Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Welford W. — Useful Optics
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Useful OpticsАвтор: Welford W. Аннотация: Students and professionals alike have long felt the need of a modern source of practical advice on the use of optical tools in scientific research. Walter T. Welford's Useful Optics meets this need.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Электромагнетизм /Оптика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1991Количество страниц: 140Добавлена в каталог: 09.10.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
"Barrel" distortion 34 "Hard-edged" beams 67 "Pincushion" distortion 34 "Thick" systems 39 "Thin" lens 37 "Thin" lens, model of Gaussian optics 9 10 59—60 Aberrations and Gaussian beams 69—70 Aberrations and optical system design 36—42 Aberrations of ray 11 25 Aberrations, chromatic 36 Aberrations, large 49—52 Aberrations, parameterizing 26 27 Aberrations, paraxial 27 Aberrations, primary 27 Aberrations, Seidel 27—29 32 33 Aberrations, small 47—49 Aberrations, spherical 28—30 37 Aberrations, third-order 27 Aberrations, wavefront 29 30 Afocal system 10 11 Airy pattern 46 69 Alkali halides 22 Amplitude point spread functions 53 Angle of diffraction, and wavelength selection 110 Angle of incidence 2 Angle of multilayers 73 Angle of refraction 2 Angular dispersion, equation for 16 Angular resolution of the eye 123 annealing 20 21 Annealing for mirrors 23 24 Antireflection coatings 77 Antireflection coatings, broad-band 77—78 Antireflection coatings, principle of 72 Antireflection coatings, single-layer 71—73 Aperture stop 8 9 Aperture stop, position of 34—35 Aplanatic doublets 37—39 Argand diagram 89 Aspheric surfaces 40 Astigmatism 15 31—34 Astigmatism, correction 38—39 Astigmatism, defined 31 Beam expander 18 69 125 Beam waist 66—68 Beam-splitters, polarizing 18 Beam-splitting cube 16 Beam-splitting prism 15 Beam-splitting surfaces 42 Bending, defined 37 38 Bessel function 44 Birefringence, stress 20 21 Blackbodies 99 Blaze angle 109 Blazing of a grating 108 Bolometers 91 94 Bragg mode 104 Brewster angle 71 81 Brightness 64 Calcium carbonate 23 Cassegrain telescope 42 Catalog of optical glass manufacturers 19 cell 124 Centering 123 Central obstruction 42 Chalcogenide glasses 23 Charge-coupled device (CCD) 93—94 Chemical attack in optical systems 21 chromatic aberration 36 Chromatic dispersion 19 Coatings 21 Coherence 52 Coherence and interferometry 86—87 Coherence, longitudinal 88 Coherence, patch 53 86 Coherence, transverse 88 Coherent illumination 52—54 Collecting angle 61 Coma 15 30—31 Coma as transverse ray aberration 32 Coma, linear 30 Coma, Seidel 30 Combining prism 15 Compensators and interferometers 85 Complex amplitude 44 45 53—55 Complex amplitude of Gaussian beams 66 Concave gratings 111—113 Condensers 60—63 Conjugate distance equation 5 7 8 10 Conjugate distances 5 Conjugate planes 5 Cooke triplet 39 copper 23 Critical angle 13 Crystal quartz 23 Curvature 110 Deflectors, acousto-optic 104—105 Degree of partial coherence, defined 87 Detection, photochemical 94—95 Detectors 91—95 Dichroic reflecting surface 15 16 Dichromated gelatin (DCG) 115 Diffraction 54—56 104 Diffraction, gratings 15 108—113 Diffraction, holographic 116 Diffraction, systems limited by 49 Diffractometers 56 Dispersing prisms 16 17 dispersion 21 Distortion 33—34 Doppler effect 104 Dove prism 15 Electromagnetic radiation 1 Electromagnetic waves 1 Entrance pupil 9 10 Entrance slit 110 Exit pupil 9 10 Exit slit 112 Expansion coefficients of optical glasses 21 extended objects 59 External photoelectric effect detectors 91 Eye, human, angular resolution limit of 123 Fabry — Perot mirrors 23 Fabry — Perot theory 80 Faraday rotation 20 21 Fermat's principle 3 Field coordinate 26 31—33 Field coordinate, correction 38—39 Field coordinate, defined 32 Field curvature 31 Field lens 61 126 Filaments, quartz-halogen 98 Filaments, tungsten 98 Finite wavelength 44 Fizeau fringes 82—86 Float glass 23 Flux 58 Flux density 58 Focal length 5 Focal lines, sagittal 32 Focal lines, tangential 32 Focal ratio (f-ratio) 59 Focus 6 Fourier transform 54—57 Fourier transform and image 52 Fourier transform of the intensity point spread 50 Fourier transform, spectroscopy 84 Frame stores 125 Free spectral range 110 Frequency response formalism 53 Fresnel formulas 71 Fresnel formulas and multilayers 74 Fresnel formulas, lens 62 Fresnel formulas, numbers 67 Fringe of constant optical path 82—85 Fringe of equal inclination 82—85 Fringe, contrast 84 Fringe, function 84 Fringe, visibility or contrast of 87 Fused silica 22 Galvanometer mirror 101 Gaussian beams 66—68 Gaussian beams and aberrations 69—70 Gaussian beams, tracing of 68—69 Gaussian beams, truncation of 69 Gaussian intensity profile 9 Gaussian optics 5 7 25 Gaussian optics, formally defined 27 Geometrical optics 1 2 Geometrical wavefront 2 Germanium 23 ghost images 63 Glass chart 20 Globar 99 Golay cells 91 94 Grating constant 108 Grating monochromator 113 Gratings, concave 111—113 Gratings, plane diffraction 108—111 Gray body 98 Haidinger fringes 82—85 Harmonic analyzer 84 Helmholtz equation 69 Holograms, making of 119—120 Holograms, rotating 102 Holograms, thick 115 Holograms, thin 115 Holographic optical elements (HOEs) 117—119 Holographic recording materials 115 Holography, principle of 114—115 Homodyne detection 96 97 Ideal wavefront 28 Illuminance 97—98 Illumination, coherent 52—54 Illumination, incoherent 50 53 Illumination, partially coherent 52—54 Image formation 5 52 Image formation and partial coherence 88 Image formation, isoplanatic 50 Image point 5 Image point, Gaussian 26 Image point, ideal 26 Image, inversion 14 Image, parabolic 17 Image, rotation 14 15 Image, sharpness of 28 Image, virtual 9 10 Incoherent illumination 59 Infinity and diffraction 55 56 Infinity and telecentric system 9 10 Infrared, defined 23 Infrared, light sources 99—100 Inhomogeneity of refractive index 20 Integration 125 Intensity 53 Intensity, point spread function 52 Interference in a thin film 72 Interference, contrast 121 Interference, effects 53 Interference, filters 80 Interferometers 80 Interferometers, distance and phase measurement 85 Interferometers, Michelson 82—87 Interferometers, Twyman — Green 86 87 Interferometry and coherence 86—87 Interferometry holographic 119—120 Irradiance 58 Isoplanatic image formation 50 Johnson noise 92 95 Koehler illumination system 61 62 Lagrange, invariant 6 7 58 65 Lambertian radiator 58 Laser beam waist 66—68 Laser speckle 53 54 Lasers and non-Gaussian beams 70 Lasers, mirrors for 23—24 Lasers, multiwavelength 16 Lasers, sources for imaging systems 63—64 Lenses, testing of 86 Light intensity 45 46 Light scattering 20 Line spread function 109 Linear coma 30 Liouville's theorem 64 Lit trow geometry 110 Lithium fluoride 22 Longitudinal chromatic aberration 36 Longitudinal coherence 88 Longitudinal color 36 Longitudinal spherical aberration 28 Lumen 97 Luminance 97 98 Magnification 123 Malus — Dupin theorem 2 Mechanical stress 20 21 Meridian section 31 Metrical precision 125 Microscope, scanning 106—107 Microscopy 52 Mirrors 24 Mirrors for high power lasers 23—24 Mirrors, combinations of 12 Mirrors, concave 41 43 Mirrors, Fabry — Perot 23 Mirrors, galvanometer 101 Mirrors, optical materials for 19 23 Mirrors, oscillating 101 Mirrors, paraboloidal 41 Mirrors, rotating 101 Mirrors, spherical 41 Mirrors, telescope 24 Modulation transfer function (MTF) 50 51 90 Monochromatic light 88 Monochromator 113 Mounting of an optical component 124 Multilayers and Fresnel formulas 74 Multilayers and interference filters 80 Multilayers, angle of incidence of 73 Multilayers, design of 74 Multilayers, dielectric 15 Multilayers, high-reflectance 77 Multilayers, intensity reflectance of 76 Multilayers, periodic 79 Multilayers, reflectance of 74 Multilayers, thin-film 71—81 Multilayers, transmittance of 74 Multilayers, types of 76—81 Multilayers, wavelength dependence of 73 Multiwavelength lasers 16 Neutral reflecting surface 16 Noise 1 90 95—97 125 Noise equivalent power (NEP) 93 Non-Gaussian beams 70 Nonlinear index changes in glasses 21 22 Nonlinear refractive index 20 Nonspheric surfaces 40 Null test 117 Numerical aperture 46—47 123 Object 5 6 52
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



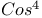 law
law