|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Messiah A. Ч Quantum mechanics. Volume 1 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
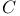 7 11 7 11
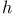 , , 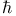 10 10
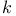 , Boltzmann constant see Boltzmann , Boltzmann constant see Boltzmann
 -function of Dirac 179 184 468Ч471 -function of Dirac 179 184 468Ч471
Absorption, emission of light 9 18 23
Absorption, of matter 60
Accidental degeneracy 355
action 10
Action, atomism of 41Ч42 115
Action, integral 36
Action, principle of least action of Maupertuis Ч Hamilton 32 53
Adjoint of an operator 255
Amplitude, scattering 372 383
Amplitude, scattering, Coulomb 424
Annihilation of matter 60
Antilinear (correspondence) 247
Average see Mean
AvogadroТs number 5 8
Balmer formula 22
Barn 371
Barrier, potential 78 86
Basis 203 273
Bauer, E 157
Bethe, formula 408
Bethe, H. A. 409
Black body radiation 10Ч11
Bloch, F. 449
Bohm, D. 157
Bohr atom 23 24
Bohr frequency 23
Bohr orbit 37
Bohr radius 414
Bohr Ч Peierls Ч Placzek relation 409
Bohr Ч Sommerfeld quantization rules 34Ч41 56 241
Bohr, N. 23 29 30 34 38 47 152
Boltzmann constant 205
Boltzmann factor 205
Born approximation for phase shifts 405Ч406 430
Born, M. 4 10 21 45 46 47 330
Bound state 73
bra, bra vector 246
Bracket see Poisson bracket
Brillouin, L. 69 216
Brownian motion 7 56
Canonical equations 32; see Hamilton
Causal, causality 156Ч159 310
Center of mass 361Ч366 380Ч385
Center of mass, system 380Ч385
Central potential 344Ч355; see Scattering
Chew, G. 372 409
Classical approximation limit 49 53 133 140Ч141 214Ч231 395 446-448
Classical doctrine 3 21
Classical mechanics, classical theory 3Ч11 23
Classical theory vs. quantum theory 15Ч18 46 154 166 294 317 361Ч363 387Ч389 420 424 444-448
Closure relation 187 268Ч271
Cloud chamber 8 142
Collision see Scattering
Collision, inelastic 24
Combination principle of Rydberg Ч Kitz 22 23
Commutator 63 163 206Ч212 250; Complete
Compatible variables 153Ч155 199 202;
Complementarity, complementary 149Ч159 401;
Complete set of commuting observables 202Ч 204 273 301
Complete set of compatible variables 155 203 294
Complete set of compatible variables, space 165
Complete set of compatible variables, system of functions, vectors 174 175 187 259
Complete set of compatible variables, theory 151
Compton, A. H. 13 15
Compton, effect 13Ч18 41 45 144 198
Compton, formula 13 16
Compton, wavelength 13
Configuration space 31 68 164
Conjugate momentum 32; see Lagrange
Conjugation between vectors, operators 254Ч256
Connection formulae for WKB Solutions 234Ч237
Conservation laws 21 42 60
Conservation of flux 108 121
Constants of the motion 210Ч211 318Ч319
Correspondence principle 27 42 46 50 61 64 68Ч71 214 317 338 446
Correspondence relations, wave-corpuscle 14 20 55 59 117Ч118
Coulomb (field, potential, interaction) 22 33 71 Chapter
Coulomb scattering 228Ч231 421Ч430
Creation of matter 60; see Operator
Cross section 74 229 369Ч371
Current 121Ч122 223 372
Dalembertian 65
Davisson and Germer 57
De Broglie relation 14 52 55 117
de Broglie wavelength 50Ч57
de Broglie, L. 46 47 48 49 61 65 66
Debye Ч Scherrer rings 57
Debye, P. 13
Decomposition into partial waves 385 389 425Ч426
Decomposition of unity 190Ч191 267
Degenerate, accidental degeneracy 355
Degenerate, degeneracy 78 172 258 354Ч355 417Ч418 453
Destruction operator see Operator
Determinant of a matrix 276 285
Diagonal see Matrix
Diagonalization 287
Diffraction 115 118 155
Diffraction, by a hard sphere 395; see Interference
Dirac, P. A. M 45 47 245 246 255 434
Direct sum 264
Dispersion law 50
Distributions (Schwartz) 182 App
Doppler effect 15
Dual space 246Ч247
Duality, wave-corpuscle 21 42 47 49 59 115 155
Effective range 406Ч409 430
Ehrenfest theorem 216
Eigendifferential 112 170 185 249
Eigenfunction 72
Eigenvalue of a matrix 287
Eigenvalue of an operator 171 185 258
Eigenvalue problem, eigenvalue equation 72 169 171Ч174 184Ч188 257-260;
Einstein 7 8 11Ч12 13 21 48
Einstein relation (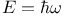 ) 72 310 ) 72 310
Electrodynamics, classical (Maxwell Ч Lorentz) 4 7 48 11 12 15 22
Electrodynamics, quantum 432 438Ч439
Electromagnetic field, particle in 43 47 49Ч50 67Ч68 70
electromagnetic, light 6 9
Electron 7 45 46 48 57Ч58 59Ч60 71
Emission of light see Absorption
equation see Dirac Hamilton Heisenberg Klein-Gordon Lagrange Schr eigenvalue radial secular
Equilibrium see Thermodynamic
Ergodic hypothesis 5
expansion see Series expansion
Fano, U. 331
FermatТs principle 54
Feshbach, H. 23 1 394
Filtering of wave packet 196Ч199 298 333
Fine structure (hydrogen atom) 38 419
Flux 369
Flux, relative 381; see Conservation
Fourier transform 118 127 130 471Ч478
Franck Ч Hertz Experiment 24 40 46
Fresnel 5
Function, characteristic 177 139 296
Function, eigen 72
Function, partition 338 448
Function, spherical Bessel 355Ч356 488Ч490
Function, spherical Coulomb 426 485Ч488; Lagrange Legendre
Furry, W. H. 231
Galilean transformation 383
Gaussian 131 449Ч451
Geiger counter 8
Gerlach see Meyer Stem
Germer see Davisson
Glauber, R. 442
| Goldberger, M. 409
Good quantum number see Quantum number
GreenТs functions 497
GreenТs Theorem 120
Ground state 23 24
Group velocity 50Ч55
Halperin, I. 463
Hamilton equations 33
Hamilton function 33 66Ч71
Hamilton Ч Jacobi formalism 223; see Action
Hamiltonian 33 68Ч71 120 310
Hamiltonian, harmonic oscillator 432
Hamiltonian, hydrogen atom 71
Hamiltonian, in polar coordinates 344Ч348
Hamiltonian, of electromagnetic field 439
Hard sphere see Scattering
harmonic oscillator Chapter XII
Harmonics see Spherical
Heisenberg, equation 316 443; УRepresentationФ
Heisenberg, W. 45 46 47 330
Hermicity, Hermitean see Operators Matrices
Hermite polynomials 441 491Ч492
Hertz 6
Hidden variables 152
Hilbert space 164 248
Hydrogen atom 22 33Ч34 37 55 71 412Ч420
Hydrogen-like atoms 39 413
Impact parameter 228 373 378 387 389
Inequality see Schwarz
Infinitesimal see Operator Transformation
Interference 94
Interference, and diffraction 4 18Ч20 41 47 56Ч59 115 118
intermediate see УRepresentationФ
Intersection of two subspaces 264
Invariance of matrix equations 285
Invariance of the Hamiltonian 343 365
Invariance of the trace 285
Inverse of a matrix 277 281
Inverse of an operator 251
Irreducibility 302
Jeffreys, H. 216
Jordan, P. 46 46 330
KeplerТs laws 30
ket, ket vector 245
Klein Ч Gordon equation 65
Kramers, H. A. 28 216
Kronecker product 252
Kronecker symbol 173
Laboratory system 380Ч385
Lagrange conjugate momentum 32
Lagrange equation 32
Lagrange function 32 33 43
Laguerre polynomials 416 419 483
Langer, R. E. 231 235 368 410
Langevin 26
LaplaceТs equation 415 422 425 480
Laplacian 63
Larmor precession (frequency) 25 43
Lenard 12
Lifetime of metastable state 401Ч403
Linear see Operator
Logarithmic derivative 81 99 389
London, F. 157
Lorentz electron theory see Electrodynamics
Lorentz transformation 383
Loschmidt 5
Low, F. 372
Macroscopic scale, limit 3 21
magnetic moment 25
magnetic quantum number 354; see Electromagnetism
Matrix 273Ч290
Matrix, diagonal 276 280
Matrix, hermitean 276
Matrix, inverse 277 281
Matrix, mechanics 40Ч48 330
Matrix, orthogonal 277
Matrix, singular 277
Matrix, transposed 277
Matrix, unitary 277 281
Matter wave see Wave
Maupertuis see Aetion
Maxwell 4 5;
Mean life 28 137 157 403
Mean life, relation to width 137Ч138
Mean value (definition) 122 126 166Ч167 243 296 331Ч333
Mean value (law of motion) 210 216Ч218 319
Measurement, and uncertainty relations 139Ч149
Measurement, ideal 196Ч199 298 333
Measurement, mechanism and complementarity 149Ч159 157
Measurement, of energy 138
Measurement, of momentum 145Ч149
Measurement, of position 142Ч145
Mechanics see Classical Matrix Wave
Metasrtable state 399Ч403; see Lifetime State
MeyerЧGerlach experiment 12
Michelson Ч Morley experiment 6
Millibam (mb) 371
Millikan 8
Mixtures 204Ч205 336
Momentum 14 52Ч53 54 64
Momentum, angular 25 37Ч39 195Ч196 208Ч209 345-349
Momentum, conjugate see Lagrange
Momentum, radial 346 366
Morse, P. M. 231 394
Neutron diffraction 56 57
Newton 3 4 6 42
Nodes, number of 88 91 109Ч110
Norm of functions, vectors 165 248
Normalizable function 185
Normalization condition 117 270
Nucleus, atomic 8 60 71
Observables 188 194 260 266Ч273 297
Observables, commuting 199Ч204 272Ч273;
Observables, fundamental 298
Old quantum theory 27Ч31 241 419 420
Operator, creation, destruction 438Ч439 453
Operator, density (or statistical) 295 331Ч338
Operator, differential 62Ч64
Operator, evolution 310Ч312
Operator, Hermitean 120 125 167Ч168 256
Operator, infinitesimal unitary 291Ч292
Operator, linear 62Ч63 250Ч252
Operator, positive-definite Hermitean 257 293
Operator, unitary 257 291
Orthogonal functions 111 165 172Ч175
Orthogonal matrix 277
Orthogonal spaces, projectors, vectors 248 258 264;
Orthonormality relations 174 187 259
Oscillator see Harmonic
Parabolic coordinates 415
Paramagnetic, paramagnetism 25
Parity of an observable 211
Parity of spherical harmonics 495
Parity of wave functions 88 112Ч113
Parseval relation 175 186 268 270 476
Partial waves method 385 389 425 426
Partition function 338
Peierls, R. E. see Bohr
Penetration factor 391 430
Periodicity condition 193
Perrin, J. 8
Phase, Coulomb 426
Phase, extension in 241
Phase, factor 121 296
Phase, Shift 353 385Ч409 428Ч430
Phase, space 33 36
Phase, velocity 50 55
Phonon 456
photoelectric effect 11Ч13 16 41
Photon 11Ч21 41 59 138Ч139 147Ч 149 156 159 438-439
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 ,
, 
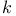 , Boltzmann constant
, Boltzmann constant  -function of Dirac
-function of Dirac 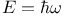 )
)