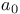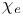јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Edward M. Purcell Ч Electricity and magnetism
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Electricity and magnetismјвтор: Edward M. Purcell јннотаци€: The subject of this volume of the Berkeley Physics Course is electricity and magnetism. The sequence of topics, in rough outline, is not unusual: electrostatics; steady currents; magnetic field; electromagnetic induction; electric and magnetic polarization in matter. However, our approach is different from the traditional one. The difference is most conspicuous in Chaps. 5 and 6 where, building on the work of Vol. I, we treat the electric and magnetic fields of moving charges as manifestations of relativity and the invariance of electric charge. This approach focuses attention on some fundamental questions, such as: charge conservation, charge invariance, the meaning of field. The only formal apparatus of special relativity that is really necessary is the Lorentz transformation of coordinates and the velocity-addition formula. It is essential, though, that the student bring to this part of the course some of the ideas and attitudes Vol. I sought to developЧ among them a readiness to look at things from different frames of reference, an appreciation of invariance, and a respect for symmetry arguments. We make much use also, in Vol. II, of arguments based on superposition.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 2 edition√од издани€: 1984 оличество страниц: 484ƒобавлена в каталог: 16.10.2010ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
"Del" notation 63 74 78 365 364 365 365 Addition of velocities, relativistic 455 Additivity of interactions 9 12 Admittance 313Ч315 317 Alnico V, B-H curve for 442 Alternating Current 303Ч318 Alternating current, representation of, by complex number 311Ч312 Alternating electromotive force 304 Alternating-current circuit 310Ч315 Alternating-current circuit, power and energy in 315Ч317 Aluminum, doping of silicon with 147Ч148 Ammonia molecule, dipole moment of 365 Ampere (SI unit of current) 2 124 212 474 Ampere, Andre-Marie 2 170 172 193 405 Angular momentum, conservation of, in changing magnetic field 450 Angular momentum, of electron spin 418Ч419 Angular momentum, orbital, relation to magnetic moment 414 Angular momentum, precession of 470 Anode of vacuum diode 127 Antimatter 4 Antineutron 3 Antiparticle 3 Antiproton 3 Atlantic telegraph cable Prob.4.4 Atom, electric current in 413 Atomic polarizability 362Ч363 B, and M, and H inside magnetized cylinder 438 B, magnetic field 173 208 B-H curves, for iron and Alnico V 442 Battery, storage, lead-sulfuric acid 155Ч157 Biot Ч Savart formula 226 328 Blakemore, R.P. 445 Bohr radius 362 418 Prob.1.21 Boltzmann factor 145 BoltzmannТs constant k 146 385 Bound and free charge 380 Bound and free charge, arbitrariness of the distinction 389 Bound currents 431Ч432 Bound-charge current 387Ч389 Bound-charge density 380 Boundary of dielectric, change in E at 377 Boundary-value problem 95 111Ч113 Bridge network 152 Prob.4.27 Capacitance 103Ч107 Capacitance of cell membrane Prob.10.7 Capacitance of prolate spheroid Prob.3.20 Capacitance, coefficients of 109 Capacitance, units of 103 Capacitance, units of, illustrated 104 Capacitor 103 Capacitor plate, force on 111 Prob.3.16 Capacitor, dielectric-filled 371Ч373 Capacitor, energy stored in 110Ч111 Capacitor, parallel-plate 105 348 Capacitor, vacuum 348 Carbon monoxide molecule, dipole moment of 365 Cathode of vacuum diode 127 Cavendish, Henry 10 Centimeter (unit of capacitance) 103 Centimeter, illustrated 104 Charge density, linear 26 Charge distribution, cylindrical, field of 62 Charge distribution, electric 20Ч21 Charge distribution, moments of 352Ч355 Charge distribution, on a surface 28 Charge distribution, spherical, field of 25Ч26 Charge, in motion see "Moving charge" Charge, magnetic, absence of 404 Charged balloon 31 Charged disk 51Ч53 Charged disk, field lines and equipotentials of 55 Charged disk, potential of 51 Charged wire, potential of 50 Circuit element 149 Circuits, alternating-current 310Ч317 Circuits, direct-current 148 151 152 Circuits, equivalent 151 Circuits, LR 282Ч284 Circuits, RC 159Ч160 Circuits, resonant 298Ч303 Circuits, RLC 298 309 315 Circulation 68 Clausius Ч Mossotti relation 384n CO (carbon monoxide) molecule, dipole moment of 365 Coefficients, of capacitance 109 Coefficients, of potential 109 Coil, cylindrical (solenoid), magnetic field of 227Ч231 Prob.6.17 Coil, toroidal, energy stored in 286 Coil, toroidal, inductance of 281Ч282 Compass needle 173 Complex-number representation of alternating current 311Ч312 Conduction band 145Ч146 Conduction, electrical 130Ч148 Conduction, in metals 142Ч144 Conduction, in semiconductors 144Ч148 Conduction, ionic 134Ч135 Conductivity, anisotropic 128 Conductivity, electrical 128Ч133 Conductivity, of metals 142Ч144 Conductivity, of various materials 133 Conductivity, units for 132 Conductors, charged, system of 91 Conductors, electrical 88Ч103 Conductors, field at surface of 92 Conductors, spherical, field around 94 Conformal mapping 111 Conservation of electric charge 4Ч5 126Ч127 Conservation of electric charge, distinguished from charge invariance 178 Conservative forces 11 Copper chloride, paramagnetism of 400 402 Copper, resistivity of 133 139 141 Coulomb (SI unit of charge) 8 45 474 CoulombТs law 7Ч11 193 CoulombТs law, tests of 10Ч11 Critical damping 302Ч303 Cross product (vector product) of two vectors 173n Curie point 439 Curie, Pierre 439 Curl 68Ч76 Curl in Cartesian coordinates 71Ч74 78 Curl, physical meaning of 74Ч76 Curlmeter 75 Current density, J 124 128 Current loop, magnetic dipole moment of 407Ч408 Current loop, magnetic field of 405 Current loop, Torque on 419 Current ring, magnetic field of 227 Current sheet 231Ч235 Current sheet, magnetic field of 221Ч223 Currents, alternating 303Ч318 Currents, bound and free 431Ч432 Currents, bound-charge 387Ч389 Currents, displacement 328Ч330 Currents, fluctuations of, random 139 Cylinder, magnetized, compared with cylinder polarized 429 Damped harmonic oscillator 298 Damped sinusoidal oscillation 301 Damping of resonant circuit 300 302 Damping of resonant circuit, critical 302Ч303 Davis, L., Jr. 11n de Coulomb, Charles 10 Decay of proton 6 Decay time for EarthТs magnetic field Prob.7.28 Deuterium molecule 176 Diamagnetic substances 400 Diamagnetism 413 418 Diamagnetism of electron orbits 417 Diamond, crystal structure of 144 Diamond, wide band gap of 147 Dielectric constant 350 Dielectric constant 350 Dielectric sphere in uniform field 378 Dielectrics 348Ч352 Diode, silicon junction Prob.4.13 Diode, vacuum 127 Dipole moment, electric 355 Dipole moment, electric, induced 361 Dipole moment, electric, permanent 63 Dipole moment, magnetic, associated with electron spin 419 Dipole moment, magnetic, of current loop 407Ч408 Dipole moment, magnetic, of electron orbit 413Ч414 Dipole, comparison of electric and magnetic 410 Dipole, electric, potential and field of 356Ч358 Dipole, electric, torque and force on, in external field 358Ч360 Disk, charged 51Ч53 55 Disk, conducting, field of 102 Displacement current 328Ч330 Displacement, electric, D 381 432Ч433 Distribution of electric charge 20Ч21 Divergence 57 Divergence in cartesian coordinates 59Ч62 78 Domains, magnetic 440 doping of silicon 147Ч148 Dot product of two vectors 12 Dynamo Probs.7.31 7.32 Dyne (CGS unit of force) 8 EarthТs magnetic field 210 Prob.11.4 EarthТs magnetic field, decay time of Prob.7.28 EarthТs magnetic field, possible source of 296 Einstein, Albert 2 170 241 Electret 429 Electric charge 2Ч29 Electric charge, additivity of 9 12 Electric charge, conservation of 4Ч5 126 178 Electric charge, distribution of 20Ч21 Electric charge, free and bound 380 389 Electric charge, fundamental quantum of 8 Electric charge, invariance of 176Ч178 Electric charge, quantization of 5Ч6 177 Electric charge, sign of 4 Electric currents 124Ч132 Electric currents and charge conservation 126Ч127 Electric currents, energy dissipation in flow of 153 Electric currents, parallel, force between 211Ч212 Electric currents, variable, in capacitors and resistors 159Ч160 Electric currents, variable, in inductors and resistors 282Ч284 electric dipole moment 355 Electric dipole moment, induced 361 Electric dipole moment, permanent 63 Electric dipole, potential and field of 356Ч358 Electric dipole, torque and force on, in external field 358Ч360 Electric displacement D 381 432Ч433 Electric field lines 19 Electric field, definition of 16 Electric field, energy stored in 32 Electric field, flux of 21Ч25 Electric field, flux of, GaussТs law 22Ч25 Electric field, in different reference frames 178Ч181 Electric field, in matter, spatial average of 369 Electric field, inside hollow conductor 96Ч97 Electric field, Line integral of 42Ч44 Electric field, macroscopic 370 371 Electric field, microscopic 370 Electric field, of a flat sheet of charge 28 Electric field, of dipole 357 Electric field, of line charge 26 Electric field, of point charge with constant velocity 182Ч185 Electric field, of stationary charges 180 Electric field, SI unit for 16 Electric field, transformation of 239 Electric field, visualization of 17Ч20 Electric quadrupole moment 355 Electric susceptibility 372 383 422 Electrical insulators 88Ч89 Electrical potential energy 13Ч15 Electrical potential energy of a system of charges 32 46 Electrical shielding 96 Electromagnet, design of Prob.11.25 Electromagnetic field components, transformation of 238Ч240 Electromagnetic force, range of 10 Electromagnetic induction 256Ч273 Electromagnetic wave 190 331Ч343 Electromagnetic wave in dielectric 389 391 Electromagnetic wave in different inertial reference frames 342 Electromagnetic wave, energy transport by 338 Electromagnetic wave, general properties of 334 Electromagnetic wave, reflection of 339 341 Prob.10.24 Electromagnetic wave, standing 336Ч337 Electromagnetic wave, traveling pulse 335 Electromotive force 155Ч157 274 Electromotive force, alternating 304 Electron motion, wave aspect of 143 Electron orbit 413Ч417 Electron orbit, diamagnetism of 417 Electron orbit, magnetic moment of 413Ч414 Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) 470 Electron radius, classical 417 Prob.1.10 Electron spin 418Ч421 Electron spin, angular momentum of 418Ч419 Electrons 3 5 6 143Ч147 413Ч421 Electrons, charge of 8 Electrons, magnetic moment of 419 Electrons, valence 144 Electrostatic field 44 see Electrostatic field, equilibrium in 65 Electrostatic field, transformation law for 181 Electrostatic unit (esu) of charge 8 Energy see also "Potential energy electrical" Energy gap 145 Energy, dissipation of, in resistor 153 Energy, electrical, of ionic crystal 14 Energy, in alternating-current circuit 315Ч317 Energy, of electric field 31Ч33 Energy, of system of charges 10 Energy, stored, in capacitor 110Ч111 Energy, stored, in electric field 32 Energy, stored, in magnetic field 285Ч286 Equilibrium of charged particle 65 Equipotential surfaces 54Ч55 92 Equipotential surfaces in field of conducting disk 102 Equipotential surfaces in field of uniformly charged disk 55 Equivalence of inertial frames 171 452 Equivalent circuit 151 Equivalent circuit for voltaic cell 157 Faller, J.G. 10n Farad (unit of capacitance) 105Ч106 160 Faraday, discovery of induction by 256Ч258 Faraday, Michael 2 240 Faraday, reconstruction of experiment by Prob.7.10 Faraday, Waterloo Bridge experiment by Prob.7.27 FaradayТs law of induction 272Ч273 Ferromagnetic substances 400 ferromagnetism 437 Field, meaning of 180 Fluctuations of current, random 139 Flux of electric field, definition of 21Ч25 Flux tube 265 Flux, magnetic 263Ч265 Force components, application of 191Ч192 Force components, Lorentz transformation of 457 Force(s), between parallel currents 211Ч212 Force(s), conservative 11 Force(s), electromotive 155Ч157 274 304 Force(s), magnetic 171Ч173 Force(s), on capacitor plate 111 Prob.3.16 Force(s), on dipole in external field 369 Force(s), on layer of charge 29
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



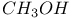 (methanol) molecule, dipole moment of
(methanol) molecule, dipole moment of 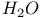 molecule, dipole moment of
molecule, dipole moment of 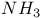 (ammonia) molecule, dipole moment of
(ammonia) molecule, dipole moment of