|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Adhikari S.K. Ч Variational Principles and the Numerical Solution of Scattering Problems |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Anomalous behavior 134Ч136 215Ч219
Anomalous behavior in complex Kohn method 219
Anomalous behavior in inverse Kohn method 134Ч136
Anomalous behavior in Kohn method 134Ч136
Anomalous behavior in Newton method 217
Anomalous behavior in Schwinger method 216Ч217
Asymptotic, behavior of GreenТs function 22 26
Asymptotic, behavior of Lippmann Ч Schwinger, equation 25Ч27
Asymptotic, behavior of spherical Bessel and, Neumann functions 15Ч16 26
Asymptotic, behavior of wave function 12 14 16Ч17 47 50
Asymptotic, boundary condition 11 14
Atom-diatom collision (reactive) 248Ч249 237Ч240 300Ч304
Atom-diatom collision (reactive), complex Kohn method 248Ч249 301 304
Atom-diatom collision (reactive), Newton method 237Ч240 300Ч304
Atomic unit 261
Basis functions,  5 5
Basis functions, Kohn method 115Ч116 138
Basis functions, Schwinger method 170Ч171
Born or Neumann (series) for bound state 92
Born or Neumann (series) for distorted wave 194
Born or Neumann (series) for scattering 69 80Ч84 160 256
Born or Neumann (series) for T matrix 79 83 213 269Ч271
Born or Neumann (series) for wave function 34
Born or Neumann (series), approximation 29Ч30 57 80
Bound-state, approximation 51
Bound-state, scattering approach, for 91Ч94
Channel 5Ч6
Channel, open 51
Close-coupling (CC) equations 9 43 49Ч54 63 85 225Ч226
Close-coupling (CC) equations for K matrix 56
Close-coupling (CC) equations for t matrix 53 227Ч229
Close-coupling (CC) equations for wave function 52
Close-coupling (CC) equations, electron-helium scattering 290
Close-coupling (CC) equations, electron-hydrogen scattering 284
Close-coupling (CC) equations, partial-wave 54Ч56
Close-coupling (CC) equations, positron-helium scattering 293
Close-coupling (CC) equations, positron-hydrogen scattering 286
Close-coupling (CC) equations, post 53Ч54
Close-coupling (CC) equations, prior 53Ч54
Collision 3 319
Contour deformation technique 68
Cross section, electron-helium scattering 291
Cross section, electron-hydrogen scattering 280
Cross section, multichannel 59Ч60
Cross section, partial-wave 18Ч20
Cross section, reaction 19
Cross section, total 20
Effective range 42
Electron-helium scattering 288Ч292
Electron-helium scattering, Bethe Ч Goldstone method 289
Electron-helium scattering, Born formula 291
Electron-helium scattering, close-coupling (CC) method 290
Harris method 282
Harris method, Born formula for phase shift 281
Harris method, close-coupling (CC) approach 281 284
Harris method, Electron-hydrogen scattering 280Ч285
Harris method, optimized anomaly-free method 289
Harris method, polarizability 290Ч291
Harris method, polarized-orbital method 289
Harris method, resonance 290Ч291
K matrix 36
K matrix, half-shell 77Ч78
K matrix, off-shell 159
K matrix, principal-value treatment 68 71Ч74 86
K matrix, unitarity 41
Kernel, compact 24 64
Kernel, Fredholm 24 43 50 63Ч69 76
Kernel, Hilbert Ч Schmidt 24 44
Kohn method 297
Kohn method for resonance 95Ч97
Kohn method, 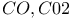 299Ч300 299Ч300
Kohn method, complex Kohn method 298
Kohn method, continuum orbitals 249Ч253
Kohn method, degenerate-kernel method 106 179
Kohn method, Electron volt 261
Kohn method, Electron-molecule scattering 297Ч300
Kohn method, Faddeev Ч Yakubovskii equation 9 40
Kohn method, Feshbach projection operator technique, Kohn method 190
Kohn method, Fock coupling scheme 50
Kohn method, Fredholm 7 62Ч69 76 79
Kohn method, GreenТs function, incoming-wave 22Ч23
Kohn method, Hartree Ч Fock, wave function 249Ч250
Kohn method, Huck model 272
Kohn method, hydrogen  297Ч298 297Ч298
Kohn method, i?-matrix method 297Ч299
Kohn method, Integral equation 7
Kohn method, Integration quadratures 66 72
Kohn method, Ionization 4
Kohn method, iterative Schwinger method 298 300
Kohn method, method of moments 103Ч104
Kohn method, multichannel 87Ч90
Kohn method, nitrogen  298 298
Kohn method, nonsingular 74Ч80
Kohn method, numerical results 280Ч285
Kohn method, outgoing-wave 22Ч23
Kohn method, phase shift 283
Kohn method, polarizability 281 283
Kohn method, polarized orbital method 282
Kohn method, principal-value 37Ч38 73
Kohn method, resonances 282Ч283
Kohn method, Schwinger (multichannel) method 297Ч300
Kohn method, Schwinger multichannel method 229Ч234
Kohn method, T matrix 8Ч9 74Ч80
Kohn method, variational principle 210Ч215
Kohn method, variational principles 101Ч107
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation 7 21
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation for K matrix 39 40
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation for t matrix 28 31
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation for wave function 23
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, (iterative) Born Ч Neumann series, solution 7Ч8 34 80
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, asymptotic behavior 25Ч27
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, multiparticle 43 49
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, nonuniqueness of solution 44 45
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation, numerical solution 65Ч74
Moller operator 12
Neumann series (see УBorn seriesФ)
Newton method 267Ч268 276Ч277 300Ч304
Newton method, nucleon-nucleon scattering 275Ч278
Newton method, optimized anomaly-free method 265Ч266 282Ч283
Newton method, optimized minimum-norm method 265Ч266 282Ч283
Newton method, positron-helium scattering 292Ч294
Newton method, positron-hydrogen scattering 285Ч288
Newton method, principal-value treatment 71Ч74
Newton method, Schwinger  method 265Ч266 method 265Ч266
Newton method, Schwinger (iterative) method 269Ч271
Newton method, Schwinger basis-set method 263Ч267 276Ч279
Newton method, separable expansion 69 276Ч279
Newton method, single-channel study 261Ч272
Newton method, variational (basis-set) method 69 263Ч269
Numerical solution of integral equation, atom-diatom (reactive) scattering 300Ч304
Numerical solution of integral equation, complex Kohn method 267Ч268 278 301 304
Numerical solution of integral equation, degenerate-kernel scheme 69
Numerical solution of integral equation, electron-atom scattering 294Ч295
Numerical solution of integral equation, electron-helium scattering 288Ч292
Numerical solution of integral equation, electron-hydrogen scattering 280Ч285
Numerical solution of integral equation, electron-molecule scattering 297Ч300
Numerical solution of integral equation, explicit matrix elements 258Ч261
Numerical solution of integral equation, four-nucleon scattering 278
Numerical solution of integral equation, inverse Kohn (minimum-norm) method 265Ч266 282Ч283
| Numerical solution of integral equation, Kohn (anomaly-free) method 265Ч266 282Ч283
Numerical solution of integral equation, Kohn (minimum-norm) method 265Ч266 282Ч283
Numerical solution of integral equation, Kohn (off-shell) method 263 265Ч267
Numerical solution of integral equation, Kohn (on-shell) method 263 281Ч283
Numerical solution of integral equation, molecular photoionization 296Ч297
Numerical solution of integral equation, multichannel model 272Ч275 284Ч285
Numerical solution of integral equation, neutron-deuteron scattering 278
Numerical solution of integral equation, T matrix (iterative) 269Ч271 278Ч279
Pade approximation 69 84 256 279
Partial-wave (expansion), Born phase shift formula 281 291
Partial-wave (expansion), GreenТs function 25
Partial-wave (expansion), K matrix 40
Partial-wave (expansion), multichannel 54Ч56
Partial-wave (expansion), scattering amplitude 18
Partial-wave (expansion), scattering cross section 18
Partial-wave (expansion), t matrix 32Ч35
Partial-wave (expansion), wave function 15Ч16 38
Partition 5Ч6
Photodisintegration of triatomic molecule 240Ч245
Photoionization 202 210
Photoionization, frozen-core Hartree Ч Fock method 252Ч253
Positron-helium scattering 292Ч294
Positron-helium scattering, close-coupling (CC) method 293
Positron-helium scattering, Kohn method 292
Positron-helium scattering, polarizability 292
Positron-helium scattering, resonance 294
Positron-hydrogen scattering 285Ч288
Positron-hydrogen scattering, close-coupling (CC) method 286
Positron-hydrogen scattering, complex-energy extrapolation 286
Positron-hydrogen scattering, Harris method 286Ч287
Positron-hydrogen scattering, Kohn method 285Ч287
Positron-hydrogen scattering, resonance 288
S matrix 18 31Ч32 192
S matrix, unitarity 32 57
Scattering, amplitude 14 18 27
Scattering, breakup 3
Scattering, complex potential 85Ч87
Scattering, cross section 15 18 27
Scattering, distorted wave 193Ч196
Scattering, eigenphase 57
Scattering, elastic 3
Scattering, electron-atom 255 294Ч295
Scattering, electron-helium 288Ч292
Scattering, electron-hydrogen 280Ч285
Scattering, few-particle 69Ч70
Scattering, four-nucleon 70 278
Scattering, GreenТs function 21Ч23
Scattering, helium atom 288Ч294
Scattering, hydrogen atom 279Ч288
Scattering, inelastic 4
Scattering, length 42
Scattering, multichannel 7 42Ч60 272Ч275 284Ч285
Scattering, nonsingular equation 74Ч80
Scattering, nucleon-nucleon 255 276Ч278
Scattering, off-shell 65 159
Scattering, on-shell 65 159
Scattering, phase shift 16Ч17 34 41
Scattering, positron-hydrogen 285Ч288
Scattering, potential 3
Scattering, reactive (rearrangement) 3Ч4 237Ч240 300Ч304
Scattering, threshold 4
Scattering, time-independent description 10Ч13
Scattering, wave-function description 13Ч27
Scattering, wave-packet description 11
Schwinger method 285Ч287
Schwinger method, Potential, exponential 261 265 267 269Ч271
Schwinger method, Reaction cross section 19
Schwinger method, Resonance 36 77 91Ч96
Schwinger method, Rydberg 261
Schwinger method, Yukawa 261 263 269Ч271
Separable expansion 257 277Ч278
Separable expansion, analytic 175
Separable expansion, Bateman 174Ч175
Separable expansion, energy-dependent 175Ч176
Separable expansion, Ernst Ч Shakin Ч Thaler 175
Separable expansion, Hilbert Ч Schmidt 173Ч174
Separable expansion, unitary pole 172Ч173
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions 15Ч16
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions, half-shell 77Ч78 159
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions, hermitian analyticity 30
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions, post 52Ч54
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions, prior 52Ч54
Spherical Bessel and Neumann functions, t (transition) matrix 18 27
Two-potential formula 196
Unitarity cut 30 35
Variational principle (method), anomalous behavior 215Ч219
Variational principle (method), anomaly 109 134Ч136
Variational principle (method), anomaly-free 136Ч137
Variational principle (method), anomaly-free Kohn 219Ч222
Variational principle (method), basis-set 108 115Ч134
Variational principle (method), complex Kohn (rearrangement) 248Ч249
Variational principle (method), complex Kohn (t matrix) 161Ч162 186Ч192 267Ч268 276Ч278
Variational principle (method), complex Kohn multichannel 245Ч249 301 304
Variational principle (method), distorted wave 193Ч198
Variational principle (method), fractional 160 162 164 165 178
Variational principle (method), general matrix element 201Ч210
Variational principle (method), GreenТs function 188Ч189
Variational principle (method), Harris 109 128Ч132 282 286Ч287 289
Variational principle (method), higher-order 183Ч186
Variational principle (method), Hulthen 108 112 114 123Ч124 130Ч132
Variational principle (method), insertion technique 199Ч201
Variational principle (method), integral equation 101Ч107
Variational principle (method), inverse Kohn 108Ч109 113 121Ч122 124 130Ч132
Variational principle (method), iterative scheme 180Ч182
Variational principle (method), Kato identity 113
Variational principle (method), Kohn 107Ч122 124 130Ч132 263 281Ч283 285Ч287 292
Variational principle (method), Kohn (anomaly-free) 136Ч137 265Ч266 273Ч275
Variational principle (method), Kohn (K matrix) 106 161Ч162 186Ч187 263 265Ч268
Variational principle (method), least squares 154Ч157
Variational principle (method), minimum-norm inverse Kohn 132Ч134 265Ч266 282Ч283
Variational principle (method), minimum-norm Kohn 132Ч134 265Ч266 273Ч275 282Ч283
Variational principle (method), multichannel i?-matrix 145Ч147
Variational principle (method), multichannel inverse Kohn 143Ч145
Variational principle (method), multichannel Kohn 137Ч143 273Ч275
Variational principle (method), Newton 106 160 176Ч180 257 267Ч268 276Ч278
Variational principle (method), Newton (distorted wave) 197Ч198
Variational principle (method), Newton basis-set 178Ч180
Variational principle (method), Newton, iterative 180Ч182
Variational principle (method), Newton, multichannel inelastic 234Ч237
Variational principle (method), Newton, multichannel reactive 237Ч240 300Ч304
Variational principle (method), Newton, photodisintegration of, triatomic molecule 240Ч245
Variational principle (method), Newton, with insertion 200Ч201
Variational principle (method), off-shell 8 159Ч162
Variational principle (method), on-shell 8 99
Variational principle (method), optimized anomaly-free 148Ч150 152Ч154 265Ч266 282Ч283 289
Variational principle (method), optimized minimum-norm 148Ч152 265Ч266 282Ч283
Variational principle (method), R matrix 109 124Ч128 145Ч147 193 290
Variational principle (method), Rayleigh Ч Ritz 107 109Ч111 128Ч129
Variational principle (method), Rubinow (see УInverse KohnФ)
Variational principle (method), Schwinger 103 160 162Ч176 257 262Ч267 276Ч278 285Ч287
Variational principle (method), Schwinger (distorted wave) 197
Variational principle (method), Schwinger (K matrix) 162 164 262Ч267
Variational principle (method), Schwinger, iterative 180Ч182 207Ч208 269Ч271
Variational principle (method), Schwinger, multichannel 227Ч234 273Ч275 284Ч285
Variational principle (method), Schwinger, with insertion 199Ч201
Variational principle (method), T matrix 161 210Ч215
Variational principle (method), trilinear 160
Virtual states 36 96Ч97
Wave function, incoming-wave 23
Wave function, outgoing-wave 23
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте