јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Fletcher H. Ч Speech and Hearing in Communication
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Speech and Hearing in Communicationјвтор: Fletcher H. јннотаци€: Stemming from the great volume of research done in this field at the Bell telephone laboratories, this book is the developed logically from a single general problem. If a talker (T) of described characteristics speaks into a transmission system S of described characteristics, how well will a listener recognize the sounds spoken at T? To provide the great range of information needed to enable the reader to deal properly with this problem, this book deals with three issues: 1. A fundamental description of the speaking process and the speech waves created by talking as well as the methods of describing the Talker (T). 2. The hearing process in the methods of describing the listener. 3. The interaction of the Talker (T) and the system (S) and the Listener. Thoroughly revised and substantially rewritten, this new second edition brings every phase of the subject up-to-date. For example, Chapter 14, the space-time pattern of hearing is entirely new, and gives a mathematical treatment of the dynamics of the hearing process. The results of this analysis are in the excellent agreement with the epochmaking experimental results of Bekesg, and mark a significant milestone in our understanding of the mechanism of hearing. This book appeals to those interested primarily in speech, such as teachers of speech and phonetic experts, to those interested chiefly in hearing such as otologists, audiologists and workers and hearing clinics, and to those interested in many applications of the subject, such as electrical, communications and radio engineers. Illustrated with charts, diagrams and graphs.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats оличество страниц: 472ƒобавлена в каталог: 19.05.2013ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Acoustic line spectra of vowel sounds 51Ч54 Acoustic line spectra, definition of 50 Acoustic line spectra, effect of pitch on 53Ч54 Acoustical Society of America 283 Acoustical speech powers 68Ч88 Acoustical speech powers, definitions 68Ч70 Adam's apple 19 Air condenser, rotary 146Ч149 Alphabet of International Phonetic Association 1 Alternating current (a-c) components 6 Alternation phonometer 181 American Medical Association 122 446 American Standards Association 70 177 308 427 Amplifiers, vacuum tube 68 Analyzer, Henrici 71 Analyzer, Level 72Ч77 Anderson, A.B. 290 Angular localization 220 221 222Ч224 228 Anvil (ossicle) 106 Aperiodic sounds 15 16 Arnold, H.D. 216 Articulation scores 318Ч414 Articulation scores, 348Ч351 Articulation scores, acknowledgments 401 Articulation scores, applications 394Ч401 Articulation scores, charts, instructions for using 376Ч381 Articulation scores, charts, systems with no noise 362Ч365 376Ч378 Articulation scores, charts, systems with noise 366Ч376 378Ч381 Articulation scores, data for ideal system 339Ч341 Articulation scores, distortion 351Ч361 Articulation scores, distortion, carbon microphone 356Ч361 Articulation scores, distortion, due to frequency shift 352 Articulation scores, distortion, due to overloading 354Ч356 Articulation scores, distortion, due to reverberation, in sending and receiving rooms 352Ч354 Articulation scores, effect of noise on 341Ч351 Articulation scores, effective gain 319Ч324 Articulation scores, F factor, calculation of 333Ч334 Articulation scores, F factor, masking effect on 329Ч332 Articulation scores, F factor, maximum 326Ч328 Articulation scores, F factor, noise present 345Ч347 Articulation scores, functions 334Ч339 Articulation scores, H factor, due to noise 348Ч351 Articulation scores, hearing loss for speech 413Ч414 Articulation scores, index A 318 Articulation scores, loudness functions 401Ч413 Articulation scores, noise present 341Ч351 344Ч345 Articulation scores, noise present, F factor 345Ч347 Articulation scores, noise present, V and E factors 344Ч345 Articulation scores, observed and calculated articulation vs. grain curves, comparisons 382Ч394 Articulation scores, V and E, determination of 324Ч326 Articulation scores, V and E, noise present 344Ч345 Articulation vs. intensity level 415Ч418 Articulation, consonant 278 418 Articulation, crews, talking levels and proficiency factors of 313Ч317 Articulation, definition of 278 Articulation, fricatives 422 Articulation, index and values, relation between 280Ч300 Articulation, index, calculation of 425Ч430 433 Articulation, measurement of 278Ч302 Articulation, semivowels 421 Articulation, sentence 299 Articulation, sentence, intelligibility list 300Ч301 Articulation, sound 278 279 280 Articulation, syllable 278 279 280 Articulation, tests 279Ч280 315Ч317 Articulation, vowel 278 416 418Ч422 Artificial deafness 424 Artificial ear 120 Audiofrequency spectra 16 Audiograms, deafness 424 Audiograms, determination of, in compensation cases 442 Audiograms, hearing acuity expressed as 136 Audiograms, masking 204Ч208 Audiograms, noise 201Ч209 Audiometer 442 Audiometer, 2A 122Ч123 Audiometer, phonograph (Western Electric 4A) 139Ч140 Audiometer, proposed standard 122Ч123 Audiometer, tone range 121Ч125 132 135 Audiometer, use in measuring hearing 119Ч143 Auditory area 134 Auditory masking see "Masking" Auditory meatus 106 107 Auditory nerve 107 Auditory nerve, action 112Ч118 Auditory nerve, tract, diagram of 268 274 Auditory perspective 217Ч229 Auditory perspective, conclusions re 228Ч229 Auditory perspective, effects of quality 228 Auditory perspective, experimental verification of theory 226Ч228 Auditory perspective, localization see "Localization" Auditory perspective, multichannel systems 218Ч221 Auditory perspective, transition systems that preserve 217Ч218 Average speech power 68 71 76Ч78 Azimuth, M.A.F. vs. 128Ч143 Basilar membrane 107 108 109 110 111 151 173 174 233 293 Basilar membrane and inner ear canals 235Ч236 Basilar membrane, relation between vibration and nerve stimulation on 259Ч263 Basilar membrane, space-time theory of hearing 235Ч244 246 249 251Ч258 273 274 Beats for measuring differential intensity sensitivity 144Ч145 Beats, binaural 214Ч216 Beats, objective 214 216 275Ч276 Beats, subjective 160 161 162 214 276 Beck, C.J. 83 Bedell, E.H. 123 Bekesy, G.V. 132 172 184 230 232 237 240 251Ч256 262 273 Beranek, L.L. 68 120 Bessels functions 243 Biddulph, R. 146 Binaural hearing effects 210Ч216 230 Binaural hearing effects, beats 214Ч216 Binaural hearing effects, due to changes in phase and intensity of sound 210Ч213 Binaural hearing effects, listening 178 Binaural hearing effects, location of complex-sounds 213Ч214 Binaural hearing effects, masking 153 154 Binaural hearing effects, threshold, measurement of 127Ч128 Binaural hearing effects, transmission system 217 Bone conduction 159 Bone conduction receiver 149 150 Bony labyrinth 106 Boston, M.E.E.I. hospital 431 Brain tumor 274Ч275 Bray, C.W. 109 Breathing to phonation, transition from 20 Brownian movements 231 Bureau of Standards 120 122 123 133 Buzzertone 8 Calibrated microphones 68 Calibrated microscope 239 251 Calibrating the receiver, methods of 120Ч121 Calibration, proposed standard 122 Carbon microphone, distortion 356Ч361 Carbon microphone, electrical noise 100 Carter, C.W. 92 280 305 Castner, T.G. 280 Cavities, nose and throat 3 5 49 Chest, part of, used in speech 7 Christensen, J.W. 100 Churcher Ч King Ч Davies 191 Cochlea 109 231 233 Cochlea, description of 107Ч108 Cochlea, dynamics of 235Ч263 Cochlea, uncoiled, in Cochlear potentials 109Ч110 Compensation cases, computation of hearing loss in 442Ч447 Compensation cases, computation of percent loss 445 Compensation cases, determination of, audiogram 442 Compensation cases, determination of, effective loss, using both ears 442Ч443 Compensation cases, determination of, percent hearing loss 443Ч444 Compensation cases, determination of, weighted average percent loss 444 Compensation cases, Fletcher method 446 Compensation cases, Fowler plan 446 447 Compensation cases, relation of compensation to percent loss 445Ч447 Component tones, loudness levels of 195Ч201 Components, frequency and magnitude of 178 Condenser, rotary air 146Ч149 Conductive deafness 137 424 437 438 Consonants, combined characteristics 87 Consonants, Crandall's study of, b vs. p 61 63 Consonants, Crandall's study of, d vs. t 63 Consonants, Crandall's study of, g vs. k 63 65 Consonants, Crandall's study of, j vs. ch 65 Consonants, Crandall's study of, th vs. th 64 65 Consonants, Crandall's study of, v vs. f 65 Consonants, Crandall's study of, z vs. s 67 Consonants, Crandall's study of, zh vs. sh 65 67 Consonants, duration of 61Ч67 Consonants, fricatives see "Fricatives" Consonants, intensity range of 86 Consonants, power 84 86 Consonants, sensation level 85 Consonants, spectrograms of 60 61 Consonants, stop 1 2 4 64 Consonants, stop, nazalized 5 Consonants, unvoiced 1 2 4 Consonants, voiced 1 2 4 Continuants 5 Conversational speech 15 Conversational speech, articulation tests for intensities used in 415Ч419 Conversational speech, differentiated from written speech 96 Conversational speech, peak powers in 77 80 Conversational speech, telephone, analysis of 92Ч96 Conversational speech, typical values in 83 Cord tone 58 Cord tone, modulation of 5 Corti, organ of 108 109 Cough, pictures of production of 23Ч24 Coupler calibrations 120 Crandall, I.B. 29 58 59 Cut-off frequency, articulation for fricatives, vs. 422 Cut-off frequency, articulation for semivowels, vs. 421 Cut-off frequency, articulation for short vowels, vs. 418Ч422 Davis, Hallowell 112 114 134 230 425 427 430 Deafness see also "Hearing loss" Deafness of children 282 Deafness, articulation tests, systems used in 430Ч441 Deafness, artificial 424 Deafness, audiograms 424Ч426 Deafness, causes of 424 Deafness, compensation cases 442Ч447 Deafness, conductive 137 424 437 438 Deafness, effect on articulation 424Ч441 Deafness, mixed 424 435 436 Deafness, nerve 137 424 438 439 Deafness, temporary 134 Deafness, total 443 Deafness, unilateral 158Ч159 Decibel, intensity level 70 Decibel, use in acoustical work 134 Depth localization, factors affecting 221Ч222 229 Dewey, Godfrey 89Ч91 Difference tones 235 Difference tones, definition of 160 Differential intensity sensitivity, data on 144Ч145 Dimock, P.V. 306 357 Diphthongs 1 2 Diphthongs, formation of 4 Direct-current (d-c) flow 6 Disc, noise from 101 Distortion, carbon microphone 356Ч361 Distortion, due to different reproducing and recording speeds 351 Distortion, due to frequency shift 352 Distortion, due to overloading 354Ч356 Distortion, due to reverberation in sending and receiving rooms 352Ч354 Distortion, effects of, on individual speech sounds 415Ч423 Distortion, filter 418Ч422 Dudley, H.W. 8 Dunn, H.K. 3 72 76 304 305 413 Duration of speech sounds 58Ч67 Ear, artificial 120 Ear, body of liquid in 111 Ear, canal 106 Ear, differential sensitivity of 144 Ear, hair cells of 108Ч110 Ear, inner 106Ч110 Ear, inner, parts of 107 235 Ear, inner, size of parts 111 Ear, middle 106 110 Ear, middle, openings into 107 Ear, outer 106 Ear, parts of 106Ч111 Ear, parts of, diagrams 107 108 109 Ear, parts of, use in sensing sound 117Ч118 Ear, pinna 106 Ear, tolerance to sound 133Ч134 Eardrum 106 110 111 231 232 Eardrum, external 232 Eardrum, minimum audible pressures at 119 Eardrum, secondary 107 Egan, J.P. 303 Electric shock, and muscle contraction 114 Electrical circuit for measuring average power-frequency distribution of sounds 71 72 Electrical circuit for measuring peak power-frequency distribution of sounds 72 Endolymphatic duct and sac 106 Epiglottis 19 European Standards Association 177 Eustachian tube 107 Falsetto mechanism 21 22 23 Farnsworth, D.W. 17 76 304 Fenestra ovalis 107 Fenestra rotunda 107 Film, noise from 101 Filter distortion on speech sounds 418Ч422 Firestone, F.A. 191 193 Fletcher, H. 133 142 192 241 278 309 413 Foot plate (of stirrup) 106 Formants 5 7 10 20 Fowler, E.P. 446 447 French, N.R. 92 290 308 357 Frequency of occurrence of parts of speech 92 Frequency of occurrence of phonetic sounds 94Ч96 Frequency of occurrence of speech sounds 89 91 Frequency of occurrence of syllable combinations 89 90 91 Frequency of occurrence of words 89 90 91 Frequency vs. distance from stapes 240 Frequency, critical bands of, determination of 171 Frequency, distribution in speech, analyses of 52Ч57 Frequency, fractional changes in 144 Frequency, fundamental (cord tone) 58 Frequency, level, minimum perceptible changes in 144Ч152 Frequency, ranges in speech 52Ч67 88 Frequency, regions 5 Frequency, shift, distortion due to 352 Frey, A.R. 243 Frey, T.C. 212 213 Fricatives 1 2 66 Fricatives, articulation for, vs. cut-off frequency 422 Fricatives, formation of 5 Fricatives, pitch of 54 56 Fricatives, unvoiced 4 Fricatives, voiced 4 Fundamental melodic stream, definition of 54 Galambos, R. 112 114 230 Galt, R.H. 278 290 293 Gardner, M.B. 312 Geiger, P.H. 191 193 Glottis 4 7 9 16 20 23 Goodale, W.D., Jr. 397 Gray, C.H.G. 123 Green, C.W. 10 Guild, S.R. 174
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



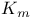 ,
,  , a, and
, a, and 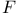
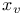
 and
and  , determination of
, determination of  and
and