јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Smil V. Ч The Earth's biosphere: evolution, dynamics, and change
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: The Earth's biosphere: evolution, dynamics, and changeјвтор: Smil V. јннотаци€: Smil, in a presentation marked by balance and clarity, synthesizes the field of science dealing with the biosphere. It is an interdisciplinary one, combining organic chemistry, geology, solar physics, microbiology, zoology, and more. Whatever characteristics the biosphere displays on a global scale depend on living matter's fundamental chemistry, so Smil diagrams the structural backbone of cells Ч molecules such as cellulose or DNA. Moving next through types of metabolism, such as the ATP cycle, Smil explains the resultant chemical products and how they become fixed or cycled through the ground, water, or atmosphere. Addressing concerns about human influences on the biosphere, Smil describes them, but he is a scientist to the core (at the University of Manitoba) and is hesitant to proclaim doom as the certain outcome. That scientific humility only enhances Smil's work. A superior, comprehensive survey.
язык: –убрика: Ѕиологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 346ƒобавлена в каталог: 11.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Impacts 48Ч49 91Ч93 Inclination 46 India 254 261 Insects 87Ч88 161Ч162 174 IPCC 23 254 Iron (Fe) 28 65 142 151 153Ч154 Iron (Fe) fertilization 153Ч154 Iron (Fe) in the ocean 150Ч151 Iron (Fe), Banded Iron Formations (BIF) 50 131 Irrigation 246 Karst 169 Kerogens 131 Krakatau 90 121 Kuiper belt 266 La Nina 127 Lake Vostok 176 Lakes 126 128 178 250 Land cover 237Ч238 Land, agricultural 184 186Ч187 Land, use changes 239Ч240 Law, 3/4 200Ч201 Law, Kleiber's 201 203 Law, Moore's 269 Law, Planck's 100 Law, Stephan Ч Boltzman's 98 Law, Wien's 100 Lead (Pb) 14 46^7 Leaf area index (LAI) 194Ч195 Legumes 221 248 Lichens 224Ч225 Life 27Ч41 229Ч230 275 Life and size 12 276 Life in the ocean 162Ч169 Life, attributes of 11Ч12 Life, biochemistry of 30Ч38 Life, carbon-based 28Ч30 Life, classification of 39 80Ч86 Life, definitions of 12 25 Life, evolution of 9 51Ч62 269 Life, extent of 155Ч178 Life, extraterrestrial 52 58Ч60 62 Life, handedness of 34 Life, inevitability of 59Ч60 Life, limits of 8 155Ч178 Life, origin of 51Ч58 Life, prerequisites of 41Ч46 Life, probabilities of 58Ч62 Life, quality of 261 Life, subterranean 53 169Ч172 184Ч185 194 196 Life, tree of 80Ч86 Life, uniqueness of 60Ч61 Lightning 128 Lignin 131 137 147 257 Limestone See Carbonate calcium Lipids 30Ч32 37 Lithosphere 117 Lithotrophs 65 Litter 196 Local Bubble 42 luminosity 43 45 49 98Ч99 111 114 Machines 269Ч271 Magnesite 137 Magnesium (Mg) 28 146 Mammals 87 93 136 166Ч169 177 185Ч186 192 200Ч204 208Ч209 216 Mammals in the ocean 166Ч169 MARS 42 45 107 Martian 52 60 Mauna Loa 15 16 136 234 Mediterranean 209Ч210 240 242Ч243 Metabolism 39 41 64Ч80 Metabolism, autotrophic 65Ч74 Metabolism, chemolithotrophic 74Ч76 Metabolism, heterotrophic 76Ч80 Meteorites 34 39 52 54 Methane 26 29 50 76Ч77 89 103 107 111 166 229 231 236 254 255 Methane 135Ч137 Methanogens 57Ч58 76Ч77 Methionine 29 Mexico 88 161 240 Microchips 269Ч270 Microcosms 227 Microfossils 56 58 Microscopes 39 Migrations 159Ч160 Milky Way 27 Mississippi 243 247 249 Mitochondria 39Ч41 202 224 Mixotrophs 7 Molecules 28Ч38 Molybdenum (Mo) 28 Monomers 31 37 Monosaccharides 76 Moon 17Ч18 49 265 Moths 162 Mount Everest 159 161 180 Mount Pinatubo 143 Mount Saint Helens 143 MUDs 141 162 172 Mutualism 220Ч225 Mycorrhizae 221 225 Namib 212 Nanobacteria 39 NASA 20 60 101 NDVI 189Ч190 Nimbus 18 96 101 Ningxia 19 Nitrate 65 76 140Ч141 233 248Ч249 Nitrate sodium 248 Nitrification 75Ч76 140 Nitrite 65 Nitrogen 17 28 49 123 136Ч141 232 Nitrogen biofrxation 248 Nitrogen cycle 17 28 49 123 136Ч141 Nitrogen fixation 67 137Ч140 248Ч249 Nitrogen oxides 233Ч234 248Ч249 Nitrogen, anthropogenic 248Ч249 Nitrogenase 139 Noosphere 12Ч13 25 266 nucleotides 31Ч34 37 83 Nucleus 39Ч40 Nutrients 241 Ocean 20 47Ч49 109 116Ч119 123Ч128 156 162Ч169 230 253 Ocean Atlantic 121 125Ч127 188 254 263 Ocean cataracts 127 Ocean circulation 126Ч127 263 Ocean euphotic layer 163 Ocean floor 116Ч117 Ocean Indian 126Ч127 242 254 Ocean level 20 128 Ocean life 162Ч169 Ocean littoral 218 Ocean pelagic 219 Ocean ridges 48Ч49 53 116Ч117 134 143 147 Ocean, abyssal 162Ч164 211 219 Ocean, benthic 164 219 Ocean, iron in 153Ч154 OceanPacific 85 118Ч119 126Ч128 133 143 153 157 165Ч166 171 185 211 241 Omnivores 78 Oort Cloud 42 266 OPEC 22 Orbits 42 44 45 Organotrophs 65 ORNL 191Ч192 Ostracoderms 80 Oxides 137 140 Oxides ferric (FeO) 50 Oxides ferrous 50 Oxides nitrogen 233Ч234 248Ч249 Oxides nitrous 26 76 103 107 140 229 236 Oxygen 6Ч7 10 11 18 28 41 71 131 140 159 167 253 255 Oxygen in combustion 233 Oxygen in photosynthesis 65Ч67 69 71 Oxygen, evolution of 50Ч51 Ozone 23Ч24 50 55 100 103 107 229 234 237Ч238 Pangea 108 120Ч121 Panspermia 51 157 Pastures 240 Penguins 168 260 Peptidoglycan 40 257 Periods Cambrian 58 64 68 131 Periods Cretaceous 69 80 88 90 92Ч93 Periods Devonian 68Ч69 80 131 Periods Miocene 108 Periods Ordovician 80 Permian 90 Pesticides 14 22 Ph 108 173 177 179Ч180 234 255 Phloem 68 196 Phosphates 37Ч38 54 147Ч148 250Ч251 Phosphoras (P) 28Ч29 51 112 147Ч149 250Ч251 Phosphoras (P) cycle 147Ч149 Phosphorites 64 Photoautrophs 56 Photosphere 98 Photosynthesis 7 19Ч20 56 65Ч74 114Ч116 163 Photosynthesis, 71 Photosynthesis, 71 73Ч74 Photosynthesis, 72Ч74 Photosynthesis, CAM 74 Photosynthesis, carbon in 69 71Ч72 Photosynthesis, efficiency of 71 73 115Ч116 Photosynthesis, water in 65 71 115 Phototrophs 65 Phytogeny 54Ч55 70 83Ч86 Phytomass 7Ч9 141 181Ч187 193Ч197 215 243 Phytoplankton 100 133 145 153 163 182 188 194Ч195 206 209 219 247 Planetesimals 47 Planets, extrasolar 6 Planets, habitable 42Ч46 59 Planets, mass of 44 Plants 67Ч70 87 112 139 183 230 Plants, 71 73Ч74 Plants, 71Ч74 Plants, evolution of 67Ч70 Plants, productivity of 187Ч192 225Ч227 240Ч241 Plants, scaling of 203Ч206 Plastids 69 224 Plates, tectonic 17 96 116Ч119 134 147 156 Pollinators 222 Polymers 31 37 Polypeptides 33Ч36 53 Population, global 264 Potassium (K) 28 117 146 Precipitation 127Ч130 254Ч255 Primates 187 Productivity and diversity 225Ч227 Productivity, gross primary (GPP) 182 189 240 Productivity, models of 190Ч191 Productivity, net ecosystem (NEP) 183 226 Productivity, net primary (NPP) 133 140 182Ч183 187Ч192 208 212 214 217 218 222 240Ч241 249 285Ч286 Productivity, primary 187Ч192 Productivity, secondary 192Ч193 Prokaryotes 39Ч41 54Ч55 66Ч67 80 86Ч87 156 169Ч180 224 Prokaryotes, acidophilic 177Ч180 Prokaryotes, alkaliphilic 178 Prokaryotes, biomass 196 Prokaryotes, extremophilic 169Ч180 194 211Ч213 Prokaryotes, halophilic 179 Prokaryotes, subterranean 184Ч185 194 196 Prokaryotes, thermophilic 54 173Ч174 Proteins 28 30Ч31 33Ч34 36Ч39 56 141 174Ч176 Proteins, antifreeze 175Ч176 Proteins, structure of 35Ч37 Proteome 37 Proteostomes 80 Protists 67 208 218 222 224 Radiation spectrum 99Ч101 Radiation, forcing 236Ч237 254 Radiation, infrared (IR) 100Ч101 104Ч105 107 109 128 176 Radiation, photosynthetically active (PAR) 115 191 208 Radiation, solar 6Ч8 44 65 96 95Ч102 110Ч116 144 264 Radiation, ultraviolet (UV) 25 51 99Ч100 103 104 155 157 159 229 232 Radiation, visible 101 103 Radiometers, AVHRR 20Ч21 Radiometers, CZCS 20 190Ч191 Rate, basal metabolic (BMR) 200Ч201 203Ч205 Rate, field metabolic (FMR) 202 recycling 25 48 119 124 134Ч135 248 Red giant 43 Reefs, coral 163 211 218Ч219 225 Reservoirs 124Ч130 246 Respiration, autotrophic 182 189 Respiration, heterotrophic 182 Ribose 54 Ribosomes 34 38Ч39 82Ч83 Ribosomes, SSU 34 84 Rivers 130 146Ч147 246Ч247 RNA 29 32Ч34 37 47 53Ч56 78 80Ч86 127 147 RNA messenger (mRNA) 34 RNA polymerase 33Ч34 40 85 RNA World 54 RNA, ribosome (rRNA) 68 81Ч86 RNA, sequencing of 40 80 85 Rocks 48 50 55Ч56 66 111 118 133Ч134 Rodents 88 161 201 203 174 213 223 243 Rodinia 119 Rotation 42 44 Rubisco 69 71Ч73 Sahara 25 159 174 190 Sahel 20 239Ч240 San Francisco 173 243 Satellites 15 18Ч22 102 106 Satellites, CERES 106 Satellites, ERBE 106 Satellites, IKONOS 20 Satellites, LANDSAT 19Ч20 189 Satellites, SPOT 20 189 Satellites, Terra 20 22 Satellites, TIROS 15 18 21 Savanna 217 227 240 Scaling 199Ч207 Scaling of organisms 199Ч207 Scaling, density 205Ч207 Scaling, ecological 202 Scaling, explanations of 203Ч205 SCEP 22 Sediments 147Ч148 230 Serengeti 218 Services, biospheric 256Ч259 Seveso 22 shells 150 Silica 146 150 154 Silicates 133Ч134 150Ч152 247 Silicates calcium 133 150 Silicon (Si) 150Ч152 Silting 246 Sloths 202 Smog 23 Sodium (Na) 28 146 SOHO 96Ч97 Soils 50Ч51 85 112 143 169Ч171 223 Soils, bacteria in 170 184Ч185 193 Soils, carbon in 131Ч137 Soils, erosion of 146Ч147 241 Soils, horizons 70 Soils, organisms in 170 197 Solfataras 75 172 Sponges 64 67 80 164 Stars 42 43 45 96Ч102 Stars, Hertzsprang Ч Russel diagram 96 98
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




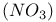
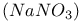



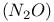
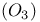
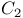 cycle
cycle 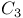 cycle
cycle  cycle
cycle