|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rickayzen G. Ч Green's functions and condensed matter |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Absorption 9 220
Acoustic phonons see also УVelocityФ
Acoustic phonons, of sound, sound waves 170 190
Adiabatic approximation 181 196
Advanced Green's function 8 23 see
After-effect function 9 see
Alloys 285 295
Amorphous semiconductors 286
Anomalous skin effect in metals 114 117 120
Antiferromagnet, spin waves in 274
Antiferromagnetism 263
Average t-matrix approximation (ATA) 298
Boltzmann equation 97 117
BornЧOppenheimer approximation 193 see
Bose distribution function 29
BoseЧEinstein condensation 245Ч246 256
Bosons 341
boundary conditions 2 3Ч6 19 27 55
Boundary conditions, periodic 101
Boundary conditions, spatial 3
Bragg scattering 175
Brillouin zone 182
canonical ensemble 32
Causal Green's function 24 28 see
Charge density 344
chemical potential 32
Closed loop 67 75
Coherence length 224
Coherent potential approximation (CPA) 302Ч311
Coherent scattering 172Ч181
Collective modes 90
Collective oscillations 152 157
Commutation relations 341
Condensate fraction 262
Condensate wave function 312
Connected diagrams 67 70 188
Conservation laws 20 93Ч94 226
Conservation of charge 123 180
Conservation of energy 72
Conservation of momentum 74
Conserved quantities 161Ч163
Conserving approximations 94
Cooper pair 203 232 233 240
Correlation 83Ч86 302 314 see
Correlation function 15Ч18 320 323 325 332
Correlation function, density-density 17 124 174
Correlation function, one-particle 348
Correlation function, order parameter 314
Correlation function, two-particle 89Ч90 95
correlation length 315 317
Correlation, spin 277
Correlation, statistical 84
Correlation, three-particle 84
Correlation, two-particle 83
Coulomb gas 121Ч140
Coulomb gas, thermodynamic potential for 131
Coulomb interaction 89 121 163 181
CPA see УCoherent potential approximationФ
Creation operators 342
Critical exponents 316Ч319
Critical magnetic field 217
Critical phenomena 312Ч340
Critical point 270
Critical region 323
Curie temperature 263 269
Current-density operator 109Ч110 344
Debye Ч Waller factor 175
Degenerate ground state 208 253
Density matrix 6 32 348
Density matrix, equation for 6
Density of states 35 286Ч289 294Ч295
Density of states, for independent electrons 99
Density of states, local 35
Density of states, of phonons 198 301 304Ч305
Density of superconducting electrons 224 232
Density operator 16
Destruction operators 342
Diagrams see УFeynman diagramsФ
Dielectric constant, Lindhard's formula for 129
Dielectric constant, of a Coulomb gas 124
Dielectric function 191
Differential cross section 171
Dirty metals 197
Disorder, random 95
Disorder, structural 289
Disorder, substitutional 289
Disorder, topological 289
Disordered systems 285Ч311
Dispersion relations 42
Dyson's equation 80
Effective field 89 268 270
effective mass 143 145Ч147 168 199
Effective potential 91 165
Electrical conductivity 109Ч118 200 306Ч310
Electron gas, energy of 89
Electron self-energy 195Ч201
ElectronЧion interaction 182
ElectronЧphonon interaction 181Ч201 203
ElectronЧphonon vertex 194
Energy gap 202 214 232
Exchange energy 88
External vertices 66Ч71
Fermi distribution function 29 352
Fermi liquid 141Ч163 181
Fermi liquid, charged 163Ч167
Fermi liquid, Landau's theory of 141 Ч 167
Fermi liquid, microscopic theory of 154Ч163
fermions 341
Ferrimagnetism 263Ч264
Ferromagnet, ground state of 267
ferromagnetism 263 317Ч318
Feynman diagrams 19 56Ч58 61 66Ч71 325Ч331
Feynman diagrams, rules for 73Ч74 185Ч189
Field operator 341
Fixed points 333
Fluctuation-dissipation theorem 22 42
Fluctuations 319Ч323
Flux quantization see УQuantization of magnetic fluxФ
For independent electrons 99
gap equation 212 220 230
Gap parameter 214Ч215 225 312
Gap parameter, phase of 226 234
Gapless superconductivity 227 232
Gauge invariance 108 225Ч7
Gibbs free energy 312 319
Ginzburg criterion 323
grand canonical ensemble 32 45 347
Green's functions see also УAdvanced Green's functionФ УCausal УManyparticle УRetarded УSpin and
Green's functions, analytic properties of 24Ч33 51
Green's functions, classical 1Ч6 20
Green's functions, definitions 22Ч24
Green's functions, density-density 168
Green's functions, double-time 22Ч24
Green's functions, equations of motion for 42Ч45
Green's functions, for a ferromagnet 271Ч284
Green's functions, for an electron in a metal 106
Green's functions, Fourier transforms of 25
Green's functions, higher order 39Ч41 70
Green's functions, in an external field 47Ч50
Green's functions, two-particle 70 295
gyromagnetic ratio 151 344
Hamiltonian, for free-electron model of a metal 126
Hamiltonian, for phonons 170
Hamiltonian, for scattering by impurities 100
Hartree approximation 19 82 88Ч89 91 125Ч127 166 218
HartreeЧFock approximation 19 61 83Ч87 91 219 275
HartreeЧFock equation 86
Heisenberg representation 7
Heisenberg's equations of motion 44 63 347
Heisenberg's Hamiltonian 266
| Hubbard Hamiltonian 275
Hubbard model 274Ч282
Impurities, in a metal 98Ч120
Impurities, in superconductors 227Ч234
Impurity band 286 304
Impurity levels 286 293Ч295
Incoherent scattering 172Ч181
Independent particles 36Ч37 346Ч348
Internal vertices 66Ч71
Ising model 316 318
Isotope effect 203
Jellium model 121
Josephson tunnelling 235 238
kinetic energy 344
Kondo effect 119 229 284
Kondo temperature 284
KramersЧKronig relations 22 41Ч2 52
Kubo's formula 8 20 109 see
Landau's function 143 167
Landau's parameters 146
Life-time 39 82 119 135Ч140 199Ч200 285
Linear response 6Ч10 17 19 90 223
Liquid 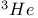 142 147 148 152Ч153 205 142 147 148 152Ч153 205
Liquid  242 see 242 see
Liquid  , dispersion curve for 244 , dispersion curve for 244
Liquid  , microscopic theory of 246Ч256 , microscopic theory of 246Ч256
Liquid  , specific heat of 243 , specific heat of 243
Liquid state 18
Liquid-gas transition 317Ч318
Localized states 289 304 310
London limit 224
Low-density Bose gas 256Ч259
Magnetic impurities 119 227
Magnetic impurity, classical 96
magnetic moment 344
Magnetism 263Ч268
Magnons 263 286
Many-particle Green's functions 65 see
Mass enhancement parameter 195 199 220
Mean field theory 323 see
Mean free path 107
Meissner effect 203 204 220 224 232
Migdal's theorem 193Ч195
Molecular-field 147 149 152 164 265 268 275 see byФ
Mott Ч Hubbard transition 280 282
Neel temperature 263
Neutron scattering 168Ч181 242 259 263
Non-linear response 40
Number conservation 207 247
Number density 88
Number operator 343
Occupation number representation 343Ч348
Occupation numbers 142
Optical phonons 196
Optical theorem 108
Order parameter 259 270 310 319
Pairing field 208 210
Particle density 344
ParticleЧhole pair 61 155Ч8
ParticleЧhole scattering 167
Pauli spin matrices 210 344
Penetration depth 203 224
Persistent current 202
Perturbation expansion 19 324Ч331
Perturbation theory, and a Bose Ч Einstein condensation 246Ч256
Perturbation theory, for interacting particles 59Ч71
Perturbation theory, for phonons 186Ч189
Perturbation theory, with a single-particle potential 54Ч59
Phonon propagator 170 188 191
Phonon scattering 98
Phonon self-energy 189 195Ч6
Phonon spectrum 244 286
Phonon vertex 168
Phonons 12 168Ч201 286
Plasma frequency 122 165 182
Plasma oscillation 122
Plasmons 90 122Ч124
Polarization diagrams 190
Polarization vectors 170
potential energy 344
Potential scattering 57
Probability amplitude 14
probability density 16
Propagator 56Ч57 59 see
Quantization of circulation 244 259Ч261
Quantization of magnetic flux 202 234Ч235
Quantum fluid 18 232 УSuperfluid УSuperconductivityФ
Quantum of flux 235
Quasi-particles 37Ч39 81 142 155 211 223 279
Random phase approximation 19 71 89Ч94 127Ч131
Reciprocal lattice 169
Relaxation time approximation 114
Renormalization 331
Renormalization group 285 316 324 331Ч340
Renormalization group equations 333
Resonance broadening 281
Resonant enhancement 295
Response function 9 19 90
Response function, rules for 70
Retarded Green's function 8 22Ч24
Roton spectrum 244
Rotons 178
Rules for Feynman diagrams see УFeynman diagrams rules
Scale transformations 325
Scaling theory 316 318 334
Scattering length 172
Screened interaction 135 193
Screened potential 127
screening 89Ч93 122 124Ч125 165 182 189Ч193
Second order phase transition 312Ч316
Second order phase transition, Landau's theory of 320
Second quantization 341Ч348
Self-consistent equation 272 276 302
Self-consistent field 89Ч93 209
Self-energy 19 78Ч82 104 252
Self-energy, exchange 91
Self-energy, proper 79 82 329
Semiconductors 285
Simple harmonic oscillator 10Ч12 52
Single-particle Green's functions 13 19 33Ч39 59 see
Single-particle operators 343
Sound absorption 119
Sound waves 90 256
Spatial averages 101
Specific heat 45 314 321 326
Spectral form 25Ч33
Spectral function 27 107 286
Spectral function, sum rule for 27
Spin 43 75
Spin fluctuations 152
Spin Green's functions 263
Spin susceptibility 151Ч157
Spin waves 178 263Ч265 273 see
Spin-disorder scattering 281
Spin-flip lifetime 231
Split band limit 303 310
Spontaneous magnetic moment 268 312
Strong-coupling superconductors 198 236
Structure factor 168
Sum rules 26 178Ч181 306Ч307
Sum-over-states 319Ч323 347
Superconductivity 202Ч241 312 323
Superconductor, critical magnetic field of 203
Superconductor, critical magnetic field of, density of states 215Ч216 232 236
Superconductor, electromagnetic effects in 220
Superconductor, Green's function for 210 220
Superconductor, model Hamiltonian for 209
Superconductor, phase of wave function 207Ч208
Superconductor, thermodynamic potential for 217
Superconductor, thermodynamics of 209
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте