|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Klein F. — Elementary Mathematics From an Advanced Standpoint: Arithmetic, Algebra, Analysis |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Abel 84 138 154
Abridged reckoning 10
Actually infinitely small quantities 214 218 219
Algorithmic method see "Processes of growth plan
Analysis situs 267
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus 221
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus, in the theory of fractions 29
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus, in the theory of fractions, complex numbers 56—58
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus, in the theory of fractions, irrational numbers 33
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus, in the theory of fractions, natural numbers 14
Applicability and logical consistency in infinitesimal calculus, in the theory of fractions, negative numbers 23—25
Applied mathematics 4 15
Approximation, mathematics of 36
Archimedes 80 209 219 222 237
Archimedes, axiom of 218
Arithmetization 266
Arrangement within an assemblage 262
Assemblage of algebraic and transcendental numbers 250 254—256
Assemblage of continuous and real functions 206 259—261
Bachmann 39 48
Ball 74
Baltzer 72
Bauer 86
Baumann 220
Berkeley 219
Bernoulli, Daniel 205
Bernoulli, Jacob 200
Bernoulli, Johann 200 205 216
Bernstein 261
bessel 191
Branch points 107 109
Braunmuehl 175
Briggs 172 173
Brouwer 265
Budan 94
Buergi 147
Burkhardt 23 29 191 205
Calculating machines 17—21
Calculating machines and formal rules of operation 21 22
Cantor, Georg 12 32 35 204 221 250 266 267
Cardanus 55 80 134
cardinal number 251
Cartesius see "Descartes"
Casus irreducibilis of the cubic equation 135
Cauchy 84 154 202 213 219 228 231 235
Cavalieri 210 214
Cayley 68 73 74
Chernac 40
Chisholm 179
Circular functions see also "Trigonometric functions"
Circular functions, analogy with hyperbolic functions 166
Clebsch 84
Closed fundamental series 264
Coble 143
Complex numbers, higher 58—75
Consistency, and applicability, of infinitesimal calculus 221
Consistency, and applicability, of the theory of fractions 30
Consistency, and applicability, of the theory of fractions, complex numbers 55—58
Consistency, and applicability, of the theory of fractions, irrational numbers 34
Consistency, and applicability, of the theory of fractions, natural numbers 14
Consistency, and applicability, of the theory of fractions, negative numbers 23
Consistency, proofs of 13 25 57
Constructions with ruler and compasses 49
Continued fractions 42—44
Continuity, analysis of, based on theory of assemblages 263—266
Copernicus 81 171
Coradi 198
Curriculum proposals, the Meran 16
Cut, after Dedekind 33
Cyclometric functions, definition of, by means of quadrature of the circle 163—168
Cyclotomic numbers 47
D'Alembert 103 212
De Moivre 153 168
Decimal system 6 9 20
Dedekind 13 33
Dehn 267
Delambre 180 181
Dense 31 249 263 264
Denumerability of a denumerable infinity of de-numerable assemblages 254
Denumerability of algebraic numbers 253
Denumerability of rational numbers 252
Derivative calculus 220 234
Descartes 81 94
Development of infinitesimal calculus 208—220
Diagonal process 254 259 261
Differences, calculus of 228 230—232
Differentials, calculation with, direction of mathematics of approximation 215 216
Differentials, calculation with, formal direction 215
Differentials, calculation with, naive intuitional direction 208—210
Differentials, calculation with, speculative direction 214 216 217
Dimension, invariance of the dimension of a continuum by reversibly unique mapping 264 265
Dirichlet 42 199 202 203 204 206
Discriminant curve of the quadratic and cubic equation 92
Discriminant surface of the biquadratic equation 98—101
Dyck 94
Enriques 55 267
Equations, cyclotomic 50
Equations, of fifth degree 141—142
Equations, pure 110—115 131—134
Equations, reciprocal 51
Equations, the dihedral Equations 115—120 126
Equations, the icosahedral Equations 120—130
Equations, the octahedral Equations 120—130
Equations, the tetrahedral Equations 120—130
Equivalence, of assemblages 251—262
Equivalence, theorem of 260
Eratosthenes 40
Eudoxus 219
Euklid 32 80 219
Euler 50 56 77 82 155 166 200 202 212 234 237
Exhaustion, method of 209
Exponential function, definition by quadrature of hyperbola 149 156—157
Exponential function, function-theoretic discussion of 156
Exponential function, general Exponential function, and 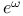 158—159 160—161 158—159 160—161
Exponential function, series for 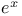 152 152
Fejer 200
Fermat 39 48 58
Fermat, great theorem of 46—49
Formal mathematics 24 26 29 56
Foundations of arithmetic, by means of intuition 11
Foundations of arithmetic, formalism 13
Foundations of arithmetic, logic 11
Foundations of arithmetic, theory of point sets 12
FOURIER 91 201 204 206 207 222 236
Fourier's series see "Trigonometric series"
Fourier's series, integral 207
Fractions, changing common into decimal 40
Function, notion of, analytic function 200—201
Function, notion of, arbitrary function 200
Function, notion of, discontinuous real functions 204
Function, notion of, relation of the two in complex region 202—203
Functions, assemblage of continuous and real 206 261—262
Fundamental laws of addition and multiplication 8—10
Fundamental laws of addition and multiplication, consistency 13
Fundamental laws of addition and multiplication, logical foundation 10—16
Fundamental regions on the sphere 111—114 117—120
Fundamental series, Cantor's 264
Fundamental theorem of algebra 101—104
Galle 17
Gamma function 239
Gauss 39 42 50 58 76 102 154 181
Gibbs 199 200
Gordan 143
Goursat 235
Graphical methods for determining the real solutions of equations 87—101
Graphical methods for equations in the complex field 102—133
Grassmann 12 58 64
Gutzmer 2
Hahn 268
Hamilton 11 58 62 73 74
| Hammer 175
hankel 26 56
Harnack 235
Hartenstein 99
Heegard 267
Hegel 217
Heiberg 80 209
hermite 238 239 245
hilbert 13 14 48 218 238 243
Historical excursus on, exponential function and logarithm 146—155
Historical excursus on, imaginary numbers 55 75—76
Historical excursus on, infinitesimal calculus 207—223
Historical excursus on, irrational numbers 31—34
Historical excursus on, negative numbers 25—27
Historical excursus on, relations between differential calculus and the calculus of finite differences 232—235
Historical excursus on, Taylor's theorem 233—234
Historical excursus on, the modern development and the general structure of mathematics 77—85
Historical excursus on, the notion of function 200—207
Historical excursus on, transcendence of e and  237—238 237—238
Historical excursus on, trigonometric series 205—207
Historical excursus on, trigonometric tables and logarithmic tables 170—174
Homogeneous variables in function theory 106—108
Hyperbolic functions 164—166
Hyperbolic functions, analogy with circular functions 166
Hyperbolic functions, fundamental function for 166
Impossibility, proofs of, construction of regular heptagon with ruler and compasses 51—55
Impossibility, proofs of, general 51
Impossibility, proofs of, trisection of an angle 114
Induction, mathematical 11
Infinitesimal calculus, invention and development of 207
Instruction, reform in 5
Interpolation parabolas 229
Interpolation, by means of polynomials after Lagrange 229
Interpolation, by means of polynomials after Newton 229—232
Interpolation, by means of trigonometric 190—193
Investigation, mathematical 208
Irreducibility, function-theoretic 113—114
Irreducibility, number-theoretic 52
jacobi 84
Kaestner 76 210 212
Kant 10
Kepler 208 210
Kimura 74
Koenig, J. 258
Kowalewski 215 216
Kummer 48
L'Hospital 216
Lacroix 235
Lagrange 66 82 83 153 200 220 222 234
Lagrange's interpolation formula 229
Leibniz 13 20 56 82 200 211 214 215 220 222
Lie 84
Limit, method of 211—214
Lindemann 238 243 249
Liouville 256
Logarithm, base of the natural 150—151
Logarithm, calculation of 148 172
Logarithm, definition of the natural Logarithm by means of quadrature of the hyperbola 149 156
Logarithm, difference equation for the Logarithm 148
Logarithm, function-theoretic discussion of Logarithm 156—162
Logarithm, uniformization by means of Logarithm 133 159
Luebsen 216
Lueroth 17
Maclaurin 210 212 234
Maennchen 49
Mangold 267
Markoff 236
Mean-value theorem of differential calculus 213—214
Mean-value theorem of differential calculus, extension of same 231
Mehmke 95 170
Mercator, N. 81 150 168
Michelson 198 199
Minkowski 11 39
Moebius 176 177 182
Molk, J. 8
Mollweide 181
Monge 84
Napier see "Neper"
Neper 81 147 150 172 173
Netto 86
Newton 81 82 151 168 210 212 222 230 233 237
Newton's interpolation formula 229—232
NOERLUND 236
Nomographic scales for class curves 90 95
Nomographic scales for order curves 89 94
Non-Archimedean number system 218
Non-denumerability of the continuum 256
Normal class curve of biquadratic equation 96—98
Normal curves as, class curves 90—93 95 97
Normal curves as, order curves 89—90 94
Normal equations of radicals 138—141
Normal equations of the regular bodies, solution by separation and series 130—133
Normal equations of uniformization 133—138
Normal reduction of general equations to normal equations 141—143
Number pair 28 56
Number scale 23 26 31
Number, assemblage of continuous and real numbers 250 251—253
Number, notion of 10
Number, transition from, to measure 28
Odhner 17
Ohm 76
Order, types of 263
Osculating parabolas 224—226
Osculating parabolas, limiting form of 227
Ostrowski 103
Peano 12 265
Peano curve 265
Perception, and logic 11
Perception, inner 11
Peurbach 171
Philologists, relation to 2
Picard 84 160
Picard's theorem 160
Pitiscus 172 174
Plato 80 120
Poincare 11
Point lattice 43
Point, the infinitely distant Point of the complex plane 105
poisson 216
Power of a finite number of dimensions 257—258
Power of an assemblage 251—262
Power of an assemblage, the assemblage of all continuous functions 260
Power of an assemblage, the assemblage of all real functions 261
Power of the continuum of a de-numerable infinity of dimensions 258
Precision, mathematics of 36
Prime numbers, existence of infinitely many 40
Prime numbers, factor tables 40
Principle of permanence 26
Pringsheim, A. 233
Process of growth of mathematics, Plan A Separating methods and disciplines, logical direction 75
Process of growth of mathematics, Plan B Fusing methods and disciplines, intuitive direction 77
Process of growth of mathematics, Plan C Algorithmic process, formal direction 79
Psychologic moments in teaching 4 10 16 28 30 34 268
Ptolemy 170
Pythagoras 31 250
Pythagorean numbers 44
Quaternion 60—75
Quaternion, scalar part of Quaternion 60
Quaternion, tensor of Quaternion 63 66 72
Quaternion, vector part of Quaternion 60
Quaternion, versor of Quaternion 72
Rational, in the sense of mathematics of approximation 36
Reform, movement, the beginnings of infinitesimal calculus in school instruction 223 see "Reform
Reform, proposals, Dresden proposal reform for training teachers 2
Reform, the Basel aims toward 2
Regiomontanus 171
Regular bodies, groups of 120—124
Rhaeticus 171
Rieman sphere 105—110
Rieman surfaces 105—110
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте