|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Knuth D.E. Ч The art of computer programming (vol. 1 Fundаmental algorithms) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Christian IX, King of Denmark 310 311 562
Christie Mallowan, Agatha Mary Clarissa (Miller) xvii
Chu Shih-Chieh (= Zh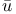 Sh Sh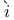 ji ji H H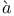 nq nq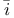 ng, Zh ng, Zh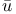 S S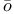 ngt ngt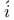 ng) 53 59 70 ng) 53 59 70
Chung, Fan Rong King 514
Chung, Kai Lai 105
Circle of buffers 218Ч227 231
Circuit, Eulerian, in a directed graph 374Ч376 379Ч380 584
Circuit, Hamiltonian, in a directed graph 374 379
Circular definition 263 308; circular
Circular linking 273Ч280 302 355 411 459
Circular store 240
Circulating shift 135
Citrus 457
Cl, The comparison indicator of MIX 126 134 142 211 213 228
Clark, Douglas Wells 604
Clavius, Christopher 159
Clock, for real time 228
Clock, simulated 283 288
Clock, solitaire game 377Ч378
Closed subroutine see Subroutine
CMatb, Concrete Mathematics, a book by R. L. Graham, D. E. Knuth, and O. Patashnik 11
CMP1 (compare rI1) 134 210 211
CMPA (compare rA) 134 210 211
CMPX (compare rX) 134 210 211
COBOL, УCommon Business Ч Oriented Language 424Ч43 457 458
Codes for difficulty of exercises xvii
Coefficient extraction 92
Cofactor of element in square matrix, Determinant of the matrix obtained by replacing this element by unity and replacing all other elements in the same row or column by zero 37 381
Coffman, Edward Grady, Jr 450 451
Cohen, Jacques 421 461 614
coin tossing 101Ч102
Coin tossing, tail of distribution 106
Collins, George Edwin 461
Combinations of  objects taken objects taken 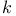 at a time 52Ч53 69 at a time 52Ч53 69
Combinations of  objects taken objects taken 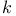 at a time, with repetitions permitted 73 95 386 388 at a time, with repetitions permitted 73 95 386 388
Combinations of  objects taken objects taken 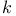 at a time, with restricted repetitions 95 at a time, with restricted repetitions 95
Combinatorial matrix 37Ч38 589
Combinatorial number system 73 560
Comfort, Webb 461
COMIT 461
Comments 2Ч3
Comments, in assembly language 145 149
Commutative law 165
Compacting memory 423 439 449 455
Comparability 270
Comparison indicator of MIX 126 134 211 213 228
Comparison operators of MIX 134 210Ч211
Compiler, algorithms especially for use in 360 424Ч434 556
Complete 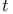 -ary tree 401Ч402 -ary tree 401Ч402
Complete binary tree 401 405 563
Complex conjugate 21
Complex number 21
Compound interest 23Ч24
Compression of messages 407
Computational error 24Ч26
Computational method 5 7Ч8
CON (constant) 149Ч150 155
Concatenation of strings 274
Concave function 406
Conditional expression 460 624
Congruence 40Ч42
Connected directed graph 363
Connected directed graph, strongly 372 377
Connected graph 363
Conservative law 170; see KirchhoffТs law
Constants in assembly language 149Ч150 155
Construction of trees 340Ч341 343 428Ч429
Contents 127 235Ч236
Context-free grammar 539
Continuants 600Ч601
Continued fractions 498
Continuous simulation 282 298
Convergence, absolute 29
Convergence, An infinite sequence (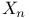 ) converges if it approaches a limit as ) converges if it approaches a limit as  approaches infinity, an infinite sum or product is said to УconvergeФ or to УexistФ if it has a value according to the conventions of mathematical calculus see Eq. 1.2.3Ч(3) approaches infinity, an infinite sum or product is said to УconvergeФ or to УexistФ if it has a value according to the conventions of mathematical calculus see Eq. 1.2.3Ч(3)
Convergence, of power series 87 396
Conversion operations of MIX 138
Convolution of probability distributions, The distribution obtained by adding two independent variables 103
Conway, Melvin Edward 19 80 151 273 408 600
Copy a data structure, binary tree 329 330 333 347
Copy a data structure, linear list 279
Copy a data structure, List 423
Copy a data structure, two-dimensional linked list 306
Copying and compacting 421
Corless, Robert Malcolm 395
coroutines 193Ч200 222Ч223 283Ч296 320
Coroutines, history 229
Coroutines, linkage 194 200 223 291
Correspondence between binary trees and forests 334Ч335 346
Cousins 317
Coxeter, Harold Scott Macdonald 80 162 407 408
Crelle, August Leopold 58 632
Critical path time 217
Crossword puzzle 163
Crowe, Donald Warren 601
Cumulants of a probability distribution 103Ч106
Cycle, detection of 271
Cycle, fundamental 366Ч370 377
Cycle, in directed graph 363
Cycle, in graph 363
Cycle, in permutation 164Ч167 176Ч178 182Ч184
Cycle, in random permutation 179Ч184
Cycle, notation for permutations 164 167 172Ч175 182
Cycle, oriented, in directed graph 372
Cycle, singleton, in permutation 164 171 180Ч181
Dahl, Ole Ч Johan 230 461 462
Dahm, David Michael 433 434
Data (originally the plural of УdatumФ, but now used collectively as singular or plural, like УinformationФ), Representation in a precise, formalized language of some facts or concepts, often numeric or alphabetic values, to facilitate manipulation by a computational method 215
Data structure, A table of data including structural relationships 232Ч465
Data structure, linear list structures 238Ч298
Data structure, List structures 408Ч423
Data structure, multilinked structures 424Ч434
Data structure, orthogonal lists 298Ч307 424Ч434
Data structure, tree structures 308Ч408
Data, packed 128 158
Daughter, in a tree structure 311
David, Florence Nightingale 66
Davies, David Julian Meredith 445
Davis, Philip Jacob 50
Dawson, Reed 584
de Bruijn, Nicolaas Govert 121 122 375 379 380 478 504 543 565
De Moivre, Abraham 74 83 87 106 182 536
de Morgan, Augustus 17
deallocation see Liberation
Debugging, Detecting and removing bugs (errors) 192Ч193 201 257 297 413 556
DEC1 (decrease rI1) 134 210
DECA (decrease rA) 134 210
Decimal number system 21 619
DECX (decrease rX) 134 210
Defined symbol, an assembly language 153
Definition, circular see Circular definition
Degree, of node in tree 308 317 377
Degree, of vertex in directed graph 372
Deletion of a node, from available space list see Reservation
Deletion of a node, from deque 251 297
Deletion of a node, from doubly linked list 281 290Ч291 297
Deletion of a node, from doubly linked ring structure 358
Deletion of a node, from linear list 239
Deletion of a node, from linked list 236 255 276 305
Deletion of a node, from queue 242 244Ч245 254 261 265 273Ч274
Deletion of a node, from stack 241 242 244Ч245 247 254 259 269 273Ч274 278 458
Deletion of a node, from tree 358
Deletion of a node, from two-dimensional list 305
Demuth, Howard B. 120
Depth-first search 578 581
Deque, deletion from 251 297
Deque, Double-ended queue 239Ч243 269
Deque, input-restricted 239 243 416
Deque, insertion into 251 297
Deque, linked allocation 280 297
Deque, output-restricted 239 243 269 274
| Deque, sequential allocation 251
Derangements 180 183
Derivative 90 338
Dershowitz, Nachum 518 588
Descendant, in a tree structure 311
Determinant of a square matrix 37Ч39 81 378Ч379 382
Deuel, Phillip DeVere, Jr 556
Deutsch, Laurence Peter 418 421 422
Dewar, Robert Berriedale Keith 614
Dewey notation for trees 313 317 382Ч383 460
Dewey, Melvil, notation for binary trees (due to Galton) 317 331 346 405
Diaconis, Persi Warren 491
Diagonals of polygons 408
Diagrams of structural information 234 279
Diagrams of structural information, before-and-after 260Ч261 278 281 571
Diagrams of structural information, binary trees 312 318 563
Diagrams of structural information, List structures 315Ч317 408Ч409
Diagrams of structural information, tree structures 309Ч315 337 346 349 460
Dickman, Karl Daniel 525
Dickson, Leonard Eugene 81
Dictionaries of English 1Ч2 215Ч216
Differences of polynomials 64
Differentiation 90 338Ч347 459
Differentiation, chain rule for 52
Digamma function 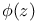 44 75 493 44 75 493
Digraph 372; see Directed graph
Dijkstra, Edsger Wijbe 17 230 231 240 459 462 545 580 605
Directed graphs 372 374 422
Directed graphs, as flow charts 364Ч365 377
Directed graphs, balanced 374 375
Directed graphs, connected 363
Directed graphs, regular 379
Directed graphs, strongly connected 372 377
Discrete system simulation 203 282 298
Discrete system simulation, synchronous 282 298
Disk files 136Ч137 435 463
Disk input, buffered 228
disposal see Garbage collection Liberation
Dissection of a polygon 408
Distributed-fit method of storage allocation 450Ч451 456
Distribution, binomial 101 102
Distribution, negative binomial 107
Distribution, normal 104Ч106 122
Distribution, Poisson 106 502 524
Distribution, tails of 104 106 107
Distribution, uniform 102 253 446
Distributive law 28 37 42 598
DIV (divide) 131Ч133 139 208
Divergent series 28 75
Division converted to multiplication 516Ч518
Dixon, Alfred Cardew 490
Dixon, Robert Dan 509
DLINK, Link downward 409 411
Doran, Robert William 229
Double generating function, A generating function of two variables 94 396 405 537Ч539
Double order for traversing trees 332 333 564
Doubly linked lists 280Ч281 288Ч291 298 357 411 441 443 452 459
Doubly linked lists, compared to singly linked 281 298
Dougall, John 490
Doyle, Arthur Conan 465
Drum memory 136Ч137 457
Dull, Brutus Cyclops 111
Dummy variable 27
Dunlap, James Robert 457
Dutka, Jacques 50 65
Dvoretzky, Aryeh 593
Dwyer, Barry 567
Dynamic storage allocation 246Ч254 256Ч259 413Ч414 435-456
Dynamic storage allocation, history 457Ч458 461Ч462
Dynamic storage allocation, running time estimates 449
Dynastic order 336; see Preorder
DYSEAC computer 231
dТImperio, Mary E. 462
Earley, Jackson Clark 462
Easter Date 159 160
Edelman, Paul Henry 598
Edge in graph 363
Edwards, Daniel James 423
Effective algorithm 6 8 9
Egorychev, Georgii Petrovich 499
Eisele, Peter 480
Eisenstein, Ferdinand Gotthold Max 479
Elementary symmetric functions 38 94 497
Elevator (lift) system 282Ч298
Embedding of partial order into linear order 262; see Topological sorting
Embedding of tree in another tree 348 386
Emulation 202
END 151 156 296
End of file 216 227
Endorder see Postorder
Engles, Robert William 462
English letter frequencies 159
ENN1 (enter negative into rI1) 133 210
ENNA (enter negative into rA) 133 210
ENNX (enter negative into rX) 133 210
ENT1 (enter into rI1) 133 210
ENTA (enter into rA) 133 210
Entity 233; see Node
Entrances to subroutines 186Ч191
Entrances to subroutines, multiple 189
ENTX (enter into rX) 133 210
Enumeration of subtrees 378 379
Enumeration of tree structures 386Ч399
Enumeration, history 406Ч407
Epictetus of Hierapolis 1
EQU (equivalent to) 146 149 155
Equivalence algorithm 360Ч361 578 581
Equivalence classes 354
Equivalence declarations 360
Equivalence relations 353Ч355 487
Equivalent algorithms 467
Equivalent binary trees 328Ч329
Equivalent forests 346
Equivalent Lists 423
Equivalent of a MIXAL symbol 156
Equivalent trees 346
Erase a data structure, linear list 273 274 279
Erase a data structure, List 413Ч414
Erase a data structure, right-threaded binary tree 333
Erd lyi, Arthur 399 lyi, Arthur 399
Erdwinn, Joel Dyne 229
Errors, avoiding 260Ч261 556
Errors, computational 305
Errors, detection of 192Ч193 201 257 297 413
Etherington, Ivor Malcolm Haddon 399
Ettingshausen, Andreas von 54
Etymology 1Ч2
Euclid 2 5
Euclid algorithm for gcd 2Ч9 80
Euclid algorithm for gcd, extended 13Ч14 42
Euclidean domains 468
Euler constant  75 114 619Ч620 75 114 619Ч620
Euler summation formula 111Ч116 120 123
Euler theorem 42
Euler, Leonhard 49 50 52 57 75 76 87 111 374 407 472 496 536 600
Eulerian circuit in directed graph 374Ч376 379 584
Eulerian circuit in directed graph, enumeration of 380
Eulerian numbers, second-order 506
Eulertotient function 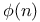 42 184 42 184
Evaluation of powers 509
Evaluation of tree functions 351 361
Evans, Arthur, Jr 202
Exchange operation (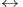 ) 3 182 274 ) 3 182 274
Exclusive OR 442 455 553
Execution time for MIX instructions 138 141
Execution time, methods for studying 96 170Ч172
Exercises, notes on xvЧxvii 284
Exits from subroutines 186Ч191
Expected value of a random variable, from a generating function 100Ч103
Expected value of a random variable, The average or УmeanФ value 98 103
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 Sh
Sh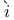 ji
ji H
H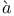 nq
nq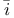 ng, Zh
ng, Zh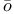 ngt
ngt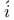 ng)
ng)  objects taken
objects taken 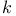 at a time
at a time 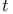 -ary tree
-ary tree 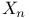 ) converges if it approaches a limit as
) converges if it approaches a limit as 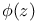

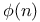
 )
)