Glass transition see Glass temperature
Glasses, creep of polymethyl methacrylate 254Ч256
Glasses, creep of polystyrene 248Ч251
Glasses, dynamic properties 256Ч261
Glasses, non Ч Hookean behavior 249Ч253
Glasses, temperature-time superposition for 260
Glasses, tensile strength of 262 ff.
Glasses, variation of activation energy for 255Ч256
Glasses, variation of free volume in 256
Gordon Ч Taylor equation 122Ч123
Griffith crack theory 269Ч270
Gyration, radius of 16 28Ч30
Heat generation, equation for 157
Heat generation, in rubbers 195Ч197
Heat of fusion 299Ч300
High elongations, elasticity at 56
Hysteresis in vulcanized rubbers 195 197
Inverse Langevin function 57
Isotactic polymer 318Ч319
Jump distance, definition 62 64
Jump frequency, and glass temperature 101Ч104 108
| Jump frequency, at high temperatures 89
Jump frequency, definition 62 64
Jump frequency, in terms of free volume 96Ч97
Jump frequency, models for 85Ч86
Junction motion in networks 138 ff. 151 197
Kelvin element see Voigt Ч Kelvin model
Kinetic theory of elasticity 37Ч45 59Ч60
Kinetic theory of elasticity, experimental tests 53Ч55
Kinetic theory of elasticity, for swollen networks 60
Kinetic theory of elasticity, result for high elongations 57
Knotty tear 331
Langevin function 39
Logarithmic decrement 189
Loss compliance 156Ч159
Loss modulus, definition 167
Loss modulus, in polymeric glasses 256Ч261
Loss tangent 158
Mass distribution function 16 19 34Ч35
Maxwell model, and stress relaxation 163 ff.
Maxwell model, relaxation time for 165
Maxwell model, sinusoidal response 166Ч168
Measurement of dynamic properties 178 ff.
Mechanical breakdown of rubber 336Ч339
Mechanical breakdown of rubber, effect of molecular weight 338
Mechanical breakdown of rubber, effect of temperature 338
Melting point, and glass temperature 295Ч298
Melting point, effect of chain ends 302
Melting point, effect of chain ends, copolymerization 303Ч305
Melting point, effect of chain ends, crystallite size 301Ч302 305Ч306
Melting point, effect of chain ends, diluent 302
Melting point, effect of chain ends, impurities 303
Melting point, effect of chain ends, stretching 311
Melting point, in terms of entropy and heat of fusion 300
Melting point, influence of crystallization temperature 309Ч310
Melting point, table of 110
Microgel 8
Modes of motion, definition 132
Modes of motion, of a polymer chain 132 ff.
Modulus of rubbers under constant stress, filled stocks 46Ч49
Modulus of rubbers under constant stress, shear stress 46
Modulus of rubbers under constant stress, swollen rubbers 60
Modulus of rubbers under constant stress, tensile stress 43
Modulus, loss 167 168
Modulus, relaxation 166
Modulus, storage 167 168
Molecular friction factor 66Ч69 79Ч80
Molecular spring constant 40
Molecular weight averages 6Ч8
Molecular weight distribution, effect on elastic compliance 223Ч224
Molecular weight distribution, effect on heat generation 195Ч197
Molecular weight distribution, most probable distribution 8
Molecular weight, effect on heat generation 195Ч197
Monomer, definition 1
Mooney Ч Rivlin equation 54 59
Mooney Ч Rivlin plot 59
Morphology of crystals 313Ч317
Motion of a polymer molecule 129 ff. 148Ч151
Mullins softening effect 49Ч51
Network, breakdown 332Ч333
Network, elasticity 41Ч45
Network, formation 9Ч11
Network, junction motion 138 ff. 151 197
Non Ч Newtonian flow 218Ч222
Normal coordinate method 149
Nuclear magnetic resonance 287 ff.
Nuclear magnetic resonance, for polyisobutylene 290Ч291
Nuclear magnetic resonance, for polyvinyl chloride 292
Nuclear magnetic resonance, method 287Ч290
Nuclear magnetic resonance, relation to mechanical resonances 290Ч293
Nuclear magnetic resonance, relaxation times 293
Nuclear magnetic resonance, resonance line width 288Ч290
Number average molecular weight, definition 6Ч7
Number average molecular weight, effect on chain end correction 45Ч46
Number average molecular weight, effect on heat generation in rubbers 195Ч197
Permanent set 334Ч336
Properties of polymeric glasses 246 ff.
Radius of gyration 16 28Ч30
Random chain scission 333
Refractive index and glass temperature 99Ч100
Relaxation modulus 166
Relaxation time spectra 153 ff. 169 172
Relaxation time spectra, for linear polymers 207Ч211 215 216
Relaxation time spectra, for SBR 186
Relaxation time, nuclear magnetic 293
Relaxation time, of Maxwell element 165
Relaxation time, of polar molecules 281Ч283
Resilience, dynamic 191
Resonance peak half-width 193
Resonant modes of motion 132
Retardation time spectra 153 ff. 161Ч162 167Ч172
Retardation time spectra, for linear molecules 207Ч211 215 216
Retardation time spectra, for SBR 182Ч183
Retardation times of a molecule 136
Root mean square length 13Ч15
Root mean square length, any chain 15
Root mean square length, definition 13
Root mean square length, for 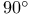 bond angle chain 25 bond angle chain 25
Root mean square length, for freely orienting chain 15
Root mean square length, table of 24
Root mean square length, tetrahedral chain 25Ч27
Rouse model 148 206 207
Rubber elasticity 37Ч60
Segmental friction factor, at high temperatures 91
Segmental friction factor, definition 66
Segmental friction factor, in terms of free volume 97
Segmental friction factor, relation to jump frequency 66 69
Segmental motion near the glass temperature 93Ч97
Shear degradation of rubber 336Ч341
Shift factor 143 146
Single Crystals 314Ч316
Sinusoidal vibration 155Ч168 (see also Vibration)
Size of polymer molecules 13Ч25
Size of polymer molecules, table of 24
Slippage factor 67
Softening by pre-stretching 50
Specific volume as function of molecular weight and temperature 115
Spherulites 316Ч317
Spring constant for a chain 40
Stark rubber 308
Statistics of rupture 225
Stick-slip tear 331
Storage compliance 156Ч159
Storage modulus 167
Stored energy function 43 59
Strength see Tensile strength
Stress relaxation, and Maxwell element 163 ff.
Stress relaxation, during network scission 332Ч333
Stress relaxation, for linear molecules 208Ч209 215Ч216
Stress relaxation, intermittent vs. continuous 334
Stress relaxation, methods 183Ч187
Stress relaxation, of SBR 183 ff.
Stress-strain relation, filled stocks 46Ч47
Stress-strain relation, for swollen network 60
Stress-strain relation, under shear stress 46
Stress-strain relation, under tensile stress 43Ч44
Submolecule, definition 129
Superposition principle of Boltzmann 153 173 187
Superposition principle of Boltzmann, applied to creep-recovery experiment 203
Superposition principle, examples of use 144Ч145 176 180 184
Superposition principle, temperature-time 143 160
Swollen networks, elasticity of 60
Syndiotactic polymer 319
Tear strength 323Ч331
Tear strength, relation to tensile strength at break 328Ч333
Tearing energy 325Ч329
Tearing of rubber 323Ч331
Temperature-time superposition principle 143 160
Temperature-time superposition principle, examples of use 144Ч145 176 180 184
Tensile strength of plastics 262 ff.
Tensile strength of plastics, and jump frequency 266Ч267
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



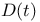
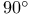 bond angle chain
bond angle chain