|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Knuth D.E. Ч The art of computer programming (Vol. 1. Fundamental algorithms) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
DECX (decrease X) 129 206
Definition, circular see УCircular definitionФ
Degree, of node in tree 305 314 345 350Ч351 376
Degree, of vertsx in directed graph 371
Deletion of node, from available space list see УReservationФ
Deletion of node, from deque 248 266 271 294
Deletion of node, from doubly linked list 278Ч279 288 294 444Ч445
Deletion of node, from linear list 235
Deletion of node, from linked list 232 252 274 278Ч279 288 294 301Ч302 357Ч358 440 442 444Ч445
Deletion of node, from queue 237Ч238 240Ч241 257Ч258 262 271
Deletion of node, from stack 237Ч238 240Ч241 243 255Ч256 265Ч266 271 276 278Ч279 323 415Ч416
Deletion of node, from tree 357Ч358
Deletion of node, from two-dimensional list 301Ч302
Denned symbol, in assembly language 149
Deque 235Ч239 458
Deque, deletion from 248 266 271 294
Deque, input-restricted 235Ч239 415
Deque, insertion into 248 266 271 294
Deque, linked allocation 251 270 278
Deque, output-restricted 235Ч239 271
Deque, sequential allocation 240
Derivative of a formula 89 337
Descendant, in a tree structure 309
Determinant of a square matrix 35Ч37 377Ч378 474
Deuel, Phillip D. 552
Deutsch, L. Peter 417 421
Dewey, Melvil, notation for binary trees (due to Gallon) 315 329 345 405
Dewey, Melvil, notation for trees 310Ч311 314Ч315 345 381Ч382 459
Diagrams of structural information 230Ч231
Diagrams of structural information, before-and-after 256Ч257
Diagrams of structural information, List structures 312Ч313 407
Diagrams of structural information, tree structures 306Ч307 309
Dickson, Leonard Eugene 80
Difference of function 64
Difference of function, divided 472
Differentiation, algebraic 89 337Ч346 359 458
Differentiation, algebraic, chain rule for 50 see
Digamma function 94 490 616
Digraph 371 see
Dijkstra, Edsger Wybe 227 236 458
Dilworth, Robert Palmer xii
Directed graph 371Ч381 420
Directed graph, as flow chart 365 380Ч381
Directed graph, balanced 374 377
Directed graph, connected 372 376 377
Directed graph, regular 378
Directed graph, representation of 380
Directed graph, rooted 372
Directed graph, strongly connected 372 377
Discrete system simulation 199 279Ч295
Discrete system simulation, synchronous 289 295
Disk files 132Ч133 436 461Ч462
Distribution, binomial 100 103
Distribution, normal 102Ч103
Distribution, Poiason 103 519
Distribution, uniform 100Ч101
Distributive law 27 35 40
DIV (divide) 127Ч128 135 204
Divided differences 472
Division converted to multiplication 513
Dixon, Alfred Cardew 489
Dixon, Robert Dan 504
DLINK: Link downward 408 410
Doig, Alison 406
Domino problem 382Ч385
doubly linked list 278Ч279 285Ч288 294Ч295 409Ч411 441Ч442 443Ч445 453 458
Dougall, John 489
Drum 132Ч133 456 461Ч462
Dual order for traversing tree 330 331
Dull, Brutus Cyclops 107
Dummy variable 27
Dunham, Bradford 346
Dunlap, James Robert xii 456
Dvoretnky, Aryah 531
Dynamic storage allocation 242Ч251 253Ч254 411Ч413 419Ч420 435Ч455
Dynamic storage allocation, history 456Ч457 460Ч461
Dynamic storage allocation, running time estimates 419Ч420 445Ч450
Dynastic order 335 see
Easter Date 155Ч156
Edge in a graph 362
Edwards, Daniel James 421
EDX (load X) 125 135 204Ч205
Effective algorithm 6 8 9
Eisenstein, Ferdinand Gotthold 479
Elementary symmetric functions 93 94 494
Elevator system 280Ч295
Embedding of partial order into linear order 259 see
Embedding of tree in another tree 347 385
END 148 151
End of file 212Ч213 S24
Endorder for binary tree 316Ч317 310 324 328Ч330
Endorder for tree 334Ч335 345 349
English letter frequencies 155
ENN1 (enfer negative 1) 129 200
ENNA (enter negative A) 29 206
ENNX (enter negative X) 129 206
ENT1 (enter 1) 129 206
ENTA (enter A) 129 206
Entity 229 see
Entrances to subroutines 183Ч187
ENTX (enter X) 129 206
Enumeration of free structures 377Ч378 385Ч399 404
Enumeration of free structures, history 405Ч406
EQU (equivalent to) 142 145Ч146 151 152
Equivalence algorithm (Algorithm 233E) 354Ч355 360Ч361 376 572 575
Equivalence between two algorithms 466
Equivalence classes 353
Equivalence declaration 355 360Ч361
Equivalence problem 353 360Ч361
Equivalence relation 353
Equivalent of a MIXAL symbol 152
Equivalent trece 326 331 345
Erase a data structure, binary tree 331
Erase a data structure, linear hat 270 271 277
Erase a data structure, List 412Ч413
Erd&yi, Arthur 398 531
Erdwinn, Joel Dyne 226
Errors, avoiding 256Ч257
Errors, computational 24 26 302
Errors, detection of 189 197 294
Ethermgton, Ivor Malcolm Haddon 398 531
Ettingahausen, Andreas von 52
Euclides (Ч Euclid) 2 4 5
Euler, constant 74 110
Euler, Leonhard 48 51 56 86 108 110 373 405 494 531
Euler, summation formula 108Ч112 116 119
Euler, theorem of 41
Euler, totient function 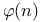 41 181 41 181
Eulerian circuit 373Ч375 377Ч379
Evaluate tree function 351 362
Evans, Arthur, Jr 198
Exchange operation 3 179
Exclusive OR 443 454 550
Execution time, methods for determining 95Ч104 166Ч169
Execution time, methods for MIX instructions 134Ч137
Exercises, notes on xviiЧxix
Exits from subroutines, multiple 186 266
Expected value of a probability distribution 98
Exponents, laws of 21Ч22 25
Expressions, arithmetic see УAlgebraic formulesФ
Extended binary tree 399Ч405
External path length 399Ч405
Faa di Bruno, Francesco, formula of 50 92 103
Factorial 45Ч51 53 111
Factorial powers 70 609
Factorization into primes 18 41 46 49 68
FADD (floating add) 127 304
Fail-safe program 267Ч268
Family tree 307Ч309 314
Family-order sequential representation of trees 349Ч350 359
| Farber, David Jack 460
Farey, John, series 157
FATHER link in tree 352Ч355 359Ч360 426Ч432
Father, in a tree structure 307 314 333Ч334
FCMP (floating compare) 127 502 556
FDIV (floating divide) 127 304
Ferguson, David Elton xii 227 332
Fermat, Pierre de 17
Fermat, theorem 39
Feynman, Richard Phillips 26
Fibonacci, Leonardo 78Ч79
Fibonacci, number system 85
Fibonacci, numbers 13 18 78Ч85 454
Fibonacci, numbers, generating function 81Ч82
Fibonacci, numbers, table of 615
Fibonacci, Quarterly 80
Fibonacci, sequence 13 18 78Ч85 454
Fibonacci, string sequence 85
Field, partial, of MIX word 122Ч127 135 130 203 232Ч233
Field, within a node 229
Field, within a node, notations for 231Ч233 457Ч458
FIFO 236 458 see
Fifty percent rule 445^46
Final vertex of arc 371
Fine, Nathan Jacob 483
First-fit method of storage allocation 436Ч438 447Ч450 452Ч453 605
First-in-first-out 236 sec
Fischer, Michael John 353
Fixed element of permutation 177Ч179
Fixed-point arithmetic 154Ч157
Flag see УSentinelФ
Floating-point arithmetic 127 304
Floating-point operators of MIX 127 554Ч556
Floor function 37Ч38 40Ч4Ч1
Flow chart 2 18 364Ч3H5
Floyd, Robert W. xii 17 10 20 420 473 504 552
FLPL 459Ч460
FMUL (floating multiply) 127 304
Ford, Donald Floyd 511
Foreeasting 221
Forest 306 407 see
Formulae, algebraic see УAlgebraic formulasФ
Formulae, algebraic, logical 346
Forstemann, Wilhelin 488
FORTRAN 355 459
Fractional pari 38
Fragmentation problem 438Ч440 450
Franklin, Joel N. xii
Free lattice 346Ч347
Free storage see УAvailable spateФ
Free trees 362Ч371 373 377Ч378 386Ч388 396 397
Free trees, enumeration 377Ч378 388 306 397
Free trees, minimum cost 370
Fridshal, R. 346
Front of queue 237
FSUB (floating subtract) 127 304
Fundamental cycles in graph 366Ч368 376
Furch, Robert 117
Future reference (in MIXAL) 149 151
Future reference (in MIXAL), restrictions on 152
Galler, Bernard Aaron 353
Gallon, Francis 558
Games, solution of 85 270
Gamma function 48Ч51 71 78 112 115Ч116
Gamma function, incomplete 113Ч119
Garbage collection 254 412Ч422 438Ч410 450 454Ч455 460 541
Gardner, Martin 79
Garwick, Jan Vaumund 244 456
Gaskell, Robert Eugene 85
Gauss, Karl Friedrieh 48 56 94
Gauss, reduction algorithm for matrix inversion 304
Gelernter, Herbert Leo 460
General Electric Corporation 456
Generating functions 81Ч83 86Ч93 97Ч104 178 239 386 388Ч389 391Ч399 404 532Ч533
Generating functions, asymptotic values from 230 395Ч396
Generating functions, for a discrete probability distribution 97Ч104 178
Geometric progression, sum of 31 87
Gerberich, Carl Luther 459
Gill, Stanley 226 456
Glaisher, James Whit bread Lee, constant 499
Gnedenko, Boris Vladiinirovich 103
GO-button of MIX 140 208
Goldbach, Christian 48
Goldberg, Joel 522
Golden ratio 13 18 21 79 81Ч85 613 614
Goldstine, Herman Heine 18 225
Golomb, Solomon Wolf 181
Goneharov, Vasilii Leonidovich 103
Good, Irving John 374 395 482
Gora, Saul 459
Gould, Henry Wadsworth xii 62 117 484 490
Gower, John Clifford 458
Graham, Ronald Lewis 605
Graph 362Ч372 377Ч378 406
Graph, connected 362
Graph, directed see УDirected graphФ
Graphical display 159Ч160
Greatest common divisor 2 4Ч6 9 14Ч15 38Ч39 42 80Ч81
Greatest integer function see УFloor functionФ
grid 228 371
Griswold, Ralph Edward 460
Haddon, Bruce Kenneth 603
Halayudha 52
Hamilton, Dennis Eugene xii
Hamilton, Sir WiUiam Rowan, circuit 374 378
Hamlet, Prince of Denmark 228
Hansen, James Rone 459
Harary, Frank 406
Hardware-oriented algorithms 26 249 600
Hardy, Godfrey Harold 12 490 515
Harmonic numbers 73Ч78 89 110Ч111 156
Harmonic numbers, generating function 89
Harmonic numbers, table 615Ч616
Harmonic series 74
Harrison, Michael Alexander iv
Hart man is, Juris 462
Heap sort 552
Heed of list 272 278 286Ч287 299Ч300 322 332 336 408Ч110 443
Height of vertex in free tree 387
Hellerman, Herbert 458
Henkin, Leon Albert 17
Herrnite, Charles 48
Heyting, Arend 405
Hifbert, David, matrix 37
HLT (halt) 132 139
Hoare, Charles Antony Richard 457
Holmes, Thomas Sherlock Scott 463
Holt Hopfenberg, Anatol Wolf 459
Honeywell H800 120
Hopper, Grace Murray 458
Huffman, David Albert 402Ч405
Hurwitz, Adolf 42
Hurwitz, generalized binomial formula 398 488
I/O: Input or output 211
IBM 050 i 120 226 456 523
IBM 701 226
IBM 705 227
IBM 7070 120
IBM 709 120 523
Identitv permutation 101 172
II-regiater of MIX 122 138
Iliffe, John Kenneth 460
Illiac I 226
IN (input) 132Ч133 211Ч212
In-degree of vertex 371
INC1 (increase 1) 12a
INCA (increase A) 129 206
Incidence matrix 267
Inclusion and exclusion principle 178Ч179 181
Incomplete gamma function 113Ч119
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте