|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bernstein R.B. Ч Atom-Molecule Collision Theory: Guide for the Experimentalist |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Distribution, speed 9
Distribution, theoretical 705
Distribution, translational 706 735
Distribution, velocities 10 15
Distribution, vibrational 724
Distribution, vibrational state 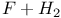 reaction 487 499 reaction 487 499
Distribution, vibrational state 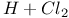 reaction 494 reaction 494
Distribution, vibrational state  reaction 489 reaction 489
Doubling,  -type 432 -type 432
Drude model 204 205
Dynamics, chemical reaction 27
Dynamics, molecular 2
Dynamics, statistical 8
Eccentricity effects 207
Ehrenfest relation 506
Ehrenfest theorem applied to 403 404
Ehrenfest theorem, application to forced harmonic oscillator 403 404
Electron jumps 608 609 616 620
Electronegativity 601
Energy release, attractive 628 633
Energy release, induced 633
Energy release, mixed 629Ч632
Energy release, repulsive 616 617 619 620 629Ч633
Energy, activation 538 539
Energy, collision 2 5
Energy, dissociation 7
Energy, epithermal 5 28
Energy, internal 8 9 29 31
Energy, resonance 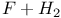 reaction 590 reaction 590
Energy, resonance 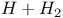 reaction 589 590 reaction 589 590
Energy, thermal 5 28
Energy, threshold, for 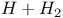 and and 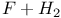 reactions 588 reactions 588
Energy, transfer, rotational 699 700 730
Energy, translational 8Ч10 14 28 29
entropy 701 703
Entropy, deficiency 32 33 695 696 703 705 710 712 713 725 744
Entropy, maximal 698 703 704 715 744 745
Equations of motion for A + BC scattering 362
Equations, close-coupled 243
Equations, integral 249
Equations, integration of 365
Equations, rigid rotor constraint 363
Equations, Runge Ч Kutta Ч Gill, Adams Ч Moulton algorithms 365
Excitation 10 12
Excitation, electronic 5 24 427Ч465
Excitation, internal 26
Excitation, rotational 5
Excitation, vibrational 5
Experiment 1Ч3 6 8 10 14
Exponential gap 728
Extrema, glory 18 19
F + HF potential surface 64 65
Factorization 260 261 320 321 323Ч326 333 334 336 343 347 348
Factorization, dynamical coefficients 260 261
Failings of, for rotational excitation 361
Filon quadrature 383 384
Flux map, 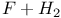 reaction 591 reaction 591
Form factors, reactive scattering 486 487
Franck-Condon overlap models (see УOverlapФ)
Functions, vibrational basis 576
Gauss Ч Mehler quadrature 515
Gaussian quadrature 383
Gear integrator 517
Glory 19
Glory part of integral cross section, FOS Ч PCI 227 228 231 232
Glory part of integral cross section, IOS Ч PCI 226 227 231 232
Glory part of integral cross section, IOS Ч SAIP 227 231 232
Glory part of integral cross section, S Ч SF 228Ч232
Glory undulations 226Ч230
Gordon integration technique 584
Gordon method 277 284Ч287 291 389
Gordon method, asymptotic boundary conditions 286
Gordon method, step size 286 287 294
H + BrH potential surface 71
H + ClH potential surface 70 71
H + HF potential surface 60 62Ч63
Hamiltonian, body-fixed 428 431
Hamiltonian, electronic 429 431 433
Hamiltonian, operator, reactive collisions 574
Hamiltonian, vibrational 574 576
Hamming integrator 517
Hankel functions 280
harmonic oscillator 406 414Ч416
Helicity representation 491
Histogram methods 358 396 399 403
HundТs cases 428
Independent electron pair approximation (IEPA) 53
Induction terms of intermolecular potential 204
Inelastic collision 259
Inelastic collision, electronic excitation 261
Inelastic collision, rotation-vibrational excitation 261
Inelastic collision, rotational excitation 260 261
Inelastic collision, vibrational excitation 261
Inelastic cross section, dwa 211 212
Inelastic cross section, sudden approximation 217Ч220
Infinite-order sudden approximation 379 382 384
Infinite-order sudden approximation with vibration present 382 385
Infinite-order sudden approximation, S matrix 383 384
Information content 31 34 695
Information theory 7 8 32 34 372 540 541 604 614 695
Informative observables (see УConstraintsФ)
Initial conditions (see УTrajectory initial
Integral cross section 213
Integral cross section with state-selected molecules 201 209
Integral cross section, arbitrary long-range dependence 225 226
Integral cross section, arbitrary quantization axis 209 210
Integral cross section, dwa 212Ч214
Integral cross section, influence of multipole terms 223Ч225
Integral cross section, sudden approximation 220Ч230
Interaction potential 270Ч272 277 289 295 390 398 415Ч417
Interaction potential for A + BC scattering 362
Interaction potential for an atom-linear^nolecule system 272
Interaction potential for an atom-molecule system 271
Interaction potential, approximation of 284
Interaction potential, asymptotic region 282
Interaction potential, long-range 282 284 385Ч387
Interaction potential, long-range behavior, importance of 410 416Ч418
Interaction, strong-coupling region 674Ч678 680 688 689
Interference, quantum 15 16
Interference, semiclassical 453 458 460
Interference, structure, averaging 392 (see also УOscillations rainbowФ УOscillations StueckelbergФ)
Intermolecular potential, atom-diatom 203 207 224 225
Intermolecular potential, azimuthal angle dependence 202 207
Intermolecular potential, cylindrical symmetry 202 203
Intermolecular potential, dispersion terms 204Ч207
Intermolecular potential, general anisotropic terms 202 203 211Ч213
Intermolecular potential, induction terms 204
Intermolecular potential, long-range 203Ч207
Intermolecular potential, mass eccentricity 207
Intermolecular potential, multipole terms 203 204
Intermolecular potential, open electron shell 208
Intermolecular potential, tetrahedral symmetry 206
Intersection of potential curves 427 429
Intersection of potential surfaces 427 445 458 459
Invariant-imbedding technique 277 280 288Ч297
Invariant-imbedding technique, boundary conditions for the two-part potential problem 290
Invariant-imbedding technique, connection formula 289
Invariant-imbedding technique, stability 291 294
inversion 179 181
Ionization, collisional 11 12 24
ITFITS model 409
Kinematic coupling 478 481 496 497 577 582
Kinetics 2
l-labeling 308 312Ч314 316 320 346 347
l-labeling,  314Ч316 314Ч316
l-labeling,  314Ч316 314Ч316
l-labeling,  320 320
l-labeling,  320 320
l-labeling, final l-labeling 312 313 316 346 347
l-labeling, initial l-labeling 308 313 316 317
| Landau Ч Zener matrix element 30 31
Landau Ч Zener theory 24
Laser 3 29 35
Legendre polynomials 547 548 550
Levinson theorem 151 174
Li + HF potential surface 72
Lifetime of quasibound molecule 670 678 679
Light and Walker, method of (see УR matrix methodФ)
Light, method of 277 287 294 389 390
Limit, adiabatic 427 435
Line shape 326
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equations 483
Log-derivative method 277 280 288 291 295Ч297 389
Log-derivative method, propagation of 297
Log-derivative method, radial equations 297
London-Eyring-Polanyi-Sato (LEPS), surface 60Ч63
Magnetic transitions 304 305 310Ч314 316 320 323Ч325 332 336 344Ч347
Magnetic transitions, definite polarization 323 325 336
Magnetic transitions, intermultiplet transitions 344
Magnetic transitions, projection on incident momentum 320
Magnetic transitions, quantization axis 304 305 311 312 314 320 332 336 347
Magnus expansion 287 294
Masses, reduced 510
Matrix, fragment 83 86 88 90 93 95 104
Matrix, Hamiltonian 83 84 86 88 93 94
Matrix, Landau Ч Zener 45 3 455
Matrix, non Ч Hermitian 89 98
Matrix, overlap 83 85 89
Matrix, overlap in reactive scattering 583 584
Matrix, rotation 84 85 90 91 93
Mechanism 6
Method, approximation 4 5 32
Method, classical 31
Method, classical path 559 605 607
Method, decent and indecent 403Ч407 414 416Ч418
Method, PRDDO 601
Method, quantal 6
Method, quasiclassical trajectory 6
Method, semiclassical approximation 6 32
Method, trajectory, accuracy of 506 507 516Ч518 541 595 621 633Ч636
Method, trajectory, bins 535 538 540 542 543 546 550
Method, trajectory, classical P matrix theory 540
Method, trajectory, classical S matrix theory 5 06 555Ч557 561 595 596 607 622 634 635
Method, trajectory, combined phase-space-trajectory theory 554
Method, trajectory, computer programs 515 516 551 552
Method, trajectory, decoupling approximations 607
Method, trajectory, end test 518
Method, trajectory, histogrammic representations 534Ч540 542Ч547 549-551
Method, trajectory, moment methods 540Ч542 547Ч551
Method, trajectory, product state distributions 530Ч535 539Ч551 627Ч635
Method, trajectory, quantized final conditions 507 508 532Ч534 539Ч542 549 552
Method, trajectory, quasiclassical (meaning) 508
Method, trajectory, quasiclassical final conditions 595 596
Method, trajectory, quasiclassical initial conditions 507 508 511Ч515 518Ч520 528 535 552 595 596
Method, trajectory, reverse histogram method 552 553
Method, trajectory, sampling (see УSamplingФ)
Method, trajectory, surface-hopping 55 9Ч5 61 605Ч607
Method, trajectory, symmetrically averaged conditions 553Ч555
Method, trajectory, unquantized conditions 553 554
Method, trajectory, Wigner distribution 557 558
Microscopic reversibility 247 649
Migration 620 623
Model, BEBO 615
Model, classical 682Ч688
Model, DIPR 616Ч621 624 625 628
Model, dynamical 7 34
Model, FOTO 615 621
Model, hard-sphere 608 609 613 683 684
Model, harpoon 31 608
Model, Langevin 609
Model, one-dimensional (or collinear) for diatomic molecule by atom 656
Model, optical potential 612
Model, overlap, reactive collisions 492Ч500
Model, phase space 689
Model, sequential impulse 612
Model, spectator-stripping 488 489
Model, square-well 684Ч688
Model, statistical 28 688 689
Model, theoretical 3
Model, two-body 683
Molecular beam 2
Molecular orbitals 601 602
Moment methods 396 403 540Ч542 547Ч551
Moment methods for rotational excitation 372
Momentum approximation 140 141
Monte Carlo method 395 402 403
Morse oscillator 406 409 413Ч415
Multipole terms of intermolecular potential 203 204
Network, vibronic 451Ч455 461
Neumann functions 280
Newton Ч Raphson method 514 515 524 533 534 546
Nonadiabatic transitions (see УTransition nonadiabaticФ)
Noncentral potentials, action integrals 207 208 229
Noncentral potentials, dispersion terms 204Ч207
Noncentral potentials, elastic cross sections 214Ч217
Noncentral potentials, general conclusions 230Ч232
Noncentral potentials, general terms 202 203
Noncentral potentials, induction terms 204
Noncentral potentials, multipole terms 203 204
Nordsieck integrator 516 517
Nozzle beams, supersonic 9
Numerical methods 259 260
Opacity function 611
Open channels 280 281 284 289 386
Optical theorem 146 177 322 326
Oscillations, diffraction 34
Oscillations, model 204Ч206
Oscillations, rainbow 449
Oscillations, Stueckelberg 447Ч449 454 semiclassicalФ)
Overlap, Franck Ч Condon 452 454
Partial averaging technique 402
persuasion 705 742
Perturbation, classical 407 408 411 412 418
Perturbation, spectroscopic 432
Perturbation, theory 410
Perturbed symmetric resonance (see УCouplingФ УDemkovФ)
Phase correction, nonadiabatic 443
Phase shift 117 118 146 147 154 156 162 163 166 167 168 171 176Ч178 183 184
Phase shift, general 210
Phase shift, semiclassical 215 216 224
Polarization functions 50
Polarization functions, effects of 59 64 65 67
Polyatomics 35
Polynomials, Hermite 373
Polynomials, Legendre 362
Potential 2 9 16 17 33 34
Potential at large intermolecular distances 114
Potential at small separations 115
Potential curve, adiabatic 437 443 446 451
Potential curve, diabatic 437 443 444 451
Potential energy of interaction, for collision-induced dissociation 657
Potential energy surfaces 413Ч418
Potential energy surfaces,  79Ч82 79Ч82
Potential energy surfaces, adiabatic 437 438 455 458
Potential energy surfaces, anisotropic 19
Potential energy surfaces, asymptotic region of 80
Potential energy surfaces, avoided crossing of 671Ч673 676
Potential energy surfaces, calculation of 79 81
Potential energy surfaces, derivatives of 81 82 105
Potential energy surfaces, diabatic 437
Potential energy surfaces, effect of several 672 673
Potential energy surfaces, LEPS 106
Potential energy surfaces, nonreactive 53
Potential energy surfaces, reactive 55
Potential energy surfaces, representation of 79Ч81
Potential energy surfaces, semi-empirical DIM 82Ч105
Potential energy surfaces, semi-empirical SCF Ч HF 81
Potential energy surfaces, semi-empirical valence-bond 82 106 107
Potential energy surfaces, sensitivity of vibrational excitation to 415 416
Potential energy surfaces, strong-coupling region of 80
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



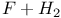 reaction
reaction 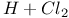 reaction
reaction  reaction
reaction  -type
-type 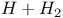 reaction
reaction 



