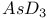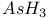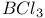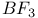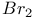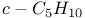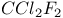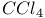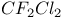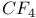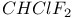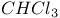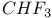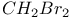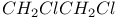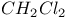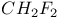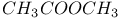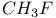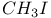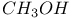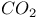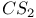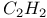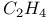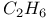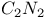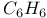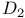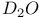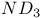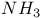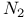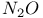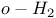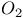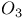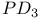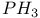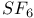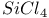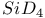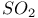|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lambert J.D. Ч Vibrational and rotational relaxation in gases |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
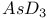 63 66 63 66
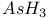 63 64 71 63 64 71
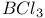 76 80 76 80
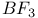 67 68 67 68
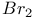 55 68 55 68
 65 65
 62 64 71 74 112 123 62 64 71 74 112 123
 112 112
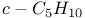 65 123 65 123
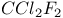 96 96
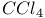 47 67 92 47 67 92
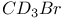 66 66
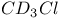 66 88 66 88
 63 66 100 123Ч126 63 66 100 123Ч126
 67 67
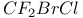 67 67
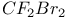 67 67
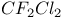 67 74 67 74
 67 67
 67 67
 67 92 67 92
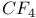 62 67 73 74 96 109 62 67 73 74 96 109
 67 67
 67 67
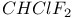 67 96 67 96
 67 67
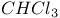 47 57 92 47 57 92
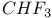 67 74 96 67 74 96
 65 65
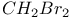 92 92
 65 65
 65 65
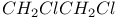 65 65
 65 65
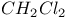 65 92 65 92
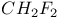 64 88 64 88
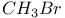 62 64 68 71 62 64 68 71
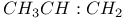 65 65
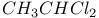 65 65
 47 62 64 68 71 87 88 96 47 62 64 68 71 87 88 96
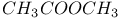 65 65
 65 65
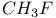 64 87 88 64 87 88
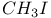 64 68 71 64 68 71
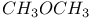 96 96
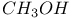 12 12
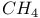 47 60Ч61 63 64 71 85 86 100 103Ч105 109 112 123 126 47 60Ч61 63 64 71 85 86 100 103Ч105 109 112 123 126
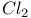 47 48 52 53 68 80 47 48 52 53 68 80
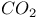 12 67 74 76Ч80 88 96 104Ч107 109 123 12 67 74 76Ч80 88 96 104Ч107 109 123
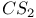 67 106 67 106
 67 67
 66 88 66 88
 66 106 66 106
 67 96 67 96
 67 67
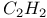 64 71 100 64 71 100
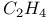 64 71 96 100 123 64 71 96 100 123
 64 71 96 64 71 96
 65 65
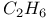 65 92 96 65 92 96
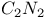 67 92 67 92
 65 65
 67 92 67 92
 112 112
 112 112
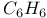 65 65
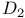 47 53Ч57 74 80 109 118Ч121 124Ч127 47 53Ч57 74 80 109 118Ч121 124Ч127
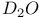 47 77 80 100 47 77 80 100
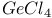 67 67
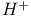 80 80
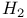 47 53Ч57 74 80 109 112 118Ч121 124Ч127 47 53Ч57 74 80 109 112 118Ч121 124Ч127
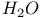 12 47 62 68 76 80 100 104 112 123 12 47 62 68 76 80 100 104 112 123
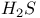 68 109 123 127 68 109 123 127
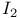 51 51
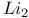 51 51
 123 127 123 127
 65 65
 65 65
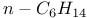 65 65
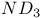 66 66
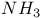 12 62 65 68 123 12 62 65 68 123
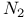 48 51 52Ч53 78 102Ч107 109 112 121Ч122 124Ч127 48 51 52Ч53 78 102Ч107 109 112 121Ч122 124Ч127
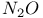 62 67 74 77 104Ч107 109 123 62 67 74 77 104Ч107 109 123
 118Ч121 124Ч127 118Ч121 124Ч127
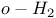 56 79 118Ч121 124Ч127 56 79 118Ч121 124Ч127
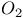 47 48 51 52Ч53 74 78 100 102 109 121Ч122 124Ч127 47 48 51 52Ч53 74 78 100 102 109 121Ч122 124Ч127
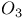 88 88
 118Ч121 124Ч127 118Ч121 124Ч127
 56 79 118Ч121 124Ч127 56 79 118Ч121 124Ч127
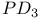 63 66 63 66
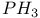 63 64 71 63 64 71
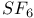 67 88 96 109 67 88 96 109
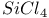 67 67
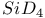 63 66 63 66
 63 64 71 63 64 71
 67 67
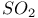 47 62 67Ч68 76 90Ч92 47 62 67Ч68 76 90Ч92
A priori distribution 80Ч82
Absorption, acoustic 14
Absorption, coefficient 17
Absorption, viscothermal 17Ч18
Acoustic methods 14Ч18
Adiabaticity parameter 6
Anti-catalysis 75Ч76
ar 74 75 76 78 112 127
Boltzmann distribution 8 13 112Ч114 129
BR 77Ч79
Breathing sphere 60
Catalysis 76Ч80 99 100
Chemical reaction 76Ч79
Chemical reaction, unimolecular 112
Chemiluminescence, infrared 38 39 101 108 127
Cl 77Ч79
Classical turning-point 2Ч3
CO 48 52 53 74 75 78 79 101Ч106 109 110Ч114 121Ч122
Collision cross-reference factor 45
Collision cross-section 9 39
Collision, diameter 2Ч4
Collision, elastic 2
Collision, inelastic 5Ч7
Collision, molecular 1Ч12
Collision, number 8 10 115
Collision, rate 4Ч5
Collision, reactive 79
Complex transfer 85
Condenser transducer 20
Conductivity, thermal 17 41Ч42
Corresponding states 12
cos 67 102Ч103 106
CS 104
DBR 57Ч59 109
DCL 47 57Ч59 80 104
df 57Ч59 109
| DI 57Ч59
Dimerization 10Ч12 68
Dipole interaction 10 57Ч59 62 68 75 101Ч110 122Ч123
Dispersion, acoustic 14Ч18
Dispersion, double 90Ч100 118 125
Distorted wave approximation (DWA) 43 117
Ehrenfest's Adiabatic Principle 6Ч7
Einstein coefficients 28
Electronic excitation 35Ч38
Electronic excitation, fluorescence 35Ч36
Electronic-vibration transfer (E-V) 77
Entropy deficiency 80
Eucken factor 42
Expansion, nozzle 114
Expansion, supersonic beam 129
f 77Ч79
FE 77Ч79
Flash photolysis 36Ч38 111
Fluorescence, electronic 35Ч36
Fluorescence, quenching 30
Fluorescence, risetime 87
Fluorescence, vibrational 29Ч30
Fourier component of force 8 46
H 77Ч79
Hard-sphere model 3Ч4
Hard-sphere model, collision rate 5
HBr 57Ч59 108Ч110 127
HCl 47 57Ч59 75 78 80 108Ч110 121Ч122 127Ч129
HD 56 57 80 118Ч121 124Ч127
HDO 100
HE 73Ч76 78 112 127
HF 57Ч59 76Ч78 108Ч110 127Ч128
HI 57Ч59 109 111 127
Hydrogen bonds 12
Hydrogen-effect 63Ч72 93 100
Impact parameter 2Ч3
Information content 80
Information content, theory 80Ч82 104 127
Infrared activity 101Ч110
Interferometer, acoustic 19Ч21
Interferometer, Mach Ч Zehnder 26
Intermode transfer 84Ч93
KR 127
Lambert Ч Salter plot 63Ч72 81Ч82 102 104 107 110 127
Landau Ч Teller plot 8 53Ч58 61Ч62 75 105 108
Landau Ч Teller theory 7Ч8
Laser 29Ч30 33Ч35 114
Lensing, thermal 34 91
Mach number 23
Maser action 129
Mason Ч Monchick theory 42
Matrix element 26 46 50
Mechanism, parallel 94
Mechanism, rotational excitation 128Ч129
Mechanism, series 85
Mechanism, vibrational excitation 110Ч114
Method A and B fittings 44
Mixtures 72Ч80 93Ч114 124Ч128
Modified wave-number approximation (MWN) 43 117
Molecular beams 39Ч41
ne 74 78 112
Nikitin theory 59Ч60 77
NO 12 47 59Ч60 101Ч103 109 111 121Ч122 124Ч127
o 77Ч79
Optic-acoustic effect 32Ч33
Polanyi Ч Woodall relation 81Ч82 127
Polar molecules (collisions) 10Ч12
Population inversion 111 114 129
Potentials, attractive 49Ч50
Potentials, intermolecular 1Ч2 10Ч12
Potentials, Krieger 91
Potentials, Lennard-Jones 1Ч2
Potentials, LEPS 79
Potentials, Monchick Ч Mason 91
Potentials, Morse 49 117
Potentials, Shin 50
Potentials, SSH 43
Potentials, Stockmayer 10Ч12
Q-switching 29
Quadrupole interaction 12 50 77 106 109
Radiation 26Ч38
Radiative transition in rotational de-excitatior 129
Raman excitation 33Ч35
Rate constant 9
Reduced mass 5 73
Relaxation constant 18
Relaxation time, adiabatic 14Ч15
Relaxation time, composite 72
Relaxation time, isothermal 14
Relaxation time, reciprocal 93
Relaxation time, rotational 9Ч10 118
Relaxation time, true 16
Relaxation time, vibrational 8Ч9 13
Relaxation, multiple 18 89Ч100 118 125
Relaxation, single 84Ч89
Resonance, double 31
Resonant transfer rotational 42 128
Resonant transfer vibrational 83Ч85 95Ч99
Reverberation method 22
Rotation-rotation transfer (R-R) 42 128
Rotation-translation transfer (R-T) 115Ч129
Rotational constant (A,B,C) 71 121Ч126
Rough-sphere model 116
Schlieren technique 26
Shock front 22Ч23
Shock-tube 22Ч26
Spectrophone 32Ч33
SSH theory 43Ч52 83Ч84
Steric factors 45
Tanczos equation 45Ч49 83Ч84
Trajectory computations 81 116Ч117 125Ч126
Trajectory, collisional 3Ч4
Transition dipole 101Ч110
Transition probability, rotational 117 127
Transition probability, vibrational 44Ч49 83Ч84
Transition, multi-quantum, rotational 110 127
Transition, multi-quantum, vibrational 47 53 100
Translation factor 48Ч49
Transport properties 41Ч42
Treanor distribution 113
Tube effects 19
Unimolecular chemical kinetics 112
Vibration-rotation transfer (V-R) and (V-(T,R)) 50Ч52 69Ч72
Vibration-rotation transfer (V-R) and Shin classical theory 51
Vibration-translation transfer (V-T) 41Ч82
Vibration-vibration transfer (V-V) 83Ч114
Vibrational amplitude coefficient 46Ч47 68 88
Vibrational factor 46 88
Vibronic transition 59Ч60
Virial coefficient, second 12 17
viscosity 5 17 41Ч42
Viscothermal absorption 17Ч18
Viscothermal dispersion 14
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте