|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Berne B. — Statistical Mechanics. Part A: Equilibrium Techniques |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
 -expansion 1 31—34 7 -expansion 1 31—34 7
 -ordering 58—70 -ordering 58—70
 -ordering, lowest-order approximation 62 -ordering, lowest-order approximation 62
 -ordering, lowest-order approximation and the mean spherical approximation 62 -ordering, lowest-order approximation and the mean spherical approximation 62
 -ordering, relation to the mean spherical approximation 59 7 -ordering, relation to the mean spherical approximation 59 7
 -ordering, second-order approximation 62—64 -ordering, second-order approximation 62—64
 -ordering, second-order approximation in ionic and dipolar systems 64 72—73 -ordering, second-order approximation in ionic and dipolar systems 64 72—73
 -ordering, second-order approximation in orientation-independent systems 65— 67 73 -ordering, second-order approximation in orientation-independent systems 65— 67 73
 -ordering, thermodynamic properties from 67—69 -ordering, thermodynamic properties from 67—69
 -parameterization 48 58 -parameterization 48 58
Activity 95—102 106—115
Activity, coefficient 92 93 104
And integral equations 126 127
Articulation circles 115
Articulation points 5
Bijl — Jastrow wave function 183
Black circles 106 107 109 111
Blip function theory 25—29
BOND 2
Bond function 6 8
Brownon model 88
Chain sum 60
Circles, articulation 115
Circles, black 106 107 109 111
Circles, cutting 124
Circles, white 106 107
Cluster (see Microcluster)
Cluster expansion 145 105—123
Cluster expansion for ionic systems 122 123
Cluster expansion, chemical potential 115 116
Cluster expansion, correlation functions 117 123
Cluster expansion, density 114
Cluster expansion, direct correlation function 124
Cluster expansion, grand partition function 107 112 113 117
Cluster expansion, Helmholtz free energy 115—117
Cluster expansion, Helmholtz free energy for ionic systems 118—122
Cluster expansion, Mayer resummation 118—123
Cluster functions 112 117 118
Compressibility, definition 51
Configuration integral 53 96 98
Correlation functions for BO system 96
Correlation functions for ionic systems 122 123
Correlation functions for MM system 99
Correlation functions, asymptotic behavior of 50—52 77—82
Correlation functions, cluster expansion 117 123
Correlation functions, integral equations 123—128
Correlation functions, limiting form 128
Correlation functions, pair 95 105
Correlation functions, quality tests 129—131
Cosphere 90
Cutting circles 124
Debye kappa 120
Debye — Hueckel linearized DH equation 127 128
Debye — Hueckel theory 1 16 24
Debye-Hueckel limiting law value for  121 121
DHLL + 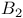 approximation 122 approximation 122
dielectric constant 88 90 118
Dipolar fluids, approximate radial distributions for 71—72
Dipolar fluids, Helmholtz free energy of  -ordering for 67—68 -ordering for 67—68
Dipolar fluids, Helmholtz free energy of Pade approximant for 55
Dipolar fluids, pair potential for 50
Dipolar fluids, saturation effects in 54
Direct correlation function 124—128
Direct correlation function in  ordering 58—62 ordering 58—62
Direct correlation function in the mean spherical approximation 57
Direct correlation function, asymptotic behavior of 50—51
Direct correlation function, cluster expansion 124
Direct correlation function, definition 50
Effective ionic forces 187
Entropy estimation 170ff
Ewald energy calculation 153 163
Exponential (EXP) approximation 1 37
Field points 2
Fluid, dipolar hard sphere 31
Fluid, hard sphere 26
Fluid, Lennard — Jones 31
Fluid, Polar 44
Fluid, square well 31
Fluids, dielectric properties 44
Fluids, equilibrium structure 1
Fluids, hydrogen-bonded 3843
Fluids, inhomogeneous 44
Fluids, perturbation theory of 29—31 38
Fluids, polar 44
Fluids, statistical mechanics of 145
Fluids, thermodynamics 145
Forces in ionic solutions 86—91
Forces, dynamical 87 88
Forces, solvent-averaged 87 88 101
Free energy (see Gibbs free energy Helmholtz
Free energy estimation 170ff 7
Gas-liquid interface 185
Generalized mean spherical approximation (GMSA) 128
Gibbs free energy 92 93 102—104
grand canonical ensemble 175ff
Grand partition function for BO system 96 98
Grand partition function, cluster expansion 107 112 113 117
Grand partition function, cluster expansion, thermodynamic limit 108 117
Graph 245
Graph theory 105—106
Graph theory, articulation circle 115
Graph theory, black circle 106 107 109 111
Graph theory, connectedness of graphs 117
Graph theory, cutting circle 124
Graph theory, for many components 107—110
Graph theory, protograph 121
Graph theory, q-bond node 121
Graph theory, root 114
Graph theory, white circle 106 107
Graph, connected 5
Graph, connectivity of 4
Graph, doubly connected 5
Graph, irreducible 5
Graph, labeled 3
Graph, path in 4
Graph, symmetry number of 4
Graph, value of 6 8—9
Graphical representation (see Cluster expansions)
Graphs, ALDC 115
Graphs, ALSC 113
Graphs, connectedness of 117
Graphs, simple 106
Graphs, symmetry number of 106 122
Hamiltonian model for ionic solution 86 87
Hamiltonian model, level of description BO level 86—88 91 95 96 100 101
Hamiltonian model, level of description BOSL level 87
Hamiltonian model, level of description MM level 87—91 95 100 101 105 127
Hamiltonian model, level of description S level 86 87
Helmholtz free energy 11 102—105
Helmholtz free energy,  -ordering for 67—69 -ordering for 67—69
Helmholtz free energy,  -expansion for 53 56 -expansion for 53 56
Helmholtz free energy, asymptotic behavior of 54
Helmholtz free energy, bounds on 53
Helmholtz free energy, duster expansion 115—117
Helmholtz free energy, duster expansion for ionic systems 118—122
Helmholtz free energy, limiting law result 121
Helmholtz free energy, Pade approximants for 55—56
Helmholtz free energy, Pade approximants for dipolar fluids 55
Helmholtz free energy, Pade approximants for multipolar fluids in general 56
Helmholtz free energy, Pade approximants for quadrupolar fluids 55
High-temperature approximation 30
Hydration, hydrophobic 90
Hydrogen bond 38
Hypemetted chain (HNC) approximation 125—129 131
Hypervertex 44
Importance sampling 139 140
Integral equations 123—129
Integral equations, and Mayer resummation 126 127
Integral equations, GMSA 128
Integral equations, HNC 125—129 131
| Integral equations, linearized DH 127
Integral equations, MSA 91 128
Integral equations, PY 126—128
Integral equations, quality tests 129—131
Interfaces, Monte Carlo study 185
Ionic fluids,  -expansion for 56 -expansion for 56
Ionic fluids, approximate radial distribution functions for 71—72
Ionic fluids, Helmholtz free energy of r-ordering for 67—68
Ionic fluids, internal energy of (see Restricted primitive model)
Ionic fluids, kappa 120
Ionic fluids, mixed perturbation theory for 70—71
Ionic fluids, pair potential for 50
Ionic fluids, potential of mean force 187
Ionic fluids, saturation effects in 54
Ionic solutions 1
Ionic strength 93 94 105
Ising model 146 149
Kirkwood superposition approximation 31
Markov chain, convergence rate of 145
Markov chain, quasi-ergodic problem in 144
Markov chain, transition matrix of 144
Mayer resummation 118—123
Mayer theory of ionic solutions 16 23—25
Mayer/function 8 11 12 112
McMillan — Mayer theory 23 95—105
McMillan — Mayer theory, limitations of 100 101
McMillan — Mayer theory, LR to MM conversions 102—105
McMillan — Mayer theory, models for ionic solutions 87
McMillan — Mayer theory, thermodynamic functions 104 105
Mean spherical approximation (msa) 57 91 128
Microcluster, drop model 210
Microcluster, drop model, criticisms of 215
Microcluster, drop model, modifications of 216—224
Microcluster, equilibrium concentration 209—211
Microcluster, free energy of 209—211 216—224
Microcluster, microscopic point of view 219—224
Microcluster, surface (free) energy of 211 217—219 221- 224
Mixed perturbation theory 68 70
Mixed perturbation theory in ionic solution theory 70—71
Mixing coefficients 94
Mode expansion 34
Molecular Dynamics 87 91 100 129
Moment of correlation functions, second 130 131
Moment of correlation functions, zeroth 130 131
Moment-cumulant relation 111 115
Monte Carlo, boundary conditions 150 186 188
Monte Carlo, energy calculations cutoff approximation 154
Monte Carlo, energy calculations discussion of 155ff
Monte Carlo, energy calculations, Ewald approximation 153
Monte Carlo, energy calculations, minimum image approximation 154
Monte Carlo, error estimation 147
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation 170ff
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation at phase transitions 173ff 181
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation by thermodynamic integration 172
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation, Cold well’s method 171
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation, grand canonical ensemble 175
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation, method 87 91 100 129
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation, multistage sampling 178
Monte Carlo, free energy estimation, umbrella sampling 178
Monte Carlo, microscopic studies 185ff
Monte Carlo, microscopic studies, gas-liquid interface 185
Monte Carlo, microscopic studies, ionic mean forces 187
Monte Carlo, quantum mechanics 182ff
Monte Carlo, quantum mechanics, solving Schroedinger’s equation 184
Monte Carlo, quantum mechanics, variational calculations 182
Monte Carlo, sampling problems 179 185 189 190
Monte Carlo, various ensembles 148
Nodal approximation 48 70 73
Nodal contraction 48 69 73
Nodal ordering 48 69 73
Nucleation, homogeneous 197 208—224
Nucleation, homogeneous, classical theory 211—215
Nucleation, homogeneous, critical supersaturation 212—214
Nucleation, homogeneous, microscopic approach 219—224
Nucleation, mathematical formalism 198—208
Nucleation, steady state rate 201—208
Nucleation, steady state rate, general theory 204—206
Nucleation, steady state rate, kinetic expression 203
Nucleation, steady state rate, Maxwell's demon 204—206
Nucleation, steady state rate, thermodynamic expression 203
Nucleation, steady state rate, Zeldovich factor 207
Nucleation, time dependence 200
Nucleation, water on ions 224—228
Omstein — Zernike equation 50 124 127 128
Optimized cluster theory 35—37
Osmotic coefficient 104 105 129 130
Pade approximant 21 31 38
Pair correlation function 1—45
Pair potential 49
Pair potential, dipolar fluids 50
Pair potential, ionic fluids 50
Pair potential, monatomic fluids 50
Partial structure factors 95
Partition function 9
Partitions 109 114
Percus—Yevick (PY) approximation 1 126— 128
Periodic boundary conditions 150
Perturbation theory of fluids 29—31 38
Point function 6 8
Points, articulation 5
Points, field 2
Points, overlapping pair of 39
Points, pair of articulation 5
Points, pair of reducible 5
Points, root 2
Polymer configuration 149
Potential for ionic solutions 86—91
Potential for ionic solutions, CAV 90
Potential for ionic solutions, COR 89
Potential for ionic solutions, GUR 90
Potential in BO system 96 99
Potential in MM system 98
Potential of average force 87 96 98 99
Potential, component 100 101 112
Potential, pairwise additivity of 100 101 107 117
Potential, primitive model 89
Potential, solvent average 87—91 99—101 117
Potential, temperature dependence of 98 100
Primitive model 89 91 128 130
Principle of unreasonable utility of asymptotic estimates 48 57
Probability density function 49
Quantum mechanics, Monte Carlo solutions 184
Quantum mechanics, variational calculations 182
Radial distribution function 49
Radial distribution function, approximations for ionic and dipolar systems 71—72
Random numbers 137 139 161
Reducible points 5
Renormalization 19 (see also Mayer resummation)
Residual 6
Restricted primitive model for ionic fluids 56
Restricted primitive model for ionic fluids, internal energy of 56
Restricted primitive model for ionic fluids, internal energy of  -expansion for 56 -expansion for 56
Restricted primitive model for ionic fluids, internal energy of empirical equation for 56
Restricted primitive model for ionic fluids, internal energy of Pade approximant for 56
Root point 2
Saturation effects at low temperatures 54
Scattering, from ionic solutions 95
Schroedinger’s equation, Monte Carlo solution 184
screening 20
shielding 20
Single occupancy 174
Solvation coefficients 91 92 101
Solvent-averaged forces 187
Surface free energy 211
Symmetry number 4
Thermodynamic excess functions 92—94
Thermodynamic excess functions, LR to MM conversions 102—105
Thermodynamic limit 108 117
Topological reduction 1 15—45
Umbrella sampling, I 78
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -expansion
-expansion  -ordering, lowest-order approximation
-ordering, lowest-order approximation 
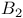 approximation
approximation  -expansion for
-expansion for