Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Weinberg S. — Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of RelativityАвтор: Weinberg S. Аннотация: Now that this book is done I can look back, and identify two purposes which led me to begin writing, and which have guided the work to completion.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1972Количество страниц: 685Добавлена в каталог: 08.04.2011Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Hoyle, F. 2 35 353 354 461 468 487 488 526 545 553 554 555 561 601 603 604 605 617 619 632 Huang, K. 295 608 Hubble, E. 417 424 435 438 440 445—446 466 467 Hubble’s constant 441—451 459 477 495 501 616 Huchra, J. 606 Hughes, V.W. 87 90 604 Hughston, L. P. 609 Humason, M. L 445—446 448 467 Hundhausen, A. J. 606 Huygens, C. 11 67 Hyades 431 433 440 Hydrodynamics (see Energy-momentum tensor Imperfect Perfect Hydrogen (see H Intergalactic Lyman Nucleo Protons Recombination and Hydrogen, decay 543—544 Hydrostatic equilibrium 128 129 300 Hyperfine precession 237 Iben, I. 488 557 601 605 606 ICARUS 199 637 Ideal gases 44 126 224 263 324 361 Impact parameter 188—190 Imperfect fluids 53—57 568—570 579 Incompressible stars 310 330 335 Induced emission of electromagnetic radiation 491—492 Induced emission of gravitational radiation 287 288 Inertial frames 15—19 86—88 239—241 474 Inf eld, L. 248 249 Infinitesimal Lorentz transformations 58 59 Infrared background (see Microwave radiation background) Infrared divergences 286 287 Ingalls, R. P. 210 633 Instabilities (see Stability and instability) Interferometry (in radio astronomy) 193 194 429 450 Intergalactic matter 478—481 491 497—506 518 Interstellar matter 436 437 443 444 446 492 559 Inverse metric tensor 75 95 98 177 Inverse square law 13—14 Ipser, J. R. 353 Irvine, W. M. 607 Isometries 375 404 409 615 Isophotal angular diameters 424 425 Isotropic form of a static isotropic metric 177 181 183 Isotropic spaces 176 378—381 388 395 403 407—411 Isotropy of inertia 86 88 Isotropy of microwave radiation background 518 526 570 576 594 Isotropy of universe 407 Israel, W 64 354 Iwana, Y. 193 Jacobian determinant 98 118 Jacobs, K. C. 609 Jammer, M. 20 Jaseja, T. S. 22 Javan, A. 22 Jeans mass and wave-number 563 570 573 577—578 Jeans, J. 562 607 Jelley, J. V. 604 Jenkins, F. A. 602 Jennison, R. C. 601 Jones, B. W. 513 603 Jordan, P. 622 632 Jupiter, deflection of light 190 Jupiter, elements of orbit 637 Jupiter, gravitational radiation 272—273 Jurgens, R. F. 210 K-term 443 446 Kant, I. 16 435 Karachentsev, J. D. 600 Kardashev, N. S. 632 Karzas, W. J. 602 Kasper, J. F. 249 Kawabata, K. 602 Keachie, S. 513 Kelleher, D. E. 89 Kellerman, K. I. 468 602 Kellogg, E. 600 Kepler, J. 14 Kepler’s laws 13—14 Kerr metric 240 349 Kerr, R. 249 Kiang, T. 599 Kibble, T. W. B. 373 Killing vectors 375—404 411 Killing, W. 404 Kislyakov, A. G. 513 603 Klein, F 6 21 391 Klein, O. 353 594 595 608 Kleppner, D. 89 Kobetich, E. J. 501 602 Kocharov, G. E. 544 605 Koehler, J. A. 601 Komar, A. 293 Konstantinov, B. P. 545 605 Koyre, A. 21 22 606 Kraft, R. P. 437 467 Kramers, H. A. 294 Kretschmann, E. 119 Kristian, J. 467 Kronecker tensor 95 97 Krotkov, R. 21 89 209 Kruskal, M. D. 210 Kundt, W. 293 Kurt, V. G. 603 Kuz’man, V. A. 604 Lagrangian (for freely falling particle) 221 Lambert, D. L. 605 Lambert, J. H. 4—5 Landau, L. D. 53 63 64 249 293 351 352 604 Lane — Emden equation 309—310 Langer, L. M. 604 Laplacian 109 Larger Magellenic cloud (see Magellenic clouds) Larson, J. V. 294 Latter, R. 602 Layzer, D. 599 603 607 Le Verrier, U. J. J. 14 Leavitt, H. S. 433 466 Lebskii, Yu. V. 513 603 Lederman, L. 64 Ledoux, P. 352 Lee, B. W. 609 Lee, H. 352 Lee, T.D. 27 64 Legendre expansion of plane waves 274 Legendre, A. M. 4—5 Leibniz, G. W. V. 16 22 Leibovitz, C. 354 Lemaitre cosmology 615—616 Lemaitre, G. 615 632 Lense — Thirring effect 239 240 Lense, J. 249 Leong, C. 600 Leung, Y. C. 352 Liabsorption experiment 88 Lichnerowicz, A. 171 354 Lie derivative 291—292 362 371 393 Lieske, J. H. 210 Lifshitz, E. M. 53 63 64 249 293 351 563 604 607 Light speed 18 26 72 222 635 Liller, W. 606 Lobachevskii, N. L 5—6 Local Group of galaxies 438 444 445 638 Locally Euclidean coordinates 8 69 Locally inertial coordinates 68 70 74 91 93 100—101 139 151 Tetrads) Longair, M. S. 468 486 600 607 Lorentz gauge 161 258 Lorentz invariance 34 Lorentz transformations 19 25 29 167 288 289 367 521—522 Lorentz, H. A. 18 22 Luminosity and luminosity distance 420 421 424—427 430—457 459 461 485 612 Lundmark, K. 417 466 Lyman aline 499 500 502 517 Lyttleton, R. A. 604 Lyubarskii, G. Ya 63 MacCallum, M. A. H. 608 MacDonald, G. F. 633 Mach, E. 16 22 239 240 Mach’s principle 17 86 88 158 239 Magellenic clouds (smaller and larger) 433 435 638 Magnetic fields 324 506 Main sequence 431 433 Mal’tsev, V. A. 513 603 Mandelstam, S. 289 295 608 Manifolds 117 Mariner satellites 205 Mars, elements of orbit 637 Mars, parallax 427 Mars, precession of perihelia 205 Marshak, R. E. 604 605 Masers 492 Mass in Kerr solution 240 Mass in Schwarzschild solution 181 Mass of stellar structure 302 (see also Chandrasekhar limit Critical Density Jeans Mass, equality of gravitational and inertial 11 13 69 Mass, equivalence with energy 33 Mass, of collapsing star 346 Massless particles 34 71 189 265 285 Matsuda, T. 607 Matukuma, T. 193 Matzner, R. A. 608 Maximally symmetric spaces 379—395 Maximally symmetric subspaces 395 404 411—412 460 Maximum temperature 590 591 Maxwell — Boltzmann statistics 551 Maxwell, J. C. 11 21 Maxwell’s equations 17 19 25 41 43 124 125 151 161 358 470 619 May, M. M. 351 354 May, R. M. 467 Mayall, N. U. 446 448 467 McColl, M. 513 603 McCray, R. 602 McCrea, W. H. 599 607 McKellar, A. 513 514 515 602 McVittie, G. C. 354 464 632 Meekins, J. F. 600 Mercury, constancy of Newton’s constant 629—630 Mercury, elements of orbit 637 Mercury, precession of perhelia 14—15 198—200 231 233 Mercury, radar echo delay 203 205 207 Metric 8—9 71—76 85—86 95 105 365-366 Maximally Maximally Post-Newtonian Robertson-Walker Schwarzschild Metric determinant 98 104 107 Michelson — Morley experiment 18 26 Michelson, A. A. 18 23 Microwave radiation background 408 409 464 480 498 501 506—528 545—546 556 559 567 570 576 595 613 617—618 Migdal, A. B. 353 Mikhailov, A. A. 193 209 Miley,G. K. 601 Millea, M. F. 513 603 Miller, A. I. 23 Miller, C. 21 22 63 89 Milne, E. A. 599 Minkowski tensor 26 35 38 85 86 Minkowski, R. 448 467 Misner,C. W. 64 172 295 351 352 354 594 603 608 609 Missing mass (see Density of the universe Intergalactic Mixed tensors 95 Moffat, R. J. D. 604 Momentum (see Energy and momentum conservation Energy-Momentum Moon, acceleration toward earth 13 Moon, acceleration toward earth as gravitational antenna 282 Moon, acceleration toward earth, laser ranging 630 Moon, acceleration toward earth, length of lunar month 630—631 Moon, acceleration toward earth, miscellaneous properties 637 Morgan, D. L. 608 Morley, E. W. 18 23 Morrison, P. 527 604 Morrison, R. J. 604 Morse, P. M. 352 Mossbauer, R. L. 82 89 Moving clusters 428 429 Mu Cassiopeiae A 558 Mu mesons in early universe 528 530 533—535 Mu mesons in neutron stars 324 Mu mesons, conservation 604 Muehlner, D. 513 603 Muhlemann, D. O. 194 Muller, E. A. 605 Multipole fields 225 229 Munk, W. H. 633 Murphy, R. V. 604 Murray, J. 22 Murray, S. 600 Nariai, H. 607 Narlikar, J. V. 464 526 600 603 619 632 Nasir al din al Tusi 4 Neugebauer, M. 606 Neutrinos emitted by, from sun 556—558 Neutrinos emitted by, neutron stars 318 322 324 Neutrinos emitted by, temperature 529 537—540 546 560 Neutrinos emitted by, viscosity 407 594 Neutrinos emitted by, white dwarfs 316 Neutrinos in early universe 528 529 534 550 560 Neutrinos, cosmic background 480—481 613 Neutrinos, degeneracy 541—545 560—561 Neutron stars 297 317 325 Neutrons in early universe 528—530 545—554 560—561 Neutrons in early universe and k-process 487 Neutrons in early universe in neutron stars 318 324 Neutrons in early universe in white dwarfs 316 Neutrons in early universe, gravitational and inertial mass 13 Neutrons in early universe, mass 636 Newcomb, S. 14 22 198 199 Newton, I. 11—16 21 67 86 337 474 562 606 Newtonian approximation 222—225 Newtonian approximation in quadrupole approximation 267 269 Newtonian approximation in steady-state cosmology 460 Newtonian approximation in weak-field approximation 253—254 Newtonian approximation, post — Newtonian approximation 223 Newtonian cosmology 338 474—475 562 571 578 587 Newtonian limit of field equations 152—157 Newtonian stars 308—317 Newton’s constant (G) 152 635 Newton’s constant (G) in Brans — Dicke theory 158 245 248 Newton’s constant, change with time 621—631 Newton’s constant, related to atomic constants 619—620 Newton’s Second Law 11 31—33 NGC 4472 (see M 100) NGC 6087 (open cluster) 437 NGC 6664 (open cluster) 437 NGC 6822 (galaxy) 427 638 NGC 6946 (galaxy) 438 NGC 7619 (galaxy) 445 NGC 7790 (open cluster) 437 NGC129 (open cluster) 437 NGC205 (galaxy) 434 638 Nijgh, G. J. 69 89 Noerdlinger, P. D. 600 602 Nonlinearity of the field equations 151 167 171 Noonan, T. W. 464 478 600 Nordstrom, G. 19 23 Normal surface element 119 North, J. D. 21 465 novae 438 559 Novikov, I. D. 350 354 598 607 608 NPO532 (Crab pulsar) 281 Nucleosynthesis 479 487—488 510—511 529 545—561 593 627—628 Null, G. 210 Number counts 451 457 461 463 486 487 616 Number density and current 49 243 303 583 Nutku, Y. 249 294 Oblateness of the sun 200—201 Ogilvie, K. W. 606
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте




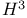 decay
decay