|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Anderson P.W. Ч The theory of superconductivity in the high-Tc curprates |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Korringa, J. 99 100
Kosterlitz Ч Thouless SC 42
Kosterlitz, M. 42
Kotliar, G. 177
Kramers Ч Kronig transform 27 38 64
Kubo formula (for conductivity), 158f 191
Kumar, N. 50 69 194Ч195
L.C.A.O. 14 15 207
L.C.A.O. down folding 15
Landau levels 198 428
Landau parameters, coefficients see УFermi liquidsФ
Landau, L. 26
Landauer theory and formula for conductivity 61Ч62 158 191
Landauer, R. 37 62 158 192
Langer, J. 167
Larkin identity 199 200
Larkin, A. 8 72 131.
Laughlin, R. 8 179 180 427
Lee, P. A. 5 18 39 158 179 190 193 431
Lee, R. H. 8 41 56
Lee, T. D. 167
Leggett, A. J. 424
Liang, S.-D. 3 7 399
Lieb Ч Wu solution (of 1D Hubbard) 38 131Ч136
Lieb.E. 131ff 176
Ligand complex-ligand field 15 see
Lin, H. 238
List, B. 7
Littlewood, P. B. 231 222 428
Local-density approx 23
localization 36Ч37 70 189 385Ч392 433
Localization, L. and interactions 267
London, F. 125
Loram, G. 112
Lower Hubbard band 90 147 178
Lu, Y. 8
Ludwig, A. 48
Luther, A. A. 48 103 138 141 158 176 185 427
Luttinger liquid 4 5 6 22 33 36Ч40 47Ч49 99 103 111 116 131Ч151 163Ч202 209Ч237 243Ч248 255Ч264 295Ч306 see
Luttinger's theorem 29 36 98 157 166 see
Luttinger, J. M. 26 33 73 171
Luttinger-Ward identities 48 192
Lye, Y 7
Magnetic scattering see УSpin scatteringФ УSpin
Magneto-polarons (Shraiman Ч Siggia) 97
Mahan, G. D. 131
Majorana fermion 4 53 131
Malozemoff, A. 7 70
Marginal Fermi liquid 40 116 173 427Ч430
Marston, B. 7
Martin, B. 63
Mattis, D. 176
Mehran, F 7
Mele, S. 8 427
Metzner, W. 8 177
Microwave conductivity (in supercond. state) 119 231Ч232
Migdal, A. A. 26
Mihaly, L 7 81
Mila, F 100 223
Millis, A. 8 81 82 159 192
Mitzi, D. 7 226
Mixed valence 22
Momentum conservation (of IL interaction) 51
Momentum distribution n(k) 132 139
Morel, P. 43 121 123
Mott limit 36Ч37 81 195
Mott limit, constant see УMott Ч Yoffe Ч RegelФ
Mott transition, Mott metal insulator T. 427
Mott Ч Hubbard gap 178 see
Mott Ч Hubbard insulator = Mott insulator 4 13 18 19 28 21 34ff 46Ч47
Mott Ч Hubbard interaction 21 218Ч219
Mott, N. F 13 18 19 21 22 28 37 61 42Ч47
Muller, A. A. 70
Multiple scattering 160 165
Nagaosa, Y. 5 39 190 193 431
Neel (ordered) antiferromagnetism 4 13 34 35 179 428
Neutron scattering 7 9 13 55 57 99 107 123 401Ч421 429
NMR 7 13 35 57 97Ч106 107 111 122 229 426 428 430 see
NMR, 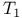 99ff 111 156 99ff 111 156
NMR, absence of Hebel Ч Slichter peak 119 229
NMR, at high T 424
NMR, Knight shift 100 111 113 428
Non-diffractive (forward) scattering 164
Non-Fermi liquid 5 43Ч49 98 132 163 265Ч290 427 433 see
Norman, M. 8
Nozieres, P. 26 151 433
Odd-gap solution 223
ODLRO (Strong Ч Talstra) 163 203 365Ч384
Ogata Ч Shiba wave function (Large U) 134 147 154
Ogata, M. 132 134. 161
Olson, C 6 7 90 93 226
One-band model ( antibonding) 33ff antibonding) 33ff
Ong., N.-P 5 7 55 63 64.66. 74 76 107 120 129 202 232 233 424 433Ч434
Optical spectroscopy 35 86
Orenstein, J. 81 82
Organic metals 6 22 206 267
Orthogonality catastrophe 48 131ff 173 279Ч90
Ott, H. R. 7
Ovshinsky, S. 423
Pair fluctuation as spin-gap mechanism 107
Pair susceptibility, (local) P.S. of ID Hubbard model 146 162
Pair susceptibility, P.S. of Lutt. LiqЧin I.L. Mech. 206 209Ч212
Pair tunneling see УJosephson effectФ
Pairing Hamiltonian, BCS-type 52Ч53
Pairing Hamiltonian, interlayer 51 126
Pauling, L 423
Peierls, R. 18
Penetration depth 223 232 239
Penetration depth, c-axis 41 43 125Ч128 208
Penetration depth, in-plane, T-dependence 122 232 239
Penney, T. 7
Peschel 1 138 158
Petroff, Y. 7 115 224 226
phase diagram see also УGeneralized P.D.Ф
Phase diagram, 2D Hubbard model 70
Phase shift 132ff 167ff 249Ч264 279Ч306
Phillips, J.C. 423
Phillips, N.E. 7
Phillips. P. 158
Phonon bumps 36
Phonon drag 192
Phonon-assited tunneling 70
Phonons, (as mech. for superconductivity) 118 424
photoemission 5 7 18 35 57 83Ч96 224Ч226
Photoemission, angle-averaged 95Ч96 115Ч116 224ff 427
Photoemission, angle-resolved (ARPES) 36 37Ч40 45 53Ч55 89Ч95 116Ч119
Photoemission, ARPES gap measurement 123 226
Photoemission, cusp structure 91 116
Photoemission, in 2D: incr. resolution 89
Photoemission, line shapes 187Ч188 226
Plasma frequency see УJosephson P.F.Ф
Plasma frequency, = interlayer 124Ч128
Plasma frequency, c-axis 41
Polaron 19 see
Polyacetylene 6 see
Polymers (conducting) 189 266
Pressure coefficient of Tc 42
Projective transformation 21 165 179 181Ч183 291Ч294
Projective transformation, P. constraints 182f
Pseudopotential see УScattering lengthФ
Pseudopotential, anomalous 175
Pseudopotential, Lee Ч Yang 167 170
Quantum Hall effect 205 428
Quasi 1D materials 189
Quasiparticles, conductivity (in SC state) 213 424
Quasiparticles, in superconductrng state 119Ч121 229
Quasiparticles, in superconductrng state, (explained) 212Ч214 226
Quasiparticles, mean free path 55 430Ч431
Quasiparticles, pair creation 55
Quasiparticles, peak (ARPES) 55 91 119 226 430
| Ramakrishnan, T.V. 384 399
Raman background (confirms IR) 38 84Ч85
Raman spectrum 5 20 36 45
Raman spectrum, "4-spinon" 84
Randeria, M. 8
Random-phase approximation (RPA) 185 99Ч100 427
Ranninger, C 427
Read. N. 18
Recoil (of scatterers) 165Ч169
Regel. A. R. 61
Ren. Y. 3 7 103 131Ч157
Renormalization 165 166 175f
Renormalization group 22 72 141 159
Renormalization, Dyson scheme 165 166
Residual interactions 206 215ff see
Resistivity, anisotropy of 36ff 189
Resistivity, c-axis 5 40 50 58 69Ч74 107 194Ч196 207f 345Ч352 359Ч364 430 434
Resistivity, experiments 34 57 58Ч69
Resistivity, in plane 34 37 112 155 189ff 353Ч358 385 392 434
Resistivity, residual 56 62Ч63 107
Resistivity, theories, of 5 158 434
Resonating valence bond = RVB 3 4 22 39 179Ч180 428 431
Resonating valence bond = RVB, (short-range, chiral) RVB 1814:48 01.02.20120
Rice, T. M. 3 8 13 21 38 100 138
Righi Ч LeDuc (thermal Hall effect) 107 120 434
Rokshar, D. 4. 8 40 180
Rowell, J. M. 7 58
Ruckenstein, A. 177
Rutter, L. 85
Saloman, M. 7 232 233
Sarker, S. 7 399
Sawatsky, G. 7 13 15 226
Scalapino, D. J. 202
Scattering length 167ff
Scattering matrix (T-matrix) 165 174
Schlesinger, Z. 7 33 81 82 83 203 228 234
Schluter, M. 13 23 35 63
Schrieffer, J. R. 37 61 192 194 428
Schulz, H. J. 131 158
Self-energy 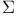 27 38 173 27 38 173
Self-trapping 19 see
Semicovalent bond 34
Semion 4
Sethna. J. 4. 40
Shankar, S. 8
Shastry, S. 3 7. 100. 131 136 200
Shen, X.-X. 7 56 118 226
Shiba.H. 132. 134 138 154
Short-range repulsion U see УMott Ч Hubbard interactionФ
Shraiman, B. 97 200
Siggia, E. 3 97
Siman, B. 7 234
Singular interaction 183Ч84 249Ч254 295Ч306
Singular interaction, commutes with B 198
Slave bosons 39 177Ч181
Slave bosons, S. Fermions 39 177Ч181
Slichter, C. P. 119 424
Smith, J. 7
Smith, N. V. 226
Solyom, J. 141
Sorella, S. 138
Specific heat 229
Specific heat, dependence on magnetic field 229
Specific heat, spin-gap effects on 112Ч113
Specific heat, T-dependence 122
Spicer, W. E. 7
Spin bags 428Ч430
Spin fluctuations 32
Spin fluctuations, as mech, for superconductivity 116 425 426 430 see
Spin fluctuations, ferromagnetic S.F. 425
Spin fluctuations, spin gap (chiral) 180
Spin gap (= "Fermi surface eaters") 43 46 49 52 56 82Ч4 99 103 107 111Ч115 203 238Ч239 393Ч400 401Ч410 431 433
Spin gap (= "Fermi surface eaters"), spin gap (RVB) 180
Spin susceptibility 20 100 107 111 180
Spin susceptibility, Curie Ч Weiss S.S. 99 426
Spin susceptibility, Pauli, SS 39 98 180
Spin velocity 39 143
Spin waves 36
Spin, impurities 45 66Ч68
Spin, scattering 75Ч76 189 234Ч235 429Ч430
Spin-charge separation see УCharge-spin separationФ
Spinon 4 5 39ff 48ff 177Ч181 433
Spinon, localized s. 67Ч68 433
Spinon, s. carries current 433
Spinon, s. drag 78
Spinon, s. pairing 365Ч384 401Ч410
Spinon, spinon-spinon scattering 75 151
Stafford, C 7 49 81 82 156. 159 192 201
Stamp, P. 3
Stechel. E. 13 23
Stripe phase 98 431
Strong, S. 7 49 50 52 56 72 85 107 111 114 187 203 232 237 433
SU(s) gauge symmetry 180Ч181
Sudbo, A. 7 111
Sum rules, (Kohn) 205Ч208
Sum rules, conductivity 42 44
Sum rules, Friedel 63
Sum rules, photoemission 45 115Ч118 224Ч225
Superconducting cuprates, (1)  4 13 19 20 37 43Ч44 46 63 70 97 99 107 124Ч128 194 196 231 237 239 4 13 19 20 37 43Ч44 46 63 70 97 99 107 124Ч128 194 196 231 237 239
Superconducting cuprates, (2)  4 13 19 30 39 47 52 63 69 70 74 83Ч85 92 97 99 103 122 128 196 203 208 228 229 231 239 4 13 19 30 39 47 52 63 69 70 74 83Ч85 92 97 99 103 122 128 196 203 208 228 229 231 239
Superconducting cuprates, (2a) Ni, Zn doped YBCO 76Ч77 236
Superconducting cuprates, (3)  18 30 47 52 95 239 18 30 47 52 95 239
Superconducting cuprates, (4)  30 33 37 42 52 196 227Ч229 231 239 30 33 37 42 52 196 227Ч229 231 239
Superconducting cuprates, (4)  (a) 1-layer n = 1 42 63 107 189 219 (a) 1-layer n = 1 42 63 107 189 219
Superconducting cuprates, (4)  (b) 2-layer n = 2 40 47 66 70 89Ч96 107 128 203 208 224 (b) 2-layer n = 2 40 47 66 70 89Ч96 107 128 203 208 224
Superconducting cuprates, (4)  (c) 3-layer n = 3 226Ч228 238 (c) 3-layer n = 3 226Ч228 238
Superconducting cuprates, (5)  42 52 196 227 238 42 52 196 227 238
Superconducting cuprates, (5)  1-layer 42 43 1-layer 42 43
Superconducting cuprates, (5)  2-layer 208 2-layer 208
Superconducting cuprates, (5)  3-layer 238 3-layer 238
Superconducting cuprates, (6)  (1, 2, 3-layer) 42 226Ч228 238 (1, 2, 3-layer) 42 226Ч228 238
Superconducting cuprates, (7)  56 56
Superconducting cuprates, (8)  47 238 47 238
Superexchange 13 20 50Ч51 70 182 393Ч410 425
Superexchange, due to interlayer hopping 238 401Ч410
susceptibility see УSpin S.Ф
Sutherland, W. 136 164
Symmetry orbitals 14 15
T-J model 21 22 23 38 100 147 177Ч180 181Ч183
Takagi, H. 7
Takigawa, M. 7 230
Talstra, Y 203
Tanner, B.H. 7 58 81 85 86
Teller, E. 423
thermal conductivity 76Ч80 129 201
Thermal conductivity, anisotropy of 76Ч80 213 230 233
Thermal conductivity, in superconducting state 119Ч120 232Ч233
Thermopower 77Ч80 201
Thermopower, anisotropy of 79
Thermopower, anomalous T 49 78
Thomas, G. 7 81
Thouless, D. J. 37 42 61
Timusk, T 7 40 58 124
Tomographic Luttinger liquid 5 48 163Ч202 210Ч237 243Ч248 249Ч254 255Ч264 295Ч306
Tomonaga (chiral) model 176
Tomonaga Ч Luttinger model 132 137 139 141ff
Transition temperature  (superconducting) 41 (superconducting) 41
Transition temperature  (superconducting), calculation of 208Ч212 (superconducting), calculation of 208Ч212
Transition temperature  (superconducting), effect of spin gap on 113 (superconducting), effect of spin gap on 113
Transition temperature  (superconducting), heuristics of 41 226Ч228 (superconducting), heuristics of 41 226Ч228
Transport theory 5 45 162 201
Transport theory, experiment 57
Trugman, S. 43
Ts'velik, A. 7 49 161 204
tt' tight binding band structure 47
Tunneling 81 96Ч98 213 230Ч231
Tunneling density of states 62
Tunneling spectroscopy 36 88
Tunneling, asymmetry 230 231
Tunneling, conductivity 96
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



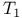
 antibonding)
antibonding) 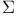




 (a) 1-layer n = 1
(a) 1-layer n = 1 
 1-layer
1-layer  (1, 2, 3-layer)
(1, 2, 3-layer) 

 (superconducting)
(superconducting)