Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Goffman C., Pedrick G. — First course in functional analysis
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: First course in functional analysisАвторы: Goffman C., Pedrick G. Аннотация: Functional analysis is a branch of mathematical analysis, the core of which is formed by the study of vector spaces endowed with some kind of limit-related structure (e.g. inner product, norm, topology, etc.) and the linear operators acting upon these spaces and respecting these structures in a suitable sense. The historical roots of functional analysis lie in the study of spaces of functions and the formulation of properties of transformations of functions such as the Fourier transform as transformations defining continuous, unitary etc. operators between function spaces. This point of view turned out to be particularly useful for the study of differential and integral equations.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1965Количество страниц: 295Добавлена в каталог: 20.02.2013Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Absolutely continuous measure 132 Adjoint of a transformation 84 Algebra 33 Algebra, Banach 248 Algebraic dual 52 Almost everywhere 113 Approximate identity 249 269 Arc length 40 Arzela — Ascoli theorem 28 Banach algebra 248 Banach lattice 236 Banach limits 64 Banach space 71 Base for a topology 206 Basis, Hamel 55 Basis, orthogonal 177 Basis, Schauder 101 Bergman kernel 188 Bessel’s inequality 176 Bounded, functional 72 233 Bounded, set 211 Bounded, totally 25 Bounded, transformation 72 Bounded, uniformly 28 Category 21 Cauchy sequence 11 Cauchy — Schwarz inequality 4 6 165 Chain 53 CHARACTER 270 Characteristic number 85 Closed graph theorem 98 Closed set 9 208 Closed transformation 97 Closure of a set 9 208 Coarser topology 206 Compact 24 208 Compact transformation 83 Compact, locally 251 Complete metric space 11 Complete set 173 191 Completion 20 Completion, functional 185 Connected 28 Continuity 27 207 Continuity, absolute 132 Continuity, equi 28 Continuity, semi 38 Continuity, uniform 27 Contraction 17 Convergence in measure 118 Convergence, exercise 2 8 Convergence, field 231 Convergence, weak 86 202 Convergent sequence 8 Convex 7 58 211 Convex, locally 217 Curve 39 Deficiency 57 Dense 9 Dense, everywhere 9 Dense, nowhere 21 DIMENSION 56 183 Directed set 246 Directed set, exercise 10 1 Directed sum 51 100 Dominated Convergence Theorem 127 Dual of 146 Dual of 93 Dual of 142 Dual of C[a, b] 94 Dual, algebraic 52 Dual, space 73 Egoroffs theorem 118 Entire functions 220 Equicontinuity 28 Ergodic theorem, individual 148 Ergodic theorem, mean 172 Everywhere dense 9 Fatou theorem 126 Field, convergence 231 Field, normed 257 Finer topology 206 First category 21 FK space 224 Fourier expansion 175—77 Frechet space 224 Fubini’s Theorem 161 Fubini’s theorem, exercise 6 4 Functional 52 Functional completion 185 Functional, bounded (see Bounded transformation) Functional, linear 52 Functional, positive 233 Graph of a transformation 98 Group, locally compact 251 Group, ordered 59 Group, topological 251 Haar functions 194 Haar measure 252 Hahn — Banach theorem 60 62 73 Hamel basis 55 Hilbert space 166 Holder inequality 2 6 136 Hyperplane 57 Ideal 254 Ideal, maximal 255 Identity, approximate 249 Independent, linearly 55 Individual ergodic theorem 148 Inner product 165 Inner product space 166 Integrable function 124 integral 120—24 128 Interior point 9 Involution 265 Isometry 20 Kernel, Bergman 188 Kernel, reproducing 186 Kothe space 239 Lattice, Banach 236 Lattice, vector 233 Lebesgue 120—24 Lebesgue integral 120—24 Lebesgue measure 115 Limit point 9 Linear, functional 52 Linear, independence 55 Linear, space (see Vector space) Linear, transformation 52 Lipschitz condition 17 Locally compact group 251 Locally convex space 217 Mapping (see Transformation) Maximal, element 53 Maximal, ideal 255 Mean ergodic theorem 172 Measurable function 115 212 Measurable set 110—14 Measure 109—15 Measure, absolutely continuous 132 Measure, convergence in 118 Measure, Haar 252 Measure, Lebesgue 115 Measure, Radon 237 Measure, signed 129 Measure, singular 134 Measure, totally a finite 115 Measure, totally finite 114 Metric 1 Metric space 1 Metric, uniform 8 Metrizable 207 219 Miintz’ theorem 181 Minkowski inequality 3 5 Neighborhood 9 Norm 71 Norm of a transformation 72 Norm, semi 71 217 Normable space 211 Normal family 35 Normed field 257 Nowhere dense set 21 Null space 57 Open mapping theorem 98 Open set 9 206 Operator (see Transformation) Operator, positive 102 Ordered set 232 Ordered set, partially 53 Orthogonal 167 Orthogonal, basis 177 Orthogonal, set 173 Orthonormal set 173 Parseval’s formula 177 Partially ordered set 53 Positive functional 233 Positive operator 102 Product, inner 165 Product, topology 208 Projection 100 170 Projection theorem 170 Rademacher system 197 Radical 265 Radon measure 237 Radon — Nikodym theorem 132 Reflexive space 91 Regular ideal 266 Regular method 87 228 Reproducing kernel 186 Riemann — Stieltjes 95 Riesz representation theorem 96 Riesz — Fischer theorem 184 Schauder basis 101 Schwarz inequality 4 6 165 Second category 21 Semi-continuity 38 Semi-simple 265 Seminorm 71 217 Separable space 9 183 Sgn z 93 Signed measure 129 Singular measure 134 Space of entire functions 220 Space of measurable functions 212 Space, Banach 71 Space, compact 208 Space, complete metric 11 Space, linear (see Vector space) Space, locally convex 217 Space, m 75 (see also Space, metric 1 Space, M[a, b] 6 Space, normable 211 Space, reflexive 91 Space, separable 9 183 Space, topological 206 Space, topological vector 210 Space, vector 50 Spectrum 263 Sphere 8 Stone — Weierstrass theorem 34 Subbase for topology 206 subspace 2 52 Summable function 123 Summand, direct 51 100 Topological group 251 Topological space 206 Topological vector space 210 topology 206 Topology, base for 206 Topology, coarser 206 Topology, finer 206 Topology, product 208 Topology, subbase for 206 Topology, weak 209 Total set 57 86 214 Total variation 131 Totally a finite measure 115 Totally bounded 25 Totally finite measure 114 Transformation, adjoint 84 Transformation, bounded 72 Transformation, closed 97 Transformation, compact 83 Transformation, graph of a 98 Transformation, linear 152 Transformation, positive 102 Tychonoff theorem 208 Uniform boundedness 28 Uniform boundedness, principle of 76 Uniform continuity 27 Uniform metric 8 Variation, total 131 Vector lattice 233 Vector space 50 Vector space, topological 210 Walsh system 200 Weak convergence 86 202 Weak convergence, exercise 2 8 Weak topology 209 Weierstrass approximation theorem 32
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



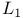
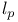
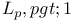
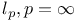 p=\infty$"/>)
p=\infty$"/>)