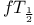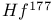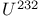"Black" nucleus approximation 334
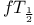 282Ч283 282Ч283
Absorption of gamma rays 231Ч233
Absorption of neutrons 231Ч233
Absorption of thermal neutrons 339
Accelerators 239Ч243
Accelerators, cyclotron 240Ч243
Accelerators, tandem Van de Graaff 240
Accelerators, Van de Graaff 240 242Ч243
Activation analysis 386
Agriculture, radioactivity in 384
Allowed transitions 275 283Ч284
Alpha-particle emission 194 260Ч265
Alpha-particle emission energetics 194
Alpha-particle emission from compound nucleus 313 315Ч316
Alpha-particle emission in helium burning 396
Alpha-particle emission to excited states 263
Alpha-particle emission, barrier penetration in 263Ч265
Alpha-particle emission, reduced width for 260Ч263
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) 220
Angular correlation 299Ч302
Angular distributions from compound nucleus 313
Angular distributions from direct reactions 353Ч362 371Ч374
Angular momentum conservation in collisions 85
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by angular-correlation studies 299Ч300
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by beta decay 283Ч284
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by direct nuclear reactions 360Ч362 364 369Ч373
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by gamma decay 298Ч299
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by internal conversion 309
Angular momentum of nuclear states (I), determination of, by isobaric analog state studies 367 368
Angular momentum of particle in a well 19Ч20
Angular momentum, addition of 26Ч27
Angular momentum, coupling of 121Ч123
Angular momentum, orbital 19Ч20
Angular momentum, orbital, z component of 24
Angular momentum, total 72
Angular momentum, total, z component of 72
Angular-momentum barrier see "Barrier penetration"
Angular-momentum transfer in direct reactions 353Ч355 358Ч361 366 369 372Ч378
Antenna patterns 299
Antineutrino 187Ч188
Antisymmetry of wave functions 37Ч38
Barn 201
Barrier penetration in alpha decay 263 265
Barrier penetration in beta decay 272 273 276
Barrier penetration in chemical reactions 389
Barrier penetration in electron capture 284Ч285
Barrier penetration in fission 265Ч267
Barrier penetration in gamma-ray emission 290
Barrier penetration in helium burning 396
Barrier penetration in neutron induced reactions 322
Barrier penetration in proton emission from compound nucleus 315 341 342
Barrier penetration in resonance reactions 331Ч332
Barrier penetration, angular momentum 255Ч258
Barrier penetration, coulomb 258Ч260
Barrier penetration, theory of 250Ч252
Bartlett force 44Ч46
Beta (deformation parameter) 154Ч155
Beta decay 187Ч192 269Ч287
Beta decay, applications of 198
Beta decay, double 190Ч191
Beta decay, energy spectrum 271Ч273
Beta decay, half-life 201Ч202
Beta decay, mass relations for 188Ч189
Beta decay, products 201
Beta decay, stability and 189Ч191 see
Beta stability, line of 189Ч190 192
Beta vibrations 151Ч156
Binding energy of deuteron 33Ч34 35
Binding energy of nuclei 160Ч172
Binding energy of nuclei, calculation from nucleon-nucleon force 172Ч174
Binding energy of nuclei, calculation from shell theory 172
Binding energy per nucleon 160Ч163 see
Biological effects of radiation 387 388
Bohr, A. 147
Bombs, atomic (fission) 337 407
Bombs, hydrogen 337 405
Bosons 51
Breit Ч Wigner formula 329 339
Breit, G. 60
Broken pairs 101Ч102
Brueckner, K.A. 65
Bubble chamber 211 223
Carbon cycle 394Ч395
Central force 41
Centrifugal stretching 150Ч151
Charge independence of nuclear force 60 136Ч143 see
Charge symmetry of nuclear force 158
Charge-exchange scattering 351 352 380
Chart of nuclides 201
Closed-shell nuclei 76 86 87
Closed-shell nuclei, first excited states of 113Ч114
Closed-shell nuclei, neutron capture in 339 401
Cloud chamber 211 223
Coherence effects in (p,i) reactions 371
Coherence effects in alpha decay 262
Coherence effects in gamma-ray emission 294
Coherence effects in pairing 95Ч96
Coherence effects in vibrational states 107 110
Coincidence measurements 233Ч236
Coincidence measurements, delayed 235Ч236
Collective states 110 see also "Rotional states" "Vibrational
Collision pattern, rhythmic see "Coherence effects"
Collisions 64Ч65 81Ч89 99 106Ч107 113 117 132 311Ч314 323Ч324
Collisions, rules for, in nuclei 84Ч85
Compound-nucleus reactions 311Ч348
Compound-nucleus reactions, classical treatment 311Ч313
Compound-nucleus reactions, induced by gamma rays 346Ч348
Compound-nucleus reactions, induced by low-energy neutrons 336Ч340
Compound-nucleus reactions, qualitative quantum treatment 313Ч316
Compound-nucleus reactions, resonances 325Ч332
Compound-nucleus reactions, statistical region 340Ч345
Compound-nucleus reactions, strength function 332Ч336
Configuration 91Ч93 105Ч107 134Ч135 315 see
Coulomb effects in beta decay 272
Coulomb effects in isobaric analog states 139
Coulomb effects in shell-theory potential 66Ч67 71 77Ч78 see
Coulomb effects on binding energy 162 165Ч166
Coulomb effects, penetration of barrier 258Ч260
Coulomb excitation 149 380Ч381
Critical mass 406
Cross section for specific nuclear reactions 329 331Ч333 343Ч344
Cross section reaction 316Ч322
Cross section reaction in resonance region 328Ч329
Cross section reaction in statistical region 341 342
Cross section, definition of 200
Cross section, total 201 330Ч331
Curies 199
Cyclotron 240Ч243
Cyclotron, spiral-ridge 241Ч242
d-d and d-t reactions 403Ч404
Dating, radioactive 244 337 383
Decay laws 196Ч198
Decay rate 196Ч199
Decay rate in complex decays 197Ч198
Decay rate, beta decay 282 393
Decay rate, electron capture 284Ч285
Decay rate, gamma-ray emission 296
Decay rate, gamma-ray emission, single-particle 290Ч293 295Ч297
Decay rate, internal conversion 305
Decay rate, nucleon emission 253 254 257 258 342 see
Decay, nuclear 185Ч199 205Ч206
Decay, nuclear, energy release in 161
Density distributions of nucleons 4
Density of states of emitted particles 269Ч271 345 see
Detectors 210Ч219
Detectors, bubble chamber 211
Detectors, charge collection 214Ч219
Detectors, cloud chamber 211
Detectors, efficiency of 231
| Detectors, gamma-ray 231Ч233
Detectors, geiger counter 217
Detectors, neutron 230Ч231 337
Detectors, photographic emulsions 211
Detectors, proportional counter 217
Detectors, scintillation 212Ч214 231Ч232
Detectors, semiconductor 218Ч219 231Ч232
Detectors, spark chamber 211Ч212
Deuteron 33Ч36
Deuteron, angular momentum of 36
Deuteron, binding energy of 33Ч35
Deuteron, magnetic moment of 40
Deuteron, quadrupole moment, electric 40
Deuteron, size 34
Dipole moment, electric 9 179
Dipole radiation, electric 288Ч290 292Ч294
Direct reactions 311 350Ч381
Direct reactions, angular distributions from 353Ч359
Direct reactions, charge exchange 351 352 380
Direct reactions, coulomb excitation 380Ч381
Direct reactions, inelastic scattering 375Ч380
Direct reactions, mechanisms in 350Ч353
Direct reactions, multinucleon transfer 373Ч375
Direct reactions, one-nucleon transfer 356 359Ч366
Direct reactions, two-nucleon transfer 369Ч375
Distorted-wave Born approximation (DWBA) 356Ч359
Distorted-wave Born approximation (DWBA), charge-exchange reactions 380
Distorted-wave Born approximation (DWBA), finite range effects 358
Distorted-wave Born approximation (DWBA), nonlocal interactions 359
Distorted-wave Born approximation (DWBA), stripping reactions 356Ч357 361
Doppler-shift attenuation method 238Ч239
Double beta decay 190Ч191
Drift velocity 214
Drip lines 192Ч193
effective mass 69Ч72 79Ч80 173
Effective range 52
Effective thermal energy 390Ч391
Elastic scattering 316Ч324 328Ч329 336Ч337 359 375 376
Electric multipole radiation 288Ч295
Electromagnetic decay processes 185Ч187 see "Internal
Electron capture 188 284Ч285
Electron capture in formation of neutron stars 398Ч399
Elements, origin of 396Ч403
Elements, origin of, helium burning 396Ч397
Elements, origin of, neutron capture 400Ч402
Elements, origin of, other processes 402Ч403
Elements, origin of, proton capture 402
Elements, origin of, silicon burning 398Ч399
Energy distribution of electrons in beta decay 270Ч273
Energy distribution of internal-conversion electrons 305Ч309
Energy distribution of particles emitted from compound nucleus 312Ч313 315 340Ч342 344Ч345
Energy distribution of particles from direct reactions 360
Energy gap 94Ч97 105 114 169Ч170
Energy gap, determination of 169Ч170
Energy levels in Pd isotopes 133Ч134
Energy levels in shell-theory potential 73Ч75 120
Energy levels in shell-theory potential, filling of 75Ч76
Energy levels in Sn isotopes 130Ч133
Energy levels in square well 14Ч17
Energy levels in three-dimensional well 19Ч23
Energy levels in well of complex shape 18Ч19
Energy levels of 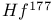 157 157
Energy levels of 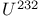 153 153
Energy levels of two nucleon system 32Ч33 34
Energy loss of charged particles 205Ч210
Energy measurements 219Ч223
Energy measurements by magnetic analysis 222
Energy measurements from pulse heights 219Ч220
Energy measurements of gamma rays 231Ч232
Energy measurements of neutrons 230Ч231 236
Energy measurements with ionization chamber 217
Energy measurements with proportional counter 217
Energy measurements with scintillation detectors 214
Energy measurements, energy resolution in 220Ч222
Energy production in fission reactions 405Ч407
Energy production in stars 392Ч395
Energy production with radioactive sources 386Ч387
Energy production with thermonuclear reactions 388Ч396 403Ч405
Energy resolution in magnetic analysis 222
Energy resolution of detectors 220Ч222
Energy resolution of gas counters 222
Energy resolution of scintillators 222
Energy resolution of semiconductor detectors 222
Energy spacings between levels see "Level density"
Energy spacings between orbits in shell-theory potential 85
Energy spacings between shells 78Ч80 85 118Ч120
Energy spacings between states (D) 326Ч327 332Ч334
Entropy, nuclear 117 341
Even-even nuclei, excited states of 105Ч118
Even-even nuclei, excited states of, noncollective 116Ч118
Even-even nuclei, excited states of, vibrational 107Ч116
Even-even nuclei, ground states of 97Ч101
Even-even nuclei, spheroidal 147Ч156
Exchange forces 42Ч46 58
expectation value 29
Experimental methods 204Ч244
Experimental methods, simplicity of 204Ч206
Fermi factor 272Ч273
Fermi gas 117
Fermi transition 276Ч282
Fermi Ч Kurie plot 272Ч273
Field particle 48
Fields, electromagnetic radiation 186
Fields, electron-neutrino 269
Fields, meson 47Ч48 50
Fission 195 244 263 265Ч267 338 405
Forbidden transitions 275 283Ч284
Four-quasi-particle (4QP) states 111
Gamma (deformation parameter) 154Ч155
Gamma rays 185Ч187 288Ч304
Gamma rays, reactions induced by 346Ч348
Gamma vibrations 151Ч156
Gamow Ч Teller transition 276Ч282
Geiger counter 217
Gyromagnetic ratio (g) 8Ч9 174
Half-life 196Ч197 205Ч206
Half-life, alpha decay 265
Half-life, beta decay 282
Half-life, fission 265
Half-life, isomerism 302Ч304
Half-life, measurement of 238
Half-life, nucleon emission 253
Half-life, partial 197
Half-life, use in isotope identification 243
Hamada Ч Johnston potential 56Ч58
Hartree Ч Fock calculations 172Ч174
Heisenberg force 44Ч46
Helium burning 396Ч397
Imaginary potential (W) 322Ч324
Imaginary potential (W) and collision frequency 323
Imaginary potential (W) and mean free path 322
Imaginary potential (W) from elastic scattering 318
Imaginary potential (W) from strength function 334Ч335
Imaginary potential (W) from stripping reactions 363
Imaginary potential (W), r dependence 323
Industrial processes, radioactivity in 387
Internal conversion 186Ч187 298 301 304Ч309
Internal pair formation 187 298
Ion source 239
Ionization chamber 214Ч217
Ionization potential 207Ч208
Isobaric analog states 137Ч143
Isobaric analog states in (p,n) reactions 378 380
Isobaric analog states in A=14 139Ч140
Isobaric analog states in A=7 140
Isobaric analog states in beta decay 278 281
Isobaric analog states in N=Z nuclei 140
Isobaric analog states in Pb-Bi 140Ч141
Isobaric analog states, coulomb-energy differences of 139 379
Isobaric analog states, elastic scattering via 367Ч368 370
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте