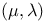Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Bäck T. — Evolutionary Algorithms in Theory and Practice
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Evolutionary Algorithms in Theory and PracticeАвтор: Bäck T. Аннотация: This book presents a unified view of evolutionary algorithms: the exciting new probabilistic search tools inspired by biological models that have immense potential as practical problem-solvers in a wide variety of settings, academic, commercial, and industrial. In this work, the author compares the three most prominent representatives of evolutionary algorithms: genetic algorithms, evolution strategies, and evolutionary programming. The algorithms are presented within a unified framework, thereby clarifying the similarities and differences of these methods. The author also presents new results regarding the role of mutation and selection in genetic algorithms, showing how mutation seems to be much more important for the performance of genetic algorithms than usually assumed. The interaction of selection and mutation, and the impact of the binary code are further topics of interest. Some of the theoretical results are also confirmed by performing an experiment in meta-evolution on a parallel computer. The meta-algorithm used in this experiment combines components from evolution strategies and genetic algorithms to yield a hybrid capable of handling mixed integer optimization problems. As a detailed description of the algorithms, with practical guidelines for usage and implementation, this work will interest a wide range of researchers in computer science and engineering disciplines, as well as graduate students in these fields.
Язык: Рубрика: Биология /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1996Количество страниц: 314Добавлена в каталог: 07.12.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Initialization in Evolutionary Programming 99 Initialization in Genetic Algorithms 120 Interleave-constructor 287 Interphase 17 Intron 15 inversion 21 k-step failure probability 202 223 k-step improvement probability 202 222 k-step improvement probability, counting ones 202 Koch curve 145 Kolmogorov — Smirnov test 151 155 Lamarckism 14 Learning 30 32 Learning by analogy 33 Learning by deduction 33 Learning by induction 33 61 Learning by instruction 33 Learning by observation and discovery 33 Learning from examples 33 Learning, unsupervised 33 Least square estimation 44 Lebesgue measure 47 48 Level set 37 Link 285 Link adapter 286 Link interface 285 Load balancer 287 Local maximum 224 Local minimum 37 39 56 140 Local minimum with respect to 38 Local optimum 143 226 Logarithmic time complexity 229 Lost alleles 114 Machine learning 30—34 Management technique 60 Markov chain 105 104—106 129 200 223 Markov chain, absorbing 200 Markov chain, ergodic 201n Markov chain, homogenous 105 Markov process 105 Master-slave algorithm 238 MCDM see "Multiple criteria decision making" Meiosis 15n 17 Meiosis, metaphase 17 Meiosis, pachytene 17 Meiosis, pachyteous 21 Mendelian laws 16 Merit factor 39 Message passing 285 Messenger ribonucleic acid 13 15n Meta-evolution 233—255 Meta-Evolutionary Algorithm 234 239 287 Metabolism 24 61 Metrics 36 Migration model 236—237 MIMD 238 285 Minimization 35 Minkowski-dimension 147n Mitosis 15n 16 Mixed-integer problem 234 Molecular Darwinism 24 23—29 47 Monotony 129 179 201 Monte — Carlo see "Uniform random search" mRNA see "Messenger ribonucleic acid" Multi-armed bandit 117 131 Multimodality 37 79 118 137 142 143 154 229 Multiple criteria decision making 35 Mutagene 20 Mutation 8 18—24 34 51 57 59 61 63 65 71 84 117 124 129 131 150 168 176 180 195 242 Mutation ellipsoid 69 70 Mutation in Evolution Strategy 71—73 Mutation in Evolutionary Programming 93—93 95 Mutation in Genetic Algorithms 113 197—197 232 Mutation of base pairs 19 197 Mutation of chromosomes 20 Mutation of genes 19 20 Mutation of genomes 20 197 Mutation, correlated 69 Mutation, generative 20 Mutation, hybrid 254 Mutation, large 20 Mutation, lethal 80 Mutation, macro- 197 Mutation, multiple 58 Mutation, normally distributed 67 Mutation, probability 19 113 198 224 233 235 240 242—255 Mutation, probability, length-independent 209 Mutation, probability, optimal 206 228 232 252 Mutation, progressive 21 Mutation, small 20 Mutation, somatic 20 Mutator-gene 131 Nabla-operator 44n NDTM see "Turing machine" Neighborhood 38 224 Neodarwinism 8 15 Network-server 286 Nonlinear parameter estimation 61 Norm 36 Normal distribution, logarithmic 72 Normal distribution, n-dimensional 69 70 NP 55—56 NP-completeness 43 55 61 Nucleotide base 11 131 133 Object variable 68 109 117 279 284 Objective function 35 167 Objective function, separable 230 Offline-performance 235 283 Offspring 74 75 118 Offspring, optimal number of 90 Oncogene 20 One Max 201 see Online-performance 235 283 Ontogenesis 16 OpenWindows 277 Optimal allocation of trials 126 Optimization 35 108 Order statistics 88 210 228 Orthogonal transformation 71 P 53—56 Parallel constructor 287 Parallelism, asynchronous 285 Parallelism, coarse-grained 237 Parallelism, fine-grained 237 Parameter optimization 108 114 199 229 Parameterization problem 233 Pareto-set 35 Payoff, average 127 Payoff, observed 127 Perceptron 31 Permutation 41 43 173 Phenotype 8 12 14 34 96 133 164 197 Phylogeny 16 198 pipe 286 Pipe-constructor 286 Plateau 140 Pleiotropy 12 95 96 Polygeny 12 96 Polynomial transformation 55 Polyploidy 23 Population 63 66 74 107 118 121 127 141 150 Population sequence 64 Population size 66 122 149 198 233 235 240 Population size, optimal 233 Primary structure 12 Principle of minimal alphabets 128 Progress, average 153 Progress, measure 151 Promoter 13 Protein 133 Protein biosynthesis 12 Pseudo boolean objective function 109 128 Pseudo boolean objective function, multimodal 224 229 Pseudo boolean objective function, unimodal 208 224 227 Pseudoboolean optimization problem 39 39 55 56 199 Punctuated equilibria 197n Purine base 11 Pyrimidine base 11 Quality factor 24 Quasi-species 26 26—29 Random walk 78 94 170 180 182n Rate equation 24 27 Reachability 129 130 201 READ 286 287 Read-write head 52 Recessivity 17 35 Recombinants 17 Recombination 34 63 125 129 131 150 177 185 Recombination in Evolution Strategy 73—77 Recombination in Evolutionary Programming 95—96 Recombination in Genetic Algorithms 114—117 Recombination of strategy parameters 75 Recombination, discrete 74 76 241 242 252 Recombination, generalized 76 Recombination, intermediate 74 76 242 Recombination, intermediate, generalized 74 Recombination, number of possible results 76—77 Recombination, panmictic 74 76 Recurrence relation 177 Repair-enzyme 131 Replication 12 Replicator 287 Replicon 15 Representation, internal 30 Representation, subsymbolic 31 Representation, symbolic 30 Reproductive plan 107 Ribosome 13 14 RNA 14 RNA-polymerase 13 Robustness 137 Rosenbrock's function 138 Rotation angle 68 70—72 279 284 Rotation matrix 70 Rote learning 32 Roulette wheel 118 RP 56 Saddle-crossing 98 Sample mean 220 Sample size 151 153 Sampling error 118 Samuel's checkers player 31n Scalability 138 Scaling 93 111—113 118 122 167 169 195 Scaling factor 103 Scaling window 113 123 150 192 235 Scaling, exponential 111 192 Scaling, linear dynamic 111 150 169 192—193 Scaling, linear static 111 Scaling, logarithmic 111 192 Scaling, sigma truncation 112 Schema 124 133 Schema theorem 126 169 192 Schema, defining length 124 128 Schema, instance 124 Schema, order 124 Schema, survival probability 124 Schemata number of 128 Scoring polynomial 31n Scripton 15 Search, heuristic 33 Secondary structure 12 Segment switch rate 116 Selection 34 51 63 64 68 112 157 163—195 Selection in Evolution Strategy 78—80 Selection in Evolutionary Programming 96—99 Selection in Genetic Algorithms 117—120 Selection, 78 98 174—179 182 Selection, 91 98 Selection, 185 Selection, 78 79 150 174—179 182 194 240 Selection, (1+1) 67 Selection, (15,100) 150 Selection, based on preservation 181 Selection, Boltzmann tournament 195n 280 Selection, control parameter 195 Selection, criterion 26 Selection, directed 164 Selection, disruptive 164 Selection, dynamic 181 Selection, elitist 129 133 157 182 200 202 232 241 247 Selection, experiments 184 193 Selection, exponential ranking 172 Selection, extinctive 131 181 183 249 Selection, extinctive, left 182 Selection, extinctive, right 182 Selection, hard 165 Selection, linear ranking 169—172 174 176 181 185 194 240 241 selection, natural 8 163—164 Selection, operator 63 Selection, preservative 133 183 Selection, probabilistic 96 Selection, probability 117 165—183 selection, proportional 117 122 128 150 167—169 181 185 188 192 194 240 244 250 Selection, pure 182 Selection, soft 98 165 Selection, stabilizing 164 Selection, static 181 Selection, taxonomy 180—183 Selection, tournament 172—174 176 181 185 194 240 241 247 252 Selective pressure 165—195 243—255 Selective pressure, control of 179 Selective value 25 Self-adaptation 68 73 75 79 92 94 116 131 139 150 217 229 241 254 Self-affinity 147 Self-organization 25 34 Self-reproduction 24 27 61 Self-similarity 144 Sequence prediction 61 Shared memory 285n Shekel's foxholes 138 Shifting balance theory 11 SIMD 238 Simulated annealing 195n Skew-symmetry 40 Software, system architecture 277 Speciation 197 Speedup 216 219 228 sphere model 85 102 103 138 139 147 185 230 Sphere model with noise 157 Spinning wheel 118 splicing 15n SPREAD 120 Stability 158 Stagnation 200 205 Stagnation probability 202 223 Standard code 110 113 221—232 Standard deviation 68 71 72 84 86 93 150 242 279 284 Start distribution 105 Start-state 52 State transition 53 Step function 139—142 188 Stirling numbers 76 Stochastic process 104 Stochastic process with discrete time 105 Stochastic Universal Sampling 120 Strategy parameter 68 69 73 241 254 Structure evolution 234 Subordinate-constructor 286 Subpopulation 107
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте