|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Vapnik V. — Estimation of dependences based on empirical data |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
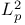 metric 192 194 259 metric 192 194 259
Accuracy 14
Algorithm, general 368
Algorithm, special 366
Baranchik theorem 120
Bayes's formula 47 52 60 67 366
Bayes's principle 51 128
Bernoulli theorem 162
Bhattacharya's theorem 118
Borel — Cantelli lemma 270 284
C metric 192 194
Canonical, space 211
Canonical, structure 211
Capacity characteristics 147 152
Cauchy — Schwarz inequality 95 188
Chebyshev inequality 31 32 279 284
Class of correctness 22
Closeness of function 15 16
Closeness of function in the 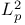 metric 16 17 18 metric 16 17 18
Closeness of function in the C metric 16 17 18
Complete sample 345
Completely continuous linear operator 21
Confidence 14
Conjugate gradients, method of 359 360
Conjugations 288
Correctness in Tihonov's sense 22 23
Covering by a finite net 149
Density, formed by a mixture 106
Density, nondegenerate at 0 100 106
Density, robust in a class 95
Density, with a bounded variance 99 106
Dichotomies 330 331
Dirichlet kernels 296
Distribution, binomial 343
Distribution, double exponential 33
Distribution, Gaussian 33 34 56 57 59 70 84 87 91 99 101 103
Distribution, Laplace 33 34 84 85 87 90 91 99 101 103
Distribution, Poisson 122 123
Distribution, uniform 33 34 84
Distribution, Wishart 59 60 62 68 69 244 245
Dual problem 356
Empirical function 27
Empirical mean 40
Empirical mean, convergence of 40
entropy 152 153 365
Entropy, mean 365
Equivalence classes 316 321 323 343 345
Estimating derivatives 13 291
Estimator, asymptotically efficient 75
Estimator, asymptotically unbiased 75
Estimator, Bayesian 71
Estimator, consistent 74
Estimator, jointly efficient 73
Estimator, linear minimax 71
Estimator, minimax 71
Estimator, of Stein-type 79
Estimator, ridge regression 122 239
Experiment 7
Experiment, closed 7
Experiment, open 7
Extreme vector 356
| Fisher matrix 113
Fisher's information quantity 72 96
Fourier transform 302 303
Fredholm integral equation 10 13 66 75 289
Functional of empirical risk 35 39
Gauss — Markov model 112 114 115
Glivenko — Cantelli theorem 37 38 41 42 155 305
Hoeffding inequality 31
Identifying linear objects 12
Inverse problem of gravimetry 290
Inverse problem of spectroscopy 11
James — Stein theorem 116
Kolmogorov — Smirnov bound 293
Koshcheev theorems 130 136
Kronecker symbol 373
Kuhn — Tucker theorem 355 356
Lagrange function see “Lagrange multipliers”
Lagrange multipliers 77 88 198 200 201 260
Linear discriminant analysis 47 48
Lipschitz condition 294 298 299
Loss function 2 183
Loss function, quadratic 141 183
Lozinskii — Kharshiladze theorem 286
Method of minimal modules 86
Mihalskii theorem 287
Minimax principle 52
Nadaraya's result 302
Newton's binomial expansion 167
Nonparametric statistics 39
Normal distribution see “Gaussian distribution”
Nuclear spectroscopy 289
Operator equation 10
Operator equation, stable 10
Operator equation, well-posed in the Hadamard sense 10 21
Parametric statistics 39
Prior information 29 34 134
Proper  -net 207 -net 207
Quadratic form 245
Rao — Cramer inequality 71 72 113
Regularization parameter 24
Relative variance of losses 183 184
Sequential search procedure 360
Set of correctness 22
Smirnov formula 299
Spline approximation 286 289
Splines, canonical 288 373
Stabilizer 23
Structure 234 236
Structure, combined 260
Tanimoto's metric 350
Taxon 347
Taxonomic structure 333-336
Tihonov's theorems 308
Training sample 313 346
Training sequence 3 328 333
Variance 30
Variance, absolute bound on 30
Variance, relative value 30
Volterra integral equation 13
Wiener — Hopf equation 12
Working sample 313 329 333 338 341 346
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



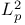 metric
metric  -net
-net