|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Chandrasekhar S. Ч Liquid Crystals |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Fluctuations, director fluctuations in smectic C 367
Fluctuations, lattice fluctuations in the columnar phase 397Ч398
Fluctuations, layer fluctuations in smectic A 312Ч314
Fluctuations, Peierls-Landau instability 312Ч314 398
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the cholesteric-isotropic transition 289Ч293
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the nematic-isotropic transition 66Ч68
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the smectic A-cholesteric transition 349
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the smectic A-nematic transition 342
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the smectic C smectic A transition 371
Fluctuations, pretransitional fluctuations, near the smectic C-nematic transition 378
Frank constants see УUnder elastic constantsФ
Free energy of elastic deformation see УContinuum theoryФ
Free standing monodomain smectic films, studies on 360Ч364
Freedericksz effect in nematics, dynamical theory 161Ч167
Freedericksz effect in nematics, static theory 98Ч101
Freedericksz effect in smectic C 365
Freely suspended monodomain discotic strands, studies on 389Ч393
Ginsburg criterion 371
Ginsburg-Pitaevskii equation 373
Goldstone mode in ferroelectric (smectic C*) liquid crystals 382Ч384
Grandjean-Cano pattern 219 257Ч258 349
Hard particle theories, Andrew's method 37
Hard particle theories, Flory's lattice model 36
Hard particle theories, hard rods with semiflexible tails 37
Hard particle theories, Onsager's theory 31
Hard particle theories, scaled particle theory 36Ч37
Hard particle theories, stiffening of the tails as a mechanism for reentrance 357Ч358
Hard particle theories, summary of theories 37 411
Hard particle theories, Zwanzig's model 31Ч36
Helfrich deformation in cholesterics (square grid pattern) 281Ч289
Helfrich deformation in columnar liquid crystals 400
Helfrich deformation in smectic A 314Ч315
Helfrich walls 135
Helfrich's model of permeation 270Ч271 321
Helfrich's theory of electrohydrodynamic instabilities in nematics 181Ч187
Hexatic phases 6
Hexatic phases, normal and tilted types 301
Hexatic phases, X-ray studies of the degree of bond-orientational ordering 360Ч364
Homeotropic orientation 6 106
Homogeneous (or planar) orientation 6 104Ч105
Homogeneous (or planar) orientation, orienting effect of grooves 104Ч105
Hybrid models: hard rods with a superposed attractive potential 60Ч61
Hydrodynamics of liquid crystals general formulation by Martin, Parodi and Pershan 319 367Ч368
Hydrodynamics of nematics, cholesterics, smectics and discotics see УContinuum theoryФ УFlow
Induced discotic phases 12
Induced smectic phases 358
Isotherms 22Ч24 37 73
Landau-de Gennes model 613
Landau-Ginsburg free energy 342
Landau-Ginsburg parameter 358
Laser light beating spectroscopy 177 319 321 367
Lennard-Jones potential 21 22
Leslie coefficients 97Ч98 260
Lifshitz point 374Ч375
Light scattering, columnar liquid crystals 400
Light scattering, nematics, dependence on temperature 59Ч60
Light scattering, nematics, depolarization 171
Light scattering, nematics, determination of elastic constants 172 347
Light scattering, nematics, determination of viscosity coefficients 176
Light scattering, nematics, eigenmodes and power spectrum 172Ч177
Light scattering, nematics, intensity and angular dependence 170Ч172
Light scattering, nematics, orientational vs density fluctuations 171
Light scattering, nematics, scattering from the free surface 82Ч83
Light scattering, nematics, scattering from the isotropic phase 66Ч68
Light scattering, smectic A, contribution of the undulation modes 317Ч322
Light scattering, smectic A, determination of the damping rate 320Ч322
Light scattering, smectic C, angular dependence of the intensity and damping rate 366Ч367
Liquid crystal display devices see УApplicationsФ
Living systems 14
Lyotropic systems, aerosol-OT-water system 12
Lyotropic systems, plant virus preparations 8
Lyotropic systems, poly-y-benzyl-glutamate in organic solvents 13 113Ч114 217Ч218
Lyotropic systems, sufractant-water compositions, soaps 8 12
Lyotropic systems, types of molecular packing 12Ч14
Magnetic birefringence (Cotton-Mouton constant) 62Ч67
Magnetic coherence length 101 135 194 278 312
Magnetic field effects in cholesterics cholesteric-nematic (unwinding) transition 277Ч280
Magnetic field effects in cholesterics square grid pattern 281Ч6 see also УElectric field induced distortionsФ
Magnetoclinic effect 371Ч372
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics 38Ч51 70Ч71
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, applications, binary mixtures 51
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, applications, dependence of elastic constants on the order parameter 57Ч60
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, applications, dielectric anisotropy 51Ч56
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, applications, odd-even effect 47Ч51
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, extension of the theory to cholesterics 298
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, extension of the theory to discotics 394Ч397
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, extension of the theory to smectic A (McMillan's model) 302Ч309
Maier-Saupe theory of nematics, limitations of the theory 47Ч49 70Ч71
Mauguin-Oseen-de Vries model 237Ч241
MBBA, backflow effects 165
MBBA, disclination patterns 122
MBBA, electrohydrodynamic distortions 180 183Ч184
MBBA, flexoelectric coefficients 207Ч209
MBBA, flow birefringence 71
MBBA, heats of transition 26
MBBA, light scattering studies, in nematic phase 60
MBBA, light scattering studies, in the isotropic phase 67Ч68
MBBA, magnetic birefringence 64
MBBA, mixtures with cholesterics, dependence of pitch on composition 298
MBBA, molecular orientation at free surface 83
MBBA, oblique rolls in electrohydrodynamic patterns 211
MBBA, roll instability threshold 198
MBBA, thermal instability 202 205
MBBA, torque in a rotating magnetic field 148
MBBA, transverse pressure and secondary flow 158
MBBA, viscosity (or Leslie) coefficients 155
MBBA, volume change at transition 26
McMillan's model of smectic A 302Ч309
Melting of inert gas crystals, Lennard-Jones and Devonshire model 17Ч19
Melting of molecular crystals, Pople-Karasz model 19Ч27
Mesomorphic groups, Hermann's classification 8
Mesomorphism, thermotropic and lyotropic 1
Metallomesogens 389 414
Miesowicz's viscosity coefficients 144Ч145 155
Miscibility criterion 300
Molecular field 38
Molecular flexibility 37 41 48Ч52 see
Molecular statistical theories, cholesterics 298
Molecular statistical theories, discotics 394Ч397
Molecular statistical theories, nematics 17Ч61 71Ч80
Molecular statistical theories, smectic A 302Ч309
Molecular statistical theories, smectic C 364
Monotropic transition 14 16 379
Multicritical point, nematic-smectic A-smectic C (NAC) 374Ч378
Multicritical point, nematic-smectic A-smectic C (NAC), Chen-Lubensky model 375Ч378
Multicritical point, nematic-smectic A-smectic C (NAC), high resolution X-ray calorimetric and light scattering studies 378
Multicritical point, nematic-smectic A-smectic C (NAC), topology of phase diagram in the temperature-concentration and pressure-temperature planes 374 376
Near neighbour correlations, antiparallel (or antiferroelectric) correlation 75Ч78
Near neighbour correlations, Bethe approximation 71
Near neighbour correlations, correlation lacking a centre of inversion 289
Near neighbour correlations, Krieger-James approximation 72Ч73
Near neighbour correlations, short range order parameter 75
Nematic liquid crystals 1Ч3 8Ч10
Nematic-isotropic transition, Bethe approximation 71Ч80
Nematic-isotropic transition, effect of pressure 27Ч30 46Ч47
Nematic-isotropic transition, Landau-de Gennes model 61Ч63
Nematic-isotropic transition, latent heat 15Ч16 26 47
Nematic-isotropic transition, Maier-Saupe theory 38Ч48
Nematic-isotropic transition, molecular statistical theories 17Ч48
Nematic-isotropic transition, pressure-induced mesomorphism 28Ч30
Nematic-isotropic transition, short range order effects 61Ч70
Nematic-isotropic transition, volume change 26 45
Nematics as solvents 39 146
Nematics, dynamic effects 161Ч167
Nematics, effect on electrohydrodynamic, hydrodynamic and thermal instabilities 179 194 196 201 205
Nematics, rotating magnetic field 144Ч148
Nematics, static effects 98Ч104 106Ч109 152Ч155
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies 39 61 308Ч309 392
Odd-even effect 48 51
Onsager's reciprocal relations 69 94
| Onsager's theory of dielectric polarization 52
Onsager's theory of the hard rod fluid 31
Optical properties of cholesterics, absorbing systems 220Ч222 232Ч236
Optical properties of cholesterics, analogy with Darwin's dynamical theory of X-ray diffraction 222Ч232
Optical properties of cholesterics, Borrmann effect 232Ч236
Optical properties of cholesterics, equivalence of the continuum and dynamical theories 241Ч245
Optical properties of cholesterics, exact solution of the wave equation: the Mauguin Oseen-de Vries model 237Ч241
Optical properties of cholesterics, oblique incidence 245Ч247
Optical properties of cholesterics, propagation along the helical axis 213Ч245
Optical properties of cholesterics, propagation normal to the helical axis 247Ч248
Optical properties of cholesterics, rotatory power, reflectivity and circular dichroism as functions of wavelength, pitch and sample thickness 217Ч220 227Ч232 239Ч241
Optical textures, cholesterics, droplets with a 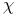 -line of strength 2 442 -line of strength 2 442
Optical textures, cholesterics, fingerprint texture 255Ч256
Optical textures, cholesterics, Grandjean-Cano pattern 258
Optical textures, cholesterics, helical configurations of disclination pairs 143 249Ч251
Optical textures, columnar liquid crystals, texture showing two orthogonal  disclinations 410 disclinations 410
Optical textures, nematics, disclination loops 127Ч128
Optical textures, nematics, schlieren textures (structures a noyaux) 6 30 117Ч120 365 412
Optical textures, nematics, singular points 129Ч132
Optical textures, nematics, threads 7Ч8
Optical textures, nematics, umbilics 136Ч138
Optical textures, smectic A, batonnets 30 333
Optical textures, smectic A, fan-shaped and polygonal textures 9 331
Optical textures, smectic A, focal conic textures 9 30 327Ч333
Optical textures, smectic A, stepped drop (goutte a gradins) 332
Optical textures, smectic A, toric domains 329
Optical textures, smectic C, edge dislocations 370
Optical textures, smectic C, toric domains 329
Order parameter, complex order parameter, smectic A 340
Order parameter, complex order parameter, smectic C 370
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, 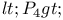 from polarized Raman studies 48Ч49 from polarized Raman studies 48Ч49
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, curves 40 45 75 77 303Ч305 308Ч309
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, definition 38Ч41
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, experimental determination of 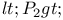 39Ч40 308Ч309 39Ч40 308Ч309
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, short range order parameter 74Ч75 77
Order parameter, orientational order parameter, variation near an interface 82 211
Order parameter, positional order parameter in melting theory 23Ч24
Order parameter, translational order parameter, amplitude of one-dimensional density wave (smectic A) 303Ч305 307 340
Order parameter, translational order parameter, density wave in two dimensions (columnar phase) 395
Orientation distribution function in MBBA derived from Raman studies 49
Oseen's equation of motion for the director 87
Oseen-Zoecker-Frank elasticity equations 94Ч97
p-azoxyanisole see УPAAФ
p-azoxyphenetole see УPAPФ
PAA, comparison of properties with hard rod and hybrid model calculations 37 60
PAA, dielectric constants 53
PAA, dielectric dispersion 56
PAA, dipole moment 55
PAA, electrohydrodynamic distortions 178
PAA, flow birefringence 69Ч71
PAA, heat of transition and volume change 26
PAA, Leslie coefficients 150
PAA, light scattering studies 59 66Ч68 83 172 176
PAA, lines of constant order parameter vs. ln V and ln T 46
PAA, magnetic and electric birefringence 62Ч65
PAA, Miesowicz coefficients 146
PAA, molar volume at the transition 44
PAA, molecular orientation at the free surface 83
PAA, molecular structure 15
PAA, orientational order parameter 27 40
PAA, P-T diagram and other pressure studies 28 46
PAA, PA A + cholesteryl nonanoate, Borrmann effect in 236
PAA, Poiseuille flow 150Ч153
PAA, surface tension 81
PAA, torque in a rotating magnetic field (Tsvetkov's experiment) 148
PAA, transitions 15
PAA, twist elastic constant 104 see also У4 4'-di-n-alkoxyazoxybenzenesФ
PAP, heat of transition and volume change 26
PAP, light scattering studies 59
PAP, Miesowicz coefficients 146
PAP, orientational order parameter 27
PAP, twist elastic constant 104 see also У4 4'-di-n-alkoxyazoxybenzenesФ
Parodi's relation 93 98
Penetration depth 314 322 342 398
Phase diagrams 28Ч29 291 295 306 353Ч356 376 397
Planar structure see УHomogeneous orientationФ
Plastic crystals 22
Poiseuille flow 148Ч152 157Ч159 268Ч269 270Ч273
Polymorphism in smectic A 350Ч352
Polymorphism in smectic C 364Ч365
Polymorphism in thermotropics 14Ч16
Pressure studies 27Ч29 46Ч47 297 356 372 374Ч376
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of cholesteric-isotropic transition: anomalous optical rotation in the isotropic phase 289Ч293
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of cholesteric-isotropic transition: coherence lengths 293
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: Bethe approximation 71Ч80
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: coherence length 68
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: flow birefringence 69Ч71
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: Landau-de Gennes model 61Ч63
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: light scattering studies 66Ч68
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of nematic-isotropic transition: magnetic and electric birefringence 63Ч66 see also УNear neighbour correlationsФ
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-cholesteric transition: analogy with the behaviour of a superconductor in a magnetic field 348Ч349
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-cholesteric transition: critical divergence of the pitch 349Ч350
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: critical divergence of twist and bend elastic constants 343
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: critical divergence of viscosity coefficients 345
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: critical exponents 347
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: high resolution X-ray, light scattering, specific heat and other studies 347
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: Landau-Ginsburg description 341Ч342
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic A-nematic transition: longitudinal and transverse coherence lengths 343
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C*-smectic A transition: critical variation of the frequencies, dielectric strengths and viscosities associated with the soft mode and Goldstone mode 384
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C*-smectic A transition: generalized Landau theory 386
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C*-smectic A transition: temperature dependence of tilt angle, polarization, pitch, electroclinic effect, dielectric constant 381Ч383
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C-nematic transition: Chen-Lubensky model 374Ч378
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C-nematic transition: critical divergence of the splay, twist and bend constants 378
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C-smectic A transition: Landau mean field description 370Ч372
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C-smectic A transition: transition induced by layer compression 372
Pretransition effects in the vicinity of smectic C-smectic A transition: variation of tilt angle, specific heat, magnetoclinic effect near the transition 370Ч372
Raman scattering studies, determination of the orientational order parameter 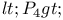 48Ч49 48Ч49
Reentrant phenomenon: in binary mixtures of polar compounds 355
Reentrant phenomenon: in discotics 394
Reentrant phenomenon: in non-polar materials 358
Reentrant phenomenon: in pure polar compounds at elevated pressures 356
Reentrant phenomenon: molecular models 357
Reentrant phenomenon: multiple reentrance 357
Rotational transitions in crystals 19
Second sound 324Ч326 402 404
Shear flow 69 152Ч157 195Ч201 274Ч277 383
Shear waves, reflexion of 159Ч161
Short-range order see УNear neighbour correlationsФ УPretransition
Smectic A 6 301 341
Smectic A* or the twist grain boundary phase: example of a compound which shows this phase 359
Smectic A* or the twist grain boundary phase: structure of smectic A* 359
Smectic A* or the twist grain boundary phase: X-ray and optical studies 359Ч360
Smectic A, absence of true long range translational order 321
Smectic A, high resolution X-ray scattering studies 313Ч314
Smectic A, polymorphic forms of smectic A and transitions between them 351Ч355 see УDefectsФ УOptical
Smectic A-nematic transition: complex order parameter 340
Smectic A-nematic transition: influence of twist and bend distortions on the transition 358Ч359
Smectic A-nematic transition: McMillan's molecular model 302Ч309
Smectic A-nematic transition: phenomenological theory 340Ч341
Smectic A-nematic transition: review of theoretical situation and its comparison with experiment 347
Smectic A-nematic transition: tricritical point 309 341
Smectic C*-smectic A transition, generalized Landau theory 386 see
Smectic C*: applications optical modulators 386Ч387
Smectic C*: applications surface stabilized ferroelectric LCDs 386Ч387
Smectic C*: applications tunable colour filters 386Ч387
Smectic C*: description of the structure and the origin of ferroelectricity 378Ч380
Smectic C*: director modes, the soft mode and the Goldston mode 382
Smectic C*: electric field effects 380
Smectic C*: electroclinic effect 380
Smectic C*: measurements of the tilt angle, spontaneous polarization, pitch, dielectric constant and dispersion 381Ч383
Smectic C*: optical properties 379
Smectic C*: rotational viscosity measurements 382Ч383
Smectic C-smectic A transition: complex order parameter and the helium analogy 370
Smectic C-smectic A transition: Landau mean field theory 370Ч371 see also УUnder pretransition effectsФ
Smectic C: molecular models 364
Smectic C: optical biaxiality 363
Smectic C: polymorphic forms in polar systems 365
Smectic C: structure and symmetry 362
Smectic C: temperature dependence of tilt angle 363
Smectic C: tilt and bond orientational order 363Ч364 see also УUnder continuum theoryФ УDefectsФ УTexturesФ
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -line of strength
-line of strength  disclinations
disclinations 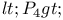 from polarized Raman studies
from polarized Raman studies