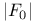|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Pepinsky R. (ed.), Robertson J.M. (ed.), Speakman J.C. (ed.) — Computing methods and the phase problem in X-ray crystal analysis |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
"Best" electron-density map 249
"Fly's eye," 18
"Fudge factor," 44 83 100 176
"Look-up," 132
"X-ray microscope," 16
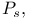 deconvolution of 280 deconvolution of 280
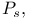 function 278 318 function 278 318
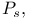 symmetry of 279 symmetry of 279
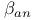 synthesis 283 synthesis 283
Abrahams, S.C. 300
Absent reflexions (accidental), allowance for 46
Absolute configuration 273 296
Absolute configuration, (EDSAC) 104
Absolute configuration, (MERCURY) 301
Absolute configuration, offerroelectrics 284
Absorption corrections 19 29 30 80 113
Agreement analysis 123
Agreement index, as criterion of trial structures 271
Ahmed, F.R. 300
Analogue computers 13
Anisotropic temperature factors 97
Anisotropic vibrations 37 38 39 120 123 192
Anomalous dispersion 159 264 318
Anomalous dispersion, corrections 82
Anomalous dispersion, from two independent atoms 291
Anomalous dispersion, method 273—299
Atlas see “MUSE”
Atomic form-factors 91
Atomic scattering factors 116
AUTOCODE 109 195 200 304
AUTOCODE, (ATLAS) 200
Automatic data collection 301
Availability of computers 154 300
Beevers — Lipson strips 15
Bendix computers 155 300
Bertaut, E.F. 307 312 313 314
Blow, D.M. 316 318
Bond angles 6 19 30 69 85 119 123 142 300 302
Bond lengths 5 6 30 69 85 U9 123 142 302
Brown, C.J. 311
Bull Gamma computer 9—11
Carlisle, C.H. 315
Cellobiose 127 302 306
Checking of computations 93
Cobalt aspartate 282
Cobalt complex ion, absolute configuration of 288
Cochran, W. 312 311 314
Contour output, in Fourier syntheses 76
Control Data Corporaition conrputers 155
Convergence of refinement 38
Convergence of refinement, condition for 267
Convolution 18 275
Coordinate generatioit 34
Correction of bond lengths for thermal vibrations 143
Cowley J.M. 310
Cruicsshank D.W.J. 10
Crystal energiesv 150
CumuiatiLs 204
Cumulant generating functions 203 206
Data processing 302
Data processing, (IBM709) 193
Delausay reductin 75
Deuce 87—101
DEUCE, af.Glasgow 301
Diagonal approximation in !e>isr squares 44
Dickerson, R.E. 307 317
Difference function 282 304
Difference Patterson function 253
Difference syntheses 97
Difference syntheses, (EDSAC) 104
Differential synthesis 34 37 104
Differential synthesis, (SWAC) 188
Differential synthesis, compared with least-squares refinement 39
Diffraction errors 303
DimeUioxybenzophejionc 216 314
Dipole-dipole energies 6 307
Direct methods, of phase determination 7 165 214—217
Direct methods, of sign determination 218 220—226
Disordered structures 306 315
Display of electron-density maps 103
Dornberger — Schiff, K. 303 307 315
Dunitz, J.D. 306 308
EDSAC II 102—106 218
Efficiency of least-squares refinement 310
Equality relations amongst reflexions with anomalous dispersion 293
Errors in structural parameters 141
Exponential functions, computation of 55
FAP 191
Feil, D. 306
Ferranti see “MERCURY” “PEGASUS”
Ferranti Mark 1 33—39
Ferroelectricity and absolute configuration 284
FERUT 34
Fluorescence accompanying anomalous dispersion 291
For structure factors 18
form factors 116
FORTRAN 191 220 304
Fourier summations, by phase-shifts 305
Fourier summations, by recurrence formula 304
Fourier syntheses 15
Fourier syntheses, (Bull Gamma) 10
Fourier syntheses, (DEUCE) 93
Fourier syntheses, (EDSAC) 104
Fourier syntheses, (IBM 650) 26
Fourier syntheses, (IBM 704) 129
Fourier syntheses, (IBM 709) 192
Fourier syntheses, (Mark I) 34 37
Fourier syntheses, (MERCURY) 113 121
Fourier syntheses, (PEGASUS) 56
Fourier syntheses, (RUFUS) 21
Fourier syntheses, (SWAC) 188
Fourier syntheses, (ZEBRA) 3
Fourier synthesis, automatic scanning of (MUSE) 199
Fourier synthesis, in general plane 301
Fourier transformation 7 18 1—19
Frieders law 274
Full matrix least-squares refinement 49 115 147 171 189
Full matrix refinement, compared with partial matrices 306 309
Gauss — Seidel iteration 99
Generalized projections 284
Glutathione 315
Gradient sharpening 126
Grant, D.F. 314
Groth Institute 158
Haemoglobin 236 260
Hagg — Laurent synthesiser 15
Hauptman, H. 304 313 314
Heavy-atom method 227—235
Hoppe — Pannke synthesiser 15
Hoppe, W. 305 315
Huggins masks 16
Human brain versus computer 308
Hydrogen atoms, location of 119 123
IBM 407 14 18 158
IBM 604 14 18
IBM 650 25—31 300
IBM 704 125—153 155 167 173 220 207
IBM 709 155 190—193
IBM 7090 155
Image, volume of in superposition 259
Image-seeking function 281
Image-seeking methods 125
IMP 109
Indexing, of oscillation photographs 80
Indexing, of reflexions with anomalous dispersion 293
Input 198
Intensities, processing of 76 80
Intensity data, accuracy needed to study anomalous dispersion 279
Intensity of image in superposition function 256
Interatomic distances 5 19 30 69 119 142 300 302
| Intermolecular contacts 6 71
Intervals in Fourier syntheses 94
Isomorphous replacement method 236—251 315 316
Isomorphous replacement method, conditions for application 259
Jeffrey, G.A. 300 307 314
Joint probability distribution 202 212
Kartha, G. 315 318 319
Katz, J.L. 300 304
Kerbstein, F.H. 300
Kjennard, O. 301
Ladell, J. 300 303
Laue symmetry, loss of due to anomalous dispersion 295
Least-squares refinement 170—187
Least-squares refinement, (DEUCE) 97
Least-squares refinement, (IBM 650) 27
Least-squares refinement, (IBM 704) 146
Least-squares refinement, (IBM 709) 192
Least-squares refinement, (MERCURY) 115 121 311
Least-squares refinement, (MUSE) 199
Least-squares refinement, (PEGASUS) 41 75 81 112 311
Least-squares refinement, (SWAC) 189
Least-squares refinement, (ZEBRA) 4
Least-squares refinement, acceleration devices in 176
Levy, H.A. 305 306
Lipscomb, W.N. 302 303 310 314
Location of heavy atoms for phase-angle determination 238
Lorentz-polarisation factor 9 19 29 80
Low-temperature data 303
Madelung sums 6 150 307
Matrix inversion 148
Matrix multiplication 10
Mean molecular plane 30 120 302
Mercury 107—124 182 194
MIFR 1 128 129—139 304
Milis, O.S. 304 311
Milledge, H.J. 303 306 308 310 313 318 319
Minimum function 128 192 302
Minimum function, application to proteins 252—265
Minimum function, for anomalous dispersion data 264
Molecular geometry 5 6 69 76 85 123 140 142 302
Molecular geometry, (IBM 650) 30
Molecular geometry, (MERCURY) 119
Molecular plane 30 120 302
Molecular plane, electron density in 37
Molecular vibration analysis 73 120 123 192
Moment generating functions 203 313
Moments 204
Monte Carlo method 161 266—272
Multiprogramming 197
MUSE 194—201
Myoglobin 236
Neutron diffraction with anomalous dispersion 295
Niggli, A. 308
Normal code 1
Normalized structure factors 203
Obsolescent computers 300
ODFAC 16
Olovsson, I. 308
Optical diffiractometer 18
Optimal shift method 161—169 270 307
Origin-peak, removal of 303
Orthogonal coordinates 5 85
Output 198
Parkinson's Law 19
Partial structure analysis 296
Patterns, recognition of 309
Patterson functions 313
Patterson methods 125
Patterson synthesis, with anomalous dispersion 275
Patterson — Tuneil strips 15
Pauling, P. 301
Peak positions 122
Pegasus 32—86
Pepinsky, R. 303 305 319
Peripheral equipment, for MUSE 198
Phase angle, computation 244
Phase angle, dependence on heavy atom 229
Phase angle, determination 237
Phase angles, uncertainty of and errors in Fourier synthesis 249
Phase problem 161—169 202 214 218 220 227—251 273—299
Phase-shifts in Fourier summations 305
Photoelectric analyzer 18
Photosummator 16
Pig 109
Point groups available for dissymmetric molecules 294
Point — Fourier synthesis 84
Potassium dihydrogen arsenate 285
Powder diagrams 6 120
Probability distributions 216
Processing of intensity data 113 120
Program sharing 196
Proteins 236
Quadratic equation method 289
Rational dependence between atomic coordinates 216
Rational independence of coordinates 314
Reduction, of intensity data 29 113 120
Reduction, of monoclinic and triclinic cells 75
Refinement, (EDSAC) 104
Refinement, by differential synthesis 37
Refinement, of heavy-atom position 242
Refinement, of heavy-atom positions and phase angles alternately 248
Rescue operations 109
Robertson strips 15
Robertson, J.M. 302
Rogers, D. 307
Rollett, J.S. 305 306 309
Rossmann, M.G. 300 303 318
Royal Precision McBee LGP 30 300
RUFUS 15 21—24
S-FAC 355
SAP 129
Sayre's equation 218—219
SCADAC 159
Scaling, of 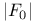 43 43
Scaling, of minimum function 128
Scaling, of normal equations 98
Scaling, of structure amplitudes 121
SCAT 191
Scattering factors 91 116
SHARE 192
Sharpening of Patterson functions 126 303
Shifts in least-squares refinement 44 83 100 176
Shoemaker, D.P. 300 304 317
Shrivastava, H.N. 303 312 317
Sign-relationships 218 221
Sign-relationships, applied three-dimensionally 314
Signs, elimination of terms with doubtful 84
Sim, G.A. 315
Simk, J.G. 301 302
Simple coo'e 1
Small-ic-iie computers 12—20
Sos 192
Sparks, P.A. 306 310 311
Speakmaw, J.C. 301 302
Special positions, refinement for atoms in 116
Spurme 216 314
standard deviations 192
Standard deviations, from least-squares refinement 47
Standard deviations, in structural parameters 141
Stereoscopic views of crystal structures (IBM 704) 305
storage of information 195
Stroboscopic pulsed method 286
Structure factors 17 28
Structure factors, (DEUCE) 89
Structure factors, (DEUCE), anisotropic 100
Structure factors, (EDSAC) 104
Structure factors, (IBM 709) 192
Structure factors, (Mark I) 34
Structure factors, (Mark I), anisotropic 38
Structure factors, (MERCURY) 122
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



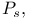 deconvolution of
deconvolution of 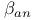 synthesis
synthesis