|
Ёлектронна€ библиотека ѕопечительского совета механико-математического факультета ћосковского государственного университета |
| √лавна€ Ex Libris ниги ∆урналы —татьи —ерии аталог Wanted «агрузка ’удЋит —правка ѕоиск по индексам ѕоиск |
© Ёлектронна€ библиотека попечительского совета мехмата ћ√”, 2004-2026 |
|
ќ проекте |
|
ќ проекте
|




 derivative of
derivative of 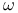 derivative of
derivative of 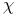 -route
-route