јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Leverenz H.W. Ч An introduction to luminescence of solids
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: An introduction to luminescence of solidsјвтор: Leverenz H.W. јннотаци€: This book is designed to provide an introductory and useful description of luminescent solids, particularly artificial (man-made) phosphors, in language comprehensible to science graduates. Much of the material is drawn from personal experience in synthesizing, studying, and applying luminescent solids since 1931, that is, during the recent era of intensive phosphor research which made possible such modern developments as electronic television, "fluorescent" lighting, radar, electron microscopy, and devices for seeing many otherwise invisible forme of energy. Although the book is intended for nonspecialists in luminescence, it is expected that it will be useful as a text in training future specialists and in aiding scientists who wish (a) to refresh and increase their knowledge of solid matter and its interactions with radiations and charged material particles, and (b) to use phosphors for detecting radiation and material particles.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 1950 оличество страниц: 569ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
"Acid" process 73 474Ч476 "Candoluminescence" 148 151 "Cold light" 139 "Dead voltage" 319 427 "Dead-voltage" layer 388 "Fluorescent" lamps 316 339 387 401 415Ч421 "Fluorescent" lamps, efficiency of 416 417 "Fluorescent" lamps, life of 418Ч421 "Fluorescent" lamps, luminance of 420 "Holes" in matter 32Ч34 37 41 94 "Noise" 153 "Radioluminescence" 148 150 "Thermoluminescence" 148 151 "White" colors 417 431 438Ч441 452 240 265 411 238 238 238 238 238 265 221 118 238 238 338 256 340 417 168 171 186 231 240 255 289 373 450 453 289 78 359 346 418 238 238 222 238 see "Exponential decay" 28 31 70 484Ч487 251Ч254 391 391 253 253 254 463 395 396 167 185 228 110 147 185 186 228 229 411 463 77 78 110 109 74 240 272 289 293 338 379 221 174 293 238 192 185 186 192 193 240 338 192 193 202 239 240 192 193 240 243 see "Power-law decay" 61 255 223 222 85 68 72 73 139 186 194 221 232 238 239 290 291 327 354 220Ч222 74 378 402 417Ч419 2-Naphthol 3-6 disulphonic acid, 410 Ab, E.A. 187 191 194 Absorption bands 119Ч123 128Ч135 Absorption bands, "tail" 122 128Ч135 Absorption bands, activator 121 122 128Ч135 141 Absorption bands, host-crystal 122 123 128Ч135 141 142 Absorption bands, induced 146Ч148 298 310Ч312 Absorption bands, long-wave edge of 120 128 Absorption bands, temperature variation 219 Absorption coefficient 154 160 Absorption edge 161Ч165 Absorption of primary energy 130 Absorption of radiation 78 90 Absorption spectra 161Ч170 341 Absorption spectra, temperature variation 161 164 Absorption, effect on efficiency 314 315 321 Absorption, selective 146Ч148 337 377 380 411 412 439 440 Accuracy of radiometric and photometric data 315 Acetone, 61 Acoustic modes 113Ч115 Acriflavine, 61 Activation energy 23 101 Activation energy, thermal 252 267 269Ч271 Activator 64Ч79 89Ч103 364 365 374 375 Activator action 239Ч241 Activator center 96 97 99-102 132Ч135 Activator concept 191 192 Activator proportions 64Ч68 77Ч79 330 358 359 375 Activator proportions, effect on efficiency 141 Activator proportions, optimum 336 337 Activator, anionic 100 Activator, cationic 89 Activator, formed by transmutation 78 Activator, induced 67 68 Activator, initial composition 89 Activator, molecular group 98 Activator, multiple functioning of 300 336Ч343 Activator, multivalent 77 100 Activator, radical 98 100 Activator, valence states of 338 Activators, cooperating 339Ч342 Activators, single 337 338 Activators, two or more 338Ч343 Additive colors 411 416 417 438 452 453 Afterglow 61 147Ч161 Al salt of 8-hydroxyquinoline 409 410 Alkali process 473 474 Alpha particle 11 Aluminized screens 75 350 354 357 423 433 438 444 448 451 461 471 Amplitude of nuclear vibration 29 38 Anion 13 89 91 Application of phosphors 381Ч389 415 416 Area contrast 447 Atmosphere during crystallization 48 62 64Ч68 71Ч74 90 200 201 214Ч217 223 228 235 236 276 338 411 476 Atomic configurations in centers 96Ч98 104 Atomic dislocations 50Ч54 Atomic models 3 484Ч487 Atomic nuclei 10Ч12 Atomic number 10 Atomic polarization 156 193 232 375 380 392 Atomic Radii 13 486 487 Atomic readjustment 132Ч134 Atomic vibration modes, acoustical 140 142 143 144 Atomic vibration modes, optical 143 144 Atomic vibrations, effect on spectra 109 110 Atomic vibrations, frequency of, in solids 101 Atomic weight 12 atoms 12Ч21 26 Atoms, densities of 13 Atoms, sizes of 13 15 Atoms, transition-group 111 Attempt frequency 177 269 270 Ausleuchtung 148 Auxiliary activator 274 Avogadro's number 13 Band emission 338 Band overlap 122 123 Band spectra 409Ч411 Band theory of solids 35Ч39 54Ч58 Band versus bond picture 38 39 119 120 BaO: 168 239 401 417 Bardeen, J. 115 Barnett, C.E. 409 Barrier layer 458 Base material 64 Benzene, 61 252 Bergmann, L. 129 Berton, A. 280 Bethe, H.A. 158 BI phosphor 308 Binders 387 388 Binding energy 486 Bioluminescence 148 172 Birefringence 155 160 Black body 137 138 Bleaching of tenebrescence 147 310Ч312 Blende 65 Boltzmann factor 33 Boltzmann's constant 31 142 Bond, covalent 24 51Ч53 484Ч487 Bond, determination of type 26 118 119 Bond, directed 27 28 Bond, electron-pair 24 51Ч53 Bond, heteropolar 22 51Ч53 Bond, homopolar 24 51Ч53 Bond, ionic 22 51Ч53 484Ч487 Bond, theory 22Ч28 38 39 Born, M. 93 Bose, H.N. 250 brackets [ ] 65 99 Bragg relation 113 Brauer, P. 139 Bremsstrahlung 156 158 Bright burn 388 448 449 Brightness see "Luminance" Bube, R.H. 177 263 266Ч268 Building atoms 12Ч20 Buildup 150 458 Butler, K.H. 227 Ca salt of 8-hydroxyquinoline 409 410 Carbonate process 69 73 Carry-over 447 458 Cascade luminescence 256 338Ч340 411 412 452Ч459 470 Cathode rays (electrons), heating by 82 83 219 311 451 452 460 Cathode rays (electrons), penetration of 90 Cathode rays (electrons), sources of 62 63 415 427 Cathode-ray tubes 427Ч462 Cathodoluminescence 148 464Ч466 Cathodoluminescence efficiency 317Ч320 322Ч334 349Ч361 367 378 383 384 400 420 427 428 430 439 447 464 Cathodoluminescence efficiency, maximum 359 367 Cathodoluminescence efficiency, reference standards for 195 Cathodoluminescence, versus current density 358 440 447 454 461 462 Cathodoluminescence, versus voltage 356 439Ч447 Cathodophosphorescence 147 255 261Ч269 280 290Ч292 Cation 13 89 91 CdO: 147 168 175 233 234 256 335 345 346 359 417 453 460 468 Center 67 99Ч102 131Ч135 Center, ionized 134 Center, sensitizer 341 Chalk, luminescent 412 413 Characteristic frequency 21 110 154 423 Chemical elements 12 16Ч20 Chemical elements, transition 20 Chemical equations 60 70 Chemical reactions 22Ч27 59 60 Chemical reactions, solid-state 48Ч50 60 64Ч75 Chemiluminescence 22 148 152 172 Chinolin 248 Close packing of spheres 40 41 Coating density 412 413 415 421 424Ч426 439 443Ч448 462 463 465Ч468 Cobalt, effect on crystal transition 84 Code numbers of CRT screens 428Ч431 Coehn's law 172 Collins, G.B. 250 Collisions of the first kind 30 Collisions of the second kind 130 247 colon (:) 64 76 Color television 452 453 466 Color, of activator compounds 99 Color, of copper sulphate 70 Complementarity 4 Conducting transparent coatings on glass 471 Conduction band 54Ч56 114 122 133 282Ч285 Conductor crystal 36 Configurational coordinate 103 131Ч135 144 Configurational-coordinate diagram 182 186 258Ч260 283 Configurations of atoms in solids 52 Conjugated double bonds 250 251 409 410 Conservation laws 5 Conservation, of energy 5 125 Conservation, of momentum 5 112Ч116 125 Constitutions of solids 103 Contact electrification 172 contrast 408 435 446 447 454 Contrast expansion 470 Conventional luminescence 105 149 150 482 483 Coolidge, W.D. 321 Cooling rate 72 73 215Ч217 237 238 280 Coordination number 40 Cosine law of radiation 433 434 Covalent bonds 24 51Ч53 484 CR oscilloscopes 428 429 Crayon, luminescent 413 Critical flicker frequency 453 Crystal violet, 252 Crystalline transitions 48 49 65 66 68 80 Crystallinity 34 Crystallinity, effect on phosphor efficiency 84Ч88 322Ч333 347 Crystallization of phosphors 69Ч75 476 Crystallization temperature 215Ч217 236Ч238 347 Crystallization temperature, effect on efficiency 324Ч332 Crystallization time, effect on efficiency 329 Crystallographic systems 42Ч44 Crystalloluminescence 151 Crystals 34 485Ч487 Crystals, activity of 42 43 Crystals, aggregation of 81 82 Crystals, anisotropy of 42Ч45 101 Crystals, charge on 44 81 171 172 Crystals, cohesion 81 82 Crystals, growth of 34 47Ч50 Crystals, ionic 26 35Ч39 51Ч53 70 83 95Ч97 143 144 486 487 Crystals, ionic, versus nonionic 51 486 487 Crystals, lattice of 41 Crystals, metastable 85 96 Crystals, models of 484Ч487 Crystals, polarization of 392 Crystals, semiionic 25 26 28 39 51Ч53 83 95Ч97 486 487 Crystals, shapes of 82 83 486 487 Crystals, sizes of 48Ч50 63 71 81Ч83 90 486 487 Crystals, sizes of, optimum 434 435 Crystals, structure of 40Ч47 485Ч487 Crystals, structure of, determination 63 Crystals, symmetry of 85Ч88 107Ч109 Crystals, transitions in 84Ч88 cub.(hex.)-(Zn:Cd)(S:Se) 87 165 166 212 cub.(hex.)-(Zn:Cd)(S:Se):Ag 355 378 438 cub.(hex.)-(Zn:Cd)(S:Se):Cu 355 378 cub.- 107 cub.- 312 cub.- 46 141 312 477Ч479 cub.- 107 108 cub.- 107 cub.- 175 cub.- 74 cub.- 118 cub.- 107 cub.- 141 cub.- 118 cub.- 238 cub.- 110 228 238 cub.- 110 186 cub.- 72 110 165 186 228 265 268
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



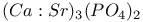 :Bi
:Bi 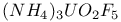
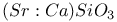 :Eu
:Eu 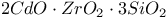 :Mn
:Mn 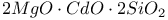 :Mn
:Mn 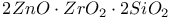 :Mn
:Mn  :Mn
:Mn 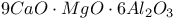 :Mn
:Mn 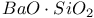 :Re
:Re 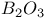
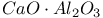 :Cr
:Cr 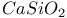 :Mn
:Mn 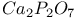 :Dy
:Dy 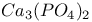 :Bi
:Bi 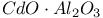 :Cr
:Cr 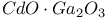 :Cr
:Cr 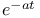 decay
decay 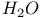
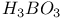 :(organic-dye)
:(organic-dye) 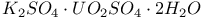
![$Mg[Pt(CN)_{4}]$](/math_tex/f5005f2e28abf57d68ff42104a21d49082.gif)
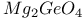 :Mn
:Mn 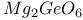 :Mn
:Mn 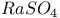
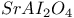 :
:![$[AIF_{3}]$](/math_tex/4869dd0d3d3be932c141972e6bd6a3c582.gif) :Mn
:Mn 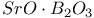 :Eu
:Eu 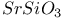 :Eu
:Eu 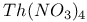
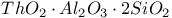 :Mn
:Mn 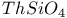 :Cu
:Cu 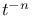 decay
decay 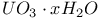
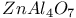
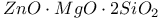 :[Si]
:[Si] 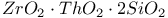 :Ag
:Ag 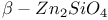
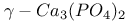 :Ce
:Ce 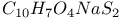
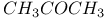
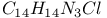
 :Pb
:Pb 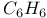
![$[(CH_{3})_{2}NC_{6}H_{4}]_{3}COH$](/math_tex/679c7d1c604ea648276be0b2d55fa53f82.gif)
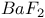 :Sm
:Sm 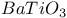
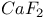
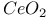 :Sm
:Sm 
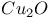 :[Cu]
:[Cu] 
 :Bi
:Bi 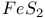

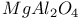 :Cr
:Cr  :Cr
:Cr