|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Barone A., Paterno G. Ч Physics and aplication of the josephson effect |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Cos 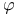 " term 39 47Ч49 153 " term 39 47Ч49 153
a.c. Josephson effect 12 291Ч318
A.C. Josephson effect, inverse 353
Adiabatic approximation 137 139
Analog, long junction, mechanical 265Ч268 272Ч275 286Ч287
Analog, small junction, mechanical 123Ч126
Array structures 234 316 318
Array structures, microwave radiation in 316
Array structures, mixing and 330
Baecklund transformation 270
Bolometers 324
Bridge structures see also "Dayem bridges"
Bridge structures of constant thickness (C.T.B.) 177Ч179
Bridge structures, fabrication of 228Ч232
Bridge structures, Ginzburg Landau theory of 181Ч185
Bridge structures, proximity effect 23 180
Bridge structures, R.S.J. model in 181 187
Bridge structures, variable thickness (V.T.B.) 23 177Ч181
Coherence length for degenerate semiconductor layer 172
Coherence length for superconductor-normal metal interface 162
Computer elements 446Ч473
Computer elements, power dissipation for 471Ч472
Computer elements, power dissipation for, logic circuits 465Ч469
Computer elements, power dissipation for, memory cells 461Ч465
Coupling of Josephson junction to microstripline 315 349 352 353
Coupling of Josephson junction to resonant cavity 312
Critical fields for large junction 106 108 109
Cryotron tunneling, current steering for 455 457
Cryotron tunneling, flip-flop configuration 451Ч453
Cryotron, thin film 446Ч449
Cryotron, tunneling junction 449Ч451
Current density and vector potential 2
Current distribution in large junctions of one-dimensional geometry 96Ч112
Current distribution in large junctions, effects of geometrical configurations in 112Ч120
Current phase relation for bridge structures 182Ч185 191
Current phase relation, piecewise linear 114
Current phase relation, sinusoidal 11 19 69
Current steps, microwave induced, current source model for 305Ч309
Current steps, microwave induced, fluctuations effects on 293Ч294 350
Current steps, microwave induced, voltage source model for 291Ч293
Current steps, microwave induced, voltage standard and 347
Current steps, self-induced see "Self-resonant modes"
Cyclability, junctions thermal 199Ч205 225
Cyclability, point contact 232
Dayem bridges 23 178 228 229 see
Detection of electromagnetic radiation 318Ч330 see
Double-junction configuration see "Interferometer"
Electrodynamics of Josephson junction 19Ч22 235Ч290
electron-beam lithography 178 216Ч217
Energy functions for long junction 269Ч271
Energy gap 4 40 41
Energy gap, current biased junction and 136 138 140
Energy gap, enhancement of 194 307
Energy gap, paramagnetic impurities effects 60 63
Energy gap, single particle tunneling and 8
Energy gap, strong coupling effects on 57
Energy gap, sub-harmonic structures 186 191
Fabrication technology 198Ч234
Fluctuations, structural 91Ч95 225Ч226
Fluctuations, thermal 143Ч158
Flux flow in bridge structures 189Ч191
Flux flow in long junctions 264Ч271 273Ч288
Flux flow in metal barrier junctions 287 288
Flux flow, effects on voltage current characteristics 285Ч288
Flux quantum 17 71 108 110 354 366 400 420 462
Flux shuttle 465
Fluxoid 355
Fluxoid, quantization of 354Ч359 361 369
Fluxon dynamics 264Ч290 see
Fluxon dynamics, losses and bias effects on 274Ч278 287 288
Fluxon dynamics, perturbative analysis of 279Ч285
Free energy for junction barrier 18Ч19
Free energy for junction barrier, flux line and 108Ч109
Galvanometer 435
Gauge invariance 2Ч3 14Ч15
Gauge invariance, and broken symmetry 32
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 1 167 169 181Ч183 185
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, time-dependent 192
Green functions 30 162
Green functions, Fourier transform of 31
Ground plane effects 112 113 118
Inductance, equivalent, for Josephson junction 22 331 384 458
Interferometer 369Ч382
Interferometer of asymmetric two-junction configuration 375Ч382
Interferometer, as magnetometers 403Ч408
Interferometer, as memory cells 461Ч463
Interferometer, as switching devices 459Ч460
Interferometer, critical current for 18 371Ч372 376Ч382 406
Interferometer, fluxoid quantization in 369
Interferometer, magnetic field patterns for 17 378Ч382 406 460
Interferometer, metastable states in 373Ч375
Interferometer, practical configurations for 421Ч424 467
Interferometer, self-resonant steps in 466 467
Inverse scattering transform method 271
Jacobian elliptic functions 101 102 103 267 269 272 273
Josephson current density in magnetic field 14Ч17 70Ч72
Josephson current density, self field effects 102Ч103 106 107
Josephson current with paramagnetic impurities 59Ч65
Josephson current, enhancement of 187 194Ч195 307
Josephson current, magnetic field dependence of, for nonuniform current density distribution 79Ч95
Josephson current, magnetic field dependence of, for uniform current density distribution 74Ч79
Josephson current, magnetic field dependence of, in large junctions 96Ч120 175 177
Josephson current, magnetic field dependence of, in small junctions 69Ч95
Josephson current, measurement techniques of 66Ч68
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, and paramagnetic impurities 62Ч64
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, B.C.S. approximation 50Ч56
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, in bridge structures 183Ч185
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, in light-sensitive junctions 175Ч176
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, in proximity effect structures 164 167Ч168
Josephson current, temperature dependence of, strong coupling effects for 56Ч58
Josephson effect, constitutive relations of 11 15
Josephson effect, discovery of 1
Josephson effect, gapless superconductivity and 62
Josephson effect, microscopic theory of 25Ч39
Josephson effect, phenomenological theory of 9Ч14 181Ч182
Josephson junctions, characteristic impedance for electromagnetic radiation 309Ч310
Josephson junctions, different geometrical configurations of 112Ч120
Josephson junctions, long, electrodynamics of 264Ч290
Josephson junctions, mechanical analog see "Analog"
Josephson junctions, mixing in 324Ч330
Josephson penetration depth 20 69Ч70
Josephson penetration depth, temperature dependence of 99
Josephson radiation, detection of 13Ч14 318Ч330
Josephson radiation, emission of 309Ч318
Josephson radiation, emitted, harmonics in 313
Josephson radiation, linewidth of 313Ч315 317
Junction electrodes see "Superconductors"
Kramers Ч Kronig relations 34 37 47
Lift-off technique 214Ч216
Light-sensitive junctions, optical response of 173Ч174
Light-sensitive junctions, preparation of 224Ч225
Light-sensitive junctions, temperature dependence of 175Ч176
Logic functions 284 465Ч470 see
London penetration depth 15 16 20
London penetration depth, measure of 76
London penetration depth, temperature dependence of 99
London penetration depth, typical values of 200
Magnetic susceptibility measurements 437Ч439
Magnetocardiogram 439Ч441 443
Magnetoencephalogram 441 444 445
Magnetometers in feedback configuration 424Ч426
Magnetometers, applications of 434Ч445
Magnetometers, coupling to superconducting transformer 428
Magnetometers, d.c.-biased 403Ч408
Magnetometers, noise in 409Ч415
Magnetometers, r.f.-biased 398Ч403
Magnetometers, sensor configurations for 416Ч424
Magnetotellurics 445
Manley Ч Rowe relations 331 332
Memory cells 461Ч465
| Memory cells, flip-flop circuit as 461 469
Memory cells, flux quantization and 462 465
Memory cells, single flux quantum 462Ч465 469Ч470
Metal barrier junctions 161Ч169
Mixers, Josephson junction as 324Ч330
Mixing between harmonics 329Ч330
Noise power spectrum 158Ч160 413
Nonequilibrium superconductivity 191 193Ч195 307
Oxide tunneling barrier, d.c. glow discharge for 207Ч209 219Ч220
Oxide tunneling barrier, r.f. glow discharge for 210Ч211
Oxide tunneling barrier, thermal oxidation for 206Ч207 219Ч220
Pair current density see "Josephson current density"
Pair current, microscopic expression for 38Ч39
Pair density 9 36
Pair density with paramagnetic impurities 59 60 62
Pair density, and strong coupling 57
Pair density, B.C.S. approximation of 39 40 41
Pair tunneling, energy momentum diagram for 12
Parametric amplification 330Ч344
Parametric amplifiers, doubly degenerate 333Ч340
Parametric amplifiers, externally pumped 332Ч343
Parametric amplifiers, internally pumped 343Ч344
Parametric amplifiers, singly degenerate 340 342Ч343
Parametric inductance, Josephson junction 22 331 384 458
Parametric quantron 463Ч464
Penetration depth, Josephson 20 69Ч70 99
Penetration depth, London 15 16 20 76 99 200
Penetration depth, magnetic 16 69 235 238
Phase plane analysis 128Ч131 282 283
Phase slip process 191 193
photolithography 178 212Ч216
Physical constants determination of 345
Plasma frequency 21Ч22 48 123 336 340 342
Plasma frequency, parametric excitation of 340
Point contact devices 24 196Ч197
Point contact devices, fabrication of 232Ч234
Point contact devices, phenomenological theory for 181Ч182
Power dissipation in Josephson devices 465 469 470Ч473
Preparation procedure see "Fabrication technology"
proximity effect 23 141 161Ч169 175
Proximity-effect bridges, fabrication of 231
Quantum interference 18 369Ч382
Quantum interference devices see "Interferometers" "SQUID"
Quasiparticle current, microscopic expression of 37Ч38
Quasiparticle current, phenomenological expression of 7
Quasiparticle density 36
Quasiparticle density with paramagnetic impurities 59Ч61
Quasiparticle density, B.C.S. approximation of 40
Quasiparticle tunneling, energy momentum diagrams 4 6 8
Quasiparticle tunneling, microscopic theory of 25Ч47
Quasiparticle tunneling, phenomenological theory of 4Ч9
Quasiparticle tunneling, photon-assisted 298 310
Radiation detectors, narrow-band 324Ч330
Radiation detectors, wide-band 318Ч324
Resistive loop devices, d.c.-biased 429Ч431
Resistive loop devices, r.f.-biased 431Ч433
Resistively shunted junction model (R.S.J.) for bridges and point contacts 181Ч182
Resistively shunted junction model (R.S.J.), autonomous case 122Ч123 126Ч128 145
Resistively shunted junction model (R.S.J.), nonautonomous case 306
Resonant modes in tunneling junctions 235Ч263 350 see
Riedel peak 41 47
Riedel peak in current-biased junctions 138 139
Riedel peak, broadening of 49 303
Riedel peak, microwave-induced steps and 296Ч304
Self field in large junctions, approximate analysis of 96Ч100
Self field in large junctions, theoretical analysis of 100Ч112
Self-resonant modes for junction of infinite length 248Ч251
Self-resonant modes in bridge structures 188 191
Self-resonant modes in high Q junctions 256Ч263
Self-resonant modes in low Q junctions 238Ч248
Self-resonant modes in zero magnetic field see "Zero field step"
Self-resonant modes, non-uniform current density effects in 251Ч255
Semiconducting barrier junctions 169Ч177
Semiconducting barrier junctions, light-sensitive 172Ч177
Semiconductor barrier, fabrication of 222Ч228
Sine Gordon equation 264
Sine Gordon equation in two-dimensional junctions 288Ч290
Sine Gordon equation, solutions for finite boundary conditions of 271Ч274
Single-junction loop in applied magnetic field 362Ч364
Single-junction loop, as magnetometers 401
Single-junction loop, as memory elements 463Ч464
Single-junction loop, flux transitions in 364Ч369
Single-junction loop, fluxoid quantization in 359
Single-junction loop, free energy for 361
Single-junction loop, Gibbs free energy for 363 364
Single-junction loop, metastable states in 360Ч361
Single-junction loop, parametric inductance effect in 384Ч388
Single-junction loop, practical configurations for 416Ч421
Single-junction loop, r.f.-biased 383Ч403
Singularities current, microwave-induced see "Current steps"
Solder blob 24 421Ч422
Soliton solution of Sine Gordon equation 267 270 271
SQUID, d.c.-biased 403Ч408
SQUID, d.c.-biased, flux sensitivity of 408 415Ч416
SQUID, r.f.-biased 383Ч403
SQUID, r.f.-biased in dispersive mode 388Ч398
SQUID, r.f.-biased in dissipative mode 398Ч403
SQUID, r.f.-biased, flux sensitivity of 401 415Ч416
Subharmonic gap structure 186 191
SUPARAMP 333Ч340
Superconducting loop 354Ч382
Superconducting loop with single junction see "Single-junction loop"
Superconducting loop with two junctions see Interferometers"
Superconducting loop, fractional turn configuration for 418Ч419
Superconducting loop, Gibbs free energy for 355
Superconducting pairs, macroscopic wave function 2
Superconducting transformer 426Ч429
Superconductor-insulator-normal metalsuperconductor (S-I-N-S) structures 166Ч169
Superconductor-normal metal-superconductor (S-N-S) junctions 164Ч166
Superconductors, hard materials 204Ч205 220Ч221
Superconductors, soft metals 199Ч200 219
Superconductors, soft-metal alloys 200Ч204
Superconductors, typical parameters of 200
Switching devices, interferometer as 459Ч460
Switching time for junction gate 449Ч451 454Ч457
Switching time, external load effects on 456 457
Switching time, Josephson inductance effects on 458Ч459
Switching time, self-resonant modes and 457
Thermal fluctuations see "Fluctuations"
Thin films, superconducting see "Superconductors"
Thin-film patterning 211Ч218
Time reversal symmetry 27 59 65
Transmission line, Josephson junction as 235Ч238 264Ч290
Transmission line, wave velocity in 237
Transmission line, wavelength for electromagnetic radiation in 295
Tunneling current, microscopic expression of 21 28Ч34
Tunneling current, microscopic expression of, B.C.S. approximation 39Ч47
Tunneling current, microscopic expression of, for constant voltage 35
Tunneling junction in external microwave radiation 294Ч305
Tunneling junction with current bias 136Ч143
Tunneling junction with shunt resistance 135 153
Tunneling junction, capacitance 20 237
Tunneling junction, inductance 237
Tunneling junction, preparation of 198Ч211 218Ч222
Tunneling junction, quality factor Q for 245 350
Tunneling junction, switching time of 449Ч451 454 455 471 473
Tunneling junction, wave velocity in 20 237
Tunneling, Hamiltonian for 10 25Ч27
Voltage current characteristics 121Ч160
Voltage current characteristics for bridge structures 122 186Ч188
Voltage current characteristics for Josephson junction 13 134 285 286
Voltage current characteristics for light-sensitive junctions 173 174 224 225
Voltage current characteristics for metal barrier junctions 165 166
Voltage current characteristics in presence of thermal fluctuations 150Ч153
Voltage current characteristics of high-current density junctions 141
Voltage current characteristics, and R.S.J. model 127 131Ч135
Voltage current characteristics, measurement of 66Ч68
Voltage standard 344Ч352
Voltmeter 436
Vortex Motion see "Flux flow"
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



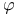 " term
" term