|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Clarke L.J. Ч Surface crystallography: an introduction to low energy electron diffraction |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
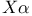 potential 124 126 potential 124 126
 exchange see exchange see 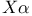 potential potential
 -plot see Wulff construction -plot see Wulff construction
Angle-resolved Auger emission spectroscopy (ARAES) 287Ч289
Angle-resolved ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (ARUPS) 91 287Ч289
Angle-resolved X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (ARXPS) 287Ч289
Angular distribution of ions produced by electron stimulation (ESDIAD) 300Ч302
Angular-momentum representation 148
Anisotropic thermal vibrations 198Ч201
Asymptotic cluster model see cluster model
Atom scattering 146 297Ч300
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) 3 4 43 75 97 108 110 155 283
Band structure 154 156
Beam area 13 96 115
Bloch-wave method 156
Bootstrap acceleration method 167Ч168
Born approximation 116
Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation 184
Bound state 139Ч140 142
Bragg energies (peaks) 182 186Ч188 193 194Ч196 214 224Ч225 258
Bragg Ч Williams model 236Ч237
Bravais lattice see lattice
CAVLEED 146 151 158 170Ч171 181 246Ч247
Centred overlayer structures 51Ч53
Chain method 169Ч170 285
Change 181 246Ч247
Channel-plate electron multiplier (channeltron) 94
Charge density waves 234
Cleavage plane 45 47 49
Cluster model 177Ч179
Coherence length 5 99Ч100 204 218
Coincidence structures see incommensurate overlayers
Combined space method (CSM) 31 168Ч171 174 176 181 186 246Ч247
Correlation (in thermal vibrations) 178 206Ч208
Correlation (within disordered surfaces) 180
Coulomb interaction 116Ч119 123 286
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns 311Ч312
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, body-centred cubic (bcc) 33 35
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, CsCl 46 48
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, diamond 33 43
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, face-centred cubic (fee) 33 39 41
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, hexagonal close-packed (hep) 33 43
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, NaCl 45Ч48
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, simple cubic (sc) 33 35
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, wurzite 48Ч49
Crystal structures and diffraction patterns, zinc-blende 48
Current image diffraction (OLD) 303Ч304
Cylindrical mirror analyser (CMA) see energy analysers
Darwin term 128
Data averaging (reduction) 1 90 209 239Ч243 286
Debye temperature 185 190Ч199 201 204Ч205 247 266 275
Debye Ч Waller factor 182 184 188 190 193 201 205Ч206 236 277 300 311Ч312
defects 90 182 215Ч218 226
Deviation (d-) factor 248 261
Diffraction beam labelling 62Ч64
Diffractometers 91
Diffractometers, flat, transmissive screen 93. see also MEMLEED
Diffractometers, hemispherical, transmissive screen 82 91Ч93
Diffractometers, high-resolution 97
Diffractometers, magnetic deflection 93.
Diffractometers, standard 74Ч75
Dirac equation 127
Discrepancy factor see deviation factor
Disordered surfaces 47 180 237Ч239 292
domains 13Ч14 90 99Ч100 204 230Ч234 283
Double-diffraction 24 233 see
Dynamical methods 157 209
Electron energy 2
electron guns 73 79Ч84
Electron stimulated desorption (ESD) 90 93Ч94 286
Electron wavelength 2
Energy analysers, cylindrical mirror (CMA) 4 283
Energy analysers, cylindrical sector 292
Energy analysers, hemispherical 292
Energy analysers, retarding field (RFA) 4
Energy selection 75
Energy-loss processes 98 100 144
Epitaxial growth 4 22 286 296
Equivalent beam averaging 244Ч247 254
Evanescent beams 151
Ewald construction (sphere) 8Ч9 218 220 223 226Ч221 230
Exact methods 156 162 164 168 247
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) 178 287 289Ч291
Fano effect 114
Faraday cup 94 103 107 114 221 301
Fermi energy (level) 2 124Ч125 143Ч144 155
Field-ion microscopy (FIM) 302Ч303
Fourier transform (analysis) 100 115 222 289
Grid (in electron gun) 155
Grids (optics system) 3Ч4 74Ч75 78Ч79 97
Grueneisen relation 188
Hall probe 101
Hartree Ч Fock method 117 123 125Ч127
Hausdorff distance 255
Helmholtz coils 102Ч103
High-energy electron diffraction 1 82 see
High-energy ion scattering (HEIS) 206 294Ч296
High-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy (HREELS) 98 204 291Ч292
I(g) method 172 225 243 248 258Ч265 267
Imaginary potential (absorptive) 252 262 see
Impurities 182 244
Incident beam angle, determination of 90 105Ч108 245
Incident beam angle, notation 62Ч64
Incommensurate overlayers 22 24 171Ч172 232
Inelastic damping 156 158 160 176Ч178 see
Inelastic low-energy electron diffraction (ILEED) 98
Infra-red spectroscopy (IR) 204 292Ч294
Inner potential 1 143Ч147 209 214 221 225 247 262Ч263 266Ч268 275
Instrument response function 99Ч100 222
Ion scattering methods (ISS) 45 205Ч206 303 see
Ion-core scattering 118 129Ч131 148Ч149 173 175 196 209 211Ч212 215 288
Irrationally-related lattices see incommensurate overlayers
Ising model 236Ч237
Islands 13 90 99 108Ч109 232
Iterative methods 161Ч170
k-space representation 149 153 164 169Ч170 174
Kinematical methods 157 159 172 180 182 187 192 196 198Ч199 209Ч215 216 239 242 258
Kohn Ч Sham Ч Gaspar (KSG) approximation 124 126
l-space representation 148 153 157 166 169Ч170 174
Labelling of diffraction beams 62Ч64
Lateral shifts (in surface atomic layer) 270Ч271 296
Lattices, Bravais lattices 64
Lattices, lattice points 5 6
Lattices, lattice rods 8
Lattices, lattice vectors 6 7 31
Lattices, real space lattice 7
Lattices, reciprocal lattice vectors 6
Lattices, reciprocal space 7
Laue condition 6 8 212 220
Laue condition, Laue nets 29 30
Laue condition, Laue patterns 33
Layer 157
Layer-doubling method 162Ч164 166 168 178 182
Layer-KKR method 156Ч157 162 164
Legendre functions 130
Levinson's theorem 136 140
Levy distance 255
Lindemann;s melting criterion 192
Low-energy ion scattering (LEIS) 206 294Ч296
Low-energy positron diffraction (LEPD) 283Ч285
Macroscopic surface plane 53Ч54 57 218 222
Magnetic field cancellation or shielding 101 see
Magnetic surface structures 48 112 173 283
Mean free path 73 101 155 179 209Ч210 283 290 see
Measurement of intensities 76
Measurement of intensities by computerized video camera 78 88 95
Measurement of intensities by Faraday cup 2 74 76Ч78 94
Measurement of intensities by photography 78 95 262
Measurement of intensities by spot photometer 76Ч78 95
Measurement of intensities of primary beam current 76
| Medium energy electron diffraction (MEED) 170 195 242 258 284Ч286
Medium energy ion scattering (MEIS) 206 289 294Ч296
MEMLEED 82 84 95Ч97 115
Micro-LEED, influence of high-energy source 84 see
Microfacet 59Ч62
Miller indices 33 41 54 56Ч62
Molecular adsorption techniques 90 174Ч179
Momentum representation 149 see
Mort detector 88 111Ч114
Mu metal 74 102
Muffin-tin approximation 117Ч122 129 247 see
Muffin-tin radius 142 170
Muffin-tin zero 118 132 143 145
MUFPOT 136
Nearly-free electron (NFE) materials 127
Neel temperature 112
Negative electron affinity (NEA) source 114Ч115
Notation, adsorbate structures 52
Notation, plane surface structures (Wood's notation) 50 53
Notation, stepped surface structures 57Ч62
Nth order interlayer scattering method (NIS) 161
Optical potential see inner potential
Order-disorder effects 204 216 234Ч239
Overall f-factor (R) 251Ч252
Overlayer coverages by LEED 108Ч110
Overlayer coverages by radioactive tracer methods 110 see
p-waves, d-waves and f-waves 142
Partial waves 132 149 156 288 see
Pauli principle 117
Peak width 100 145 237 252
Pendry r-factor 252Ч254 256 263 264Ч265 267
Penetration depth 2 155Ч156 158 193
Perturbation schemes 153 159Ч161 168 247 see
Phase shifts 131Ч143 160 169 210Ч211 216 218 284Ч285
Phase shifts, relationship with potentials 129
Phase shifts, relativistic 128Ч129 174 see
Phase transitions 43
Phonon scattering 183
Phonons 2 144 182 191 205 291
photoemission see angular-resolved photdemission
Photoionization 114
Plane 157
Plane-wave representation 149 see
Plasmon threshold 144Ч145 155Ч156 291
Plasmons 2 144 291
Poisson's equation 118
Polar surfaces (anionic, cationic species) 48Ч49
Positive electron affinity (PEA) sources 115
Potentials, exchange and correlation terms 112Ч127 173 267Ч268 283
Potentials, ion-core 117Ч118
Potentials, relativistic 127Ч129 173 see inner
Primitive unit cell see unit cell
Propagating beams 7 18 151 162 169
R-valves 248 258 262 265 268 275 277
Radioactive tracers (for coverage evaluation) 110
Ramsauer Ч Townsend effect 133
Reciprocal lattice, correspondence with diffraction pattern 8 10Ч11
Reciprocal lattice, matrix relationship 11Ч13
Reciprocal lattice, reciprocal space 50 159 see
Reconstructed surfaces 4 10 11 45 48 171 269Ч270 281 296
Reflection high-energy electron diffraction (RHEED) 170 286
Refraction 143 146Ч147 210 212
Registery 13 31 39
Registery shift 18 37
Relative beam intensities see I(g) method
Relativistic effects see spin-polarization
Reliability (of structural determinations) see reliability factors and reproducibility
Reliability factors (r-factors) 248Ч258 260 262Ч271 275
Reliability factors (r-factors), double reliability factor 254 see Pendry
Renormalized forward scattering (RFS) 161Ч162 164Ч166 167Ч168 172 182
Reproducibility 244
Resolution of a diffractometer 221 244 283
Resolution of a diffractometer, angular resolution 79 84 99Ч101
Resolution of a diffractometer, energy resolution 4 13 79 84 97Ч101 204 291
Resolution of crystal structures 175
Resolving power see resolution
Retarding field analyser (RFA) see energy analysers
Reverse scattering perturbation (RSP) 161Ч162 166Ч167 168 176
Riccati Ч Bessel function 142
Rotation diagrams 240 258
Rumpling 47 147 157 171
Rutherford backscattering (RBS) see high energy ion scattering
S-matrix 131
s-wave bound state see bound state
s-waves 133 139Ч141 156
Sample manipulation (by goniometer) 84Ч88
Sample preparation 84
Satellite beams 23 25 232
Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) 303
Scattering cross-section 133 139 179
Schroedinger equation 127 129 136
Screen (phosphorescent or fluorescent) 74Ч75 see
Secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) 300 302
Shadowing of screen 78 84 91
Slater approximation 124Ч125 127
Space-group symmetry see symmetry
Space-groups 66Ч68
Spherical Bassel differential equation 130 136
Spherical Bessel function 137Ч138 142 149
Spherical Hankel function 130 136
Spherical Neumann function 137Ч138
Spherical waves 148 .
Spin-polarized LEED (SPLEED) 88 110Ч115 173Ч174 283
Spin-polarized LEED (SPLEED), double-diffraction 112Ч114
Spin-polarized LEED (SPLEED), r-matrices 133Ч136 see
Spin-polarized LEED (SPLEED), spin interactions 127 173
Spin-polarized LEED (SPLEED), spin-orbit coupling 128
Spot photometer see measurement of intensities
sputtering 294
Stars see symmetry
Step structures 34 45 53Ч62 182 209 218Ч230 283
Step structures, cleavage plane steps 45
Step structures, facets 54Ч57 218 283 286 302
Step structures, notation 57 59Ч62
Step structures, vicinal surfaces 34 57Ч59
Structural symmetry 17 26Ч33 244Ч247 see
Subplane 157 159
Surface defects see defects
Surface free energy 55 189 229
Surface potential barrier 91 145Ч147 210 213 258
Surface resonances 91 97Ч98
Surface thermal expansion 187Ч188
Symmetry, beam stars 26 28Ч29 181
Symmetry, glide-reflection symmetry 64 68Ч72 286
Symmetry, line symmetry 64
Symmetry, mirror-reflection symmetry 64
Symmetry, point symmetry 64
Symmetry, rotational symmetry 24 49 65
Synchrotron 288 290Ч291
Systematic beam absences 51Ч52 68Ч72 234
t-matrices 129 132Ч135 158 160 173 180 182 196Ч197 199 212
T-matrix method (Beeby's) 156Ч158 180
Telephotometer see spot photometer
Thermal diffuse scattering (TDS) 190 197 253
Thermal vibrations 1 79 144 149 172 177Ч178 182Ч208 212 235Ч236 283
Transfer width 99Ч100
Two-atom per unit cell model 170
Underlayers 4
Unit cell 6 33
Unit cell, primitive unit cell 6 50
Unit cell, van der Waals forces 297
Variable phase approach 142
Vicinal surfaces see step structures
Wave vectors 7
Wehnalt 80
Werizel Ч Kramers Ч Brillouin (WKB) approximation 126
Wigner Ч Seitz cell 118 120
Wood's notation 50Ч53
work function 143 263 311Ч312 see
Wulff construction 55Ч56
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



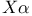 potential
potential  exchange
exchange  -plot
-plot