Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Charniak E. — Statistical Language Learning
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Statistical Language LearningАвтор: Charniak E. Аннотация: Eugene Charniak breaks new ground in artificial intelligence research by presenting statistical language processing from an artificial intelligence point of view in a text for researchers and scientists with a traditional computer science background.
Язык: Рубрика: Технология /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1994Количество страниц: 162Добавлена в каталог: 07.12.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
8 106 111 Accepting states, of Markov processes 32 Acceptors 32 adj 3 Adjective-noun attachment 20 Adjective-noun modification 129 Adv 3 Aligning corpora 148 Ambiguity, in tagging 49 Ambiguous grammars 6 Antonyms 144 artificial intelligence 1 Attachment decisions 119 AutoClass 155 AUX 3 Average mutual information 138 46 Backward probability 58 Backward probability, algorithm for 60 Backward probability, relation to PCFGs 89 Basili, R. 124 Baum — Welch algorithm 60 Bayes’ Law 22 Bigrams 40 Binary Tanimoto measure 142 bits 27 Boggess, L. 50 Bracketed corpora 108—111 117 Bracketing 109 Breadth-first numbering 131 Briscoe, T. 111 Brown Corpus 48 Brown corpus, number of word-types in 120 Brown corpus, size of 36 Brown corpus, tagged version 49 Brown, P. 136 143 148 Buckshot 155 Canadian parliament 148 Carroll, G. 105 Centroid 141 159 CFGs 4 Charniak, E. 51 105 Chart 9 Chart parsing 9—16 20 75 Chart parsing for PCFGs 91 Chart parsing, algorithm 10 19 Chart parsing, most likely parse in 101 Chomsky-normal form 8 Chomsky-normal form for PCFG proofs 89 94 Chomsky-normal form, in grammar induction 108 111 Church, K.W. 50 52 Clustering 135—136 CNF 89 Co-reference 19 Code trees 28 30 Coding theory 27 Cognitive psychology 81 Compositional semantics 17 compress 29 Computational linguistics 1 Conditional entropy 138 145 Conditional probability 22 CONJ 3 Context as direct object 139 Context as next word 136 Context as syntactically related material 142 Context as word window 139 Context in speech recognition 1 Context-free grammars 4—9 Context-free languages 75 Context-free parsers 9 Corpus 24 Cosine, as a distance metric 154 Critical points 104 Critical points in HMM training 65 Critical points in PCFG training 98 Cross entropy 33 Cross entropy as a model evaluator 34—38 Cross entropy of a language 34 Cross validation 36 Cycles in grammars 16 Database classification 1 Dependency grammars 106 117 DeRose, S.J. 50 DET 3 Distance metrics 135 Domains of discourse 125 Dominance 76 E-transitions 43 Edges in chart parsing 92 Edges of a chart 10 Edges of an HMM 43 Edges, adding and removing 12 entropy 27—31 29 Entropy of a language 31 Entropy, conditional 145 Entropy, pet word 30 Ergodic 34 36 Euclidean distance 135 Euclidean distance in sense disambiguation 154 Euclidean distance in word clustering 136 146 features 3 file compression 29 Final state, of a finite automata 32 Finite-state automaton 32 First-order predicate calculus 17 Fisher, D. 127 Forward probability 57 Forward probability, algorithm for 57 Forward probability, relation to PCFGs 89 Forward-backward algorithm 60 Fpunc 3 Francis, S. 36 French translation 148 Gale, W.A. 144 148 gaps 127 Generators 32 Grammar 4 Grammar induction 80 103—116 Greedy algorithm 138 Grefenstette, G. 142 143 144 Hansards 148 Head constituent 84 131 Hidden Markov models 39 41—45 43 53—70 87—88 Hindle, D. 121 124 126 HMMs 39 Initial state, of an HMM 43 Inside probability 89 101 Inside probability, algorithm for 93 Inside-outside algorithm, in grammar induction 104 Jackendoff, R. 8 Jelinek, F. 49 52 Key list 9 Knowledge representation 139 Kucera, H. 36 Language models, using PCFGs 83 130 Language models, using trigrams 39 Lexical items 2 Lexical rules 83 Lexicon 2 Local maxima in grammar induction 104 Local maxima in HMM training 68 Local maxima in PCFG training 98 Logical object 128 Logical subject 128 Long-distance dependencies 8 Machine Translation 148 Markov assumptions 44 Markov assumptions for PCFG language models 131 Markov assumptions for PCFG parses 78 Markov assumptions for tagging 47 Markov chains 32 Markov chains for ttigram models 40 42 Markov chains, order of 40 Markov chains, training for 60 Maximum entropy 159 modal 3 Morphology 2—4 Multiplying out features 8 Mutual information 136 146 157 Mutual information, average 138 N-gram models 39 Negative training examples 80 103 106 NLU 1 Non-terminals as chart entries 9 Non-terminals for PCFGs 75 Non-terminals in 8 Non-terminals in grammar induction 104 Non-terminals of CFGs 5 Non-terminals, multiplying out 8 Non-terminals, unexpandable 20 Noun 3 Noun-noun attachment 20 Noun-noun attachment, mistakes in 113 Noun-noun modification 129 Noun-phrase reference 19 NP 5 Null hypothesis 122 Number feature 3 Oracles 81 Order, of Markov chains 40 Outside probability 101 90 94 Outside probability, algorithm for 96 Overfitting data, of word senses 158 Overfitting parameters 67 Parallel French-English corpora 148 Parse, most probable 79 100 111 Parser, partial 121 Parses, number of possible 16 Part-of-speech tagging 45—51 52 Part-of-speech tagging, performance 51 Partial bracketing 109 Partial parsers 139 142 Parts of speech 3 83 Passive sentences 128 Paths through an HMM 45 52 53—56 PCFG 75 Per-word cross entropy 33 Per-word entropy 30 Pereira, F. 108 139 158 Person feature 3 Plural nouns 2 pos 3 Positive training examples 80 106 Pragmatics 2 Prep 3 Prepositional-phrase attachment 16 19 79 113 119—126 Pro 3 Probabilistic context-free grammars 20 75 75—99 119 Probability of a PCFG parse 76 Probability of a PCFG rule 75 Probability of an HMM transition 44 Probability of HMM output 57 Probability of most likely HMM path 53 Probability theory 21—24 PROP 3 Pseudo-words 39 51 Random variable 21 Reference 19 Regular grammars 87 Regular languages 87 Relative clauses 127 Relative entropy 141 Relative pronouns 127 Relative-clause attachment 126—129 Resnik, P. 156 Restrictive relative clauses 127 Rewrite rules for dependency grammars 106 117 Rewrite rules for PCFGs 75 Rewrite rules in Chomsky-noimal form 8 Rewrite rules of CFGs 5 Riloff, E. 127 Roget classes, as a gold standard 143 Roget’s Thesaurus 143 150 Root forms 2 Rooth, M. 121 124 126 Rule-length restrictions 104 S 5 S-maj 5 Saddle points 65 Schabes, Y. 108 Schuetze, H. 151 158 SEC corpus 113 Selectional restrictions 18 Selectional restrictions, discovery of 155—159 Semantic information, use during parsing 123—134 Semantic tags 124 129 Semantics 2 senses 16 Sentence bracketing 109 Singular nouns 2 Slash categories 9 Smoothing the trigram model 40 51 52 139 Source language, in machine translation 148 Sparse data 40 Sparse data and semantic tags 129 Sparse data for selectional restrictions 156 Sparse data for sense disambiguation 150 Sparse data for tagging 48 Sparse data for trigram models 40 Sparse data in PCFG language models 133 Sparse data in pp attachment 120 121 Speech recognition 1 25 26 30 Start state, of a finite automata 32 Starting symbol, for PCFGs 75 States, of an HMM 43 Statistical models 24—26 Subject-verb agreement 3 8 suffixes 2 Syntactic ambiguity 79 Syntactic disambiguation 119—134 Syntactic parsers 75 Syntactic structure 4 Syntax 2 T-scores 122 122 129 Tags 46 Tanimoto measure 142 Target language, in machine translation 148 Terminal symbols 5 75 Terminal symbols as chart entries 9 Terminal symbols in dependency grammars 106 Time ticks, of an HMM 44 Tishby, N. 139 158 Tokens, word 37 Training HMMs 60—70 73 Training HMMs for trigram smoothing 41 Training HMMs, algorithm for 63 Training PCFGs 96—99 109 Training PCFGs for grammar induction 101 Training sequences for HMMs 66 Training sequences for PCFGs 98 Transitions, of an HMM 43 Trigram models 39 Trigram models of English 39—43 Trigram models of English, cross entropy 139 Trigram models of English, vs PCFGs 83 Types, word 37 Ungrammatical sentences 82 Unigrams 40 Universe of all outcomes 22 UNIX 29
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



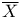 theory
theory