|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Leslie D.C. Ч Developments in the theory of turbulence |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Abridged Lagrangian Interaction (ALI) 204 214 216 218 221 226 227 228 229 230 235 236 239 240 241 242 249 250 251 252 253 254 256 262 263 264 265 267 268 269 270 272 273 275 276 277 280 283 284 317 350
Abridgement and see Abridged Lagrangian interaction 213Ч216 218Ч220 250
Adjoint 114Ч117 128 139
Adjoint Green's functions Green's function
Advanced Green's function see Green's function
Advection 11 257Ч258 302 333 350
Almost-Markovian model 147 149 257 259 260
Angular dependence (of turbulence functions) 325 328 329 330 347
Anisotropy 15 294 317 318 325 329 331 332 334 348 349 351
Approximate time-dependence and see exponential time-dependence square-exponential 92Ч95 128 227Ч230 316 317 331
Archimedes 310
Background field 320 321
Backward diffusion 157 189
Basis functions, basis operator and see eigenfunctions 112 119 124 128 132 135Ч137
Batchelor constant Ba 160 165 268 269 270 283 284
Batchelor's blob model 165Ч173 268 276
Batchelor, G.K. xvi; 1 11 18 22 30 31 35 37 157 159 160 163 164 165 166 167 168 16Ч9 171 172 173 180 183 189 238 244 256 268 273 275 278 308
Bipolar integrals 90 361
blobs see Batchelor's blob model
Boussinesq approximation, Boussinesq flow 3 286 312 316
Bradshaw, P. viii; 10 12 293 294 296 299 300 305
Burgers equation 83 140 153
Cascade and see Kolmogorov hypotheses 159
Central limit theorem 41
Central regions of flow and see inviscid core 296
Channel flow 9 II 286 291 293 301 316 327 333
Closure 40 42 50 51 109 131 140 144 145 153 190 191 236 283 285 303 305 310 312 317 334 346 347 349 354
Collective model 67Ч72
Comparisons with experiment 26 98 107 135 160 166 236Ч241 264 265 272 273 275 283 286 290 292Ч295 302 305
Complementary equations of motion 198- 202
Computational approach, computer solutions 12 13 45 86 91 123 150 153 264 265 316 317
Comte-Bellot, G. 16 293 294 295 296 297
Conduction range 272 273
Conduction response function 272Ч273
Constant stress layer and see wall layer wall 289
Convection and see diffusion 3 15 56 159 160 268 273
Convection range 159Ч162
Correlation (statistical) 7 8 37 40 41 42 57 113
Correlation function (of the velocity field) 92 95 121 128 129 131 139 148 227 230 260 263
Correlation function method (in FP theory) 129Ч130 140
Correlation tensor and see correlations of the velocity field 20 21 23 174 278 323 327 328 330 332 343 348
Correlation time 66 93 95 121 129 227 230 233 249 276 321 331 343
Correlations (empirical) 10 300 341 342
Correlations of the velocity field and see one-point correlations pair triple 9 37 38 42 43 122 141 142 153 237 252Ч256 278 320 323 327 328 330 332 343 345 348 360 361
Corrsin, S. 12 31 32 156 157 160 189 318
Crow, S.C. 153 319 320
Cumulant 41 122 123 345
Cumulant discard see quasi-normality
Deardorff, J.W. 13
Decay of turbulent energy and see dissipation 15 25 47 308
Decay time, decay constant and sec correlation time, response time 137 138
Deissler's method see series method
Deissler, R.G. 38 188
Diagram expansions 72 77 133
Diagram techniques 74 75 133 141
Diffusion of a particle pair 156 178Ч185 277Ч282 283
Diffusion of a single particle 156 173Ч178
Diffusion of particles 156 158 173Ч184
Diffusion of turbulent quantities and see advection convection 295 297 302Ч307 341Ч346
Diffusion ofscalars 3 56 57 156Ч158 162 267 282 283
Diffusivity tensor 175 182 277 280
Dirac delta function, definition of 18Ч19
Direct Interaction (DI) see subsequent citations and ALI EDI LHDI TFM
Direct Interaction (DI) and other closure methods 109 112 114 121 123 124 135 139 140 144 146 148Ч150 153 154 244 256 257 259Ч261
Direct Interaction (DI) and real flows, shear flows 285 300 310 312 320 323Ч325 332 334 335 342Ч344 354
Direct Interaction (DI), justification and improvement of 59 60 64Ч67 84Ч86 172 177
Direct Interaction (DI), Lagrangian form of and see ALI LHDI 164 184 191 204Ч206
Direct Interaction (DM. statement of 51
Dissipation length scale 29 236 315 129 347
Dissipation of turbulent energy 11 13 24Ч30 32Ч34 47 95 96 102 104 111 239 241 282 295 297 298 304 306 307 333 334 341 345 346
Dissipation range and see viscous range conduction 25 26 27Ч29 50 96 159 161 162 238 239 242 271 276 296 326 327 333 344 349
Distance-neighbour function 179 250
Driving force see stirring force
Eddv Prandtl number 271 272 283 302
Eddy size 3 12 13 16 28 29 33 318 328
Eddy thermal diffusivity 271 302
Eddy viscosity 10 13 244 245 249 270 271 300 301 303 304 307
Edwards, S.F. vii vui xvi; 47 50 92Ч95 142 189 247 327
Edwards, S.F. and divergence of response function 97 104Ч107 262 316
Edwards, S.F. and the Fokker Planck method 109 111Ч114 116Ч120 122-124 128Ч135 137 139 144 147Ч150 154
Eigenfunctions, eigenfunction expansions, eigenvalues 16Ч17 112 114Ч120 127 130 131 351
Energy see turbuleni energy and also scalar variance
Energy balance 292 295 297 298 331 334
Energy equation and see turbulent energy 23 24 55 88 91 98 104 117 120 121 124 129 131 133 134 137Ч140 144 145 148 149 154 229 259 261 292 295 312 332 334 335 339 342 344 351 353 354
Energy flow, energy flux and see Kolmogorov hypotheses 25 26 98 99
Energy range, energy-containing range: see production range
Energy spectrum 22 23 25 26 28 32 47 104 122 294 326 353
Energy tensor see correlation tensor
Energy transfers see inertial transfer
Entropy method (in FP theory) 131Ч135 263
Equilibrium spectrum see energy spectrum
Ergodic theorem 6Ч7
Eulerian DI 84 104 105 107 108 143Ч145 187 188 193 196 208Ч210 213 227 229 230 233 256 257 264 265
Eulerian DI and real flows 312 315Ч317 319 322 334 346 347 349 350
Eulerian DI and scalar convection 160 163 174 178 179 180
Eulerian framework or representation 88 134 135 147 160 177 188Ч192 196 199 204 208 221 222 228 229 257 259 262 267 277 360
Eulerian time-dependence 225 257 262
Expansion methods and see eigenfunction
Expansions, Wiener-Hermite method 37Ч38 51Ч52 121 126 129 135 140 141 144 146 154 319Ч325
Exponential time-dependence 50 92 102 107 121 124 128 129 139 140 154 227 228 230 234 263 312 316 317 321 327 331 332 334 343 346
First excited state, method of (in FP theory) 130Ч131 140
Fluctuations and see temperature fluctuations velocity 6 7 8 13 26 57 156
Fokker Ч Planck method, Fokker Ч Planck procedure 41 94 109 113 114 117 119-121 123 124 126 128 129 131 134 135 137 139 140 147Ч150 154 234 257 262 264 322 346
Fokker Ч Planck operator 113 114 121 128 129 133
Fokker Ч Planck series 41 112 126 127 129Ч134 137
Fourier transformation 16Ч19 21 23Ч25 40 56 57 140 158 168 176 211 237 238 314 317 319 320 327 344 352 353
Friction factor 28 288Ч290
Friction velocity 289 290
Fully developed flow 9 286 287 333
Galerkin, B.G. 327
Galilean invanance 209 210 257Ч262 265
Galilean transformation 186 187 188 209 210Ч212 257
Gaussian variables and see square-exponential time-dependence 30Ч33 39^12 51Ч53 61 65Ч66 92 114 116 117 121 122 130 135 139 149Ч151 153 187 188 205 211 281
Grant, Hughes, Vogel and Moilliei 160 165 169 270
Grant, Stewart and Moilliet 16 26 30 160 230 235 237Ч241 264 265 282 295
Green's function 114 115 125 126 129 137 179 199 200 204 267
Hall, W.B. 301
Hanjalic, K. 12 293 294 297 298 300 301 304Ч308 310 316 326 329 334 341Ч347
Heisenberg, W. 244
Hermite polynomials 114 115 151Ч152
Herring, J.R. 20 23 37 42 86 92 109 111 114 116 118 121 122 124 125 135 136 137 138 139 140 142 144 150 154 264 265 316 317 346 355
Hinze, J.O. 1 292 298 307 320
Homogeneity, homogeneous flows and see homogeneous isotropic turbulence 12 15Ч17 19 21 23 24 38 40 41 55
HomogeneityЧcontinued 56 88 89 156 158 159 174 183 210 221 238 252 286 312 314 317Ч321 325 327 335 337 342 346Ч349 351Ч353
Homogeneous isotropic turbulence 13 15-17 20Ч22 25 26 38 53 88 96 110 111 147 152 156 158 183 204 221 226 238 250 252 253 263 278 285 317 319 320 338 349 361
Hydrodynamics see Eulerian representation УKraichnanianФ Lagrangian
Inertial forces, inertial interaction see inertial transfer
Inertial range 27Ч29 47 96 98 104 123 124 135 159Ч162 171 184 238 239 283 296 326 327 333 334 345 349
Inertial range functional forms 26 50 92 95 96 98 104Ч106 128 133 134 171 176 184 227 228 230 234 329 331 342
Inertial range, definition of 25
Inertial range, properties of 242 244 249 251 252 254 262 263 271 278 280 281 322
Inertial transfer, II 19 24Ч26 41 42 47 50 53 54 59 95 96 99 100 105 113 122 123 135 158 229 234 236 242-249 268 283 335 336 338 339 341 345 349Ч351
Inertial-conduction range 162 163 164 272 274
Inertial-convection range 162 165 169 170 269 270 272 283
Infinitesimal response function see response function
Inhomogeneity, inhomogeneous flows 12 15 263 314 317 318 327 332 336 339 348
Intermittency 30Ч34 241
Inviscid core, inviscid flow, inviscid region 290 296 309 327 339 344 345
Irreducible diagrams 76Ч78 80
Isotropy and see homogeneous isotropic turbulence 15 16 19 21Ч22 24 38 88 91 147 159 160 295 306 317 318 322 325 329 349
Jones, W.P. 309
Kadomtsev B.B. 106 107
| Kolmogorov constant 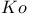 26 27 36 105Ч107 134Ч135 160 165 171 228 230 231 233Ч235 236 237 239 240 262 263 264 265 270 278 283 284 295 329 26 27 36 105Ч107 134Ч135 160 165 171 228 230 231 233Ч235 236 237 239 240 262 263 264 265 270 278 283 284 295 329
Kolmogorov hypotheses 16 25Ч26 30 32 33 95 96 98 104Ч107 121 123 124 135 171 235 236 283 295 322 333 339
Kolmogorov microscale 28 32 33 161 235 236 318 344
Kolmogorov, A.N. 16 25Ч26 30 32 33 47 92 95 98 105 235 236 304 318
Kraichnan, R.H. vu viii xv xvi 1 33 264 265 283 284 295 313 315 317 318 324 332 333 358Ч360
Kraichnan, R.H. and Lagrangian DI closures 186 188Ч191 193 195 197 204 209 210 212Ч214 217 220 221 224 226
Kraichnan, R.H. and scalar convection 157 159-161 163 164 171Ч173 175 177 184 267Ч269 271 273 277 279 280 282
Kraichnan, R.H. and the basis of DI 47 49 50 53 54 56 312
Kraichnan, R.H. and the consequences of the DI equations 91 92 94 95 97Ч99 102 104Ч108 227 229 230 232 235 237 239 247 249 250 252 254Ч256
Kraichnan, R.H. and the justification of DI 59 60 62 63 67 70 72 73Ч75 78 80 81Ч87
Kraichnan, R.H., and closure methods other than DI 109 114 121 124 126 128 129 132 141 144Ч147 149 150 154 257Ч263
Labelling time 189Ч191 194 209
Lagrangian equations 191 193 204 209 210 212 214 217 221 225 227 229 258
Lagrangian History DI (LHDI) 204 209 210 217
Lagrangian representation 88 150 157 161 164 177 184 188Ч193 204 209 210 214 221 225 228 229 233 234 250 252 257 267 268 277 278 283 294 312 329 347 351 361
Langevin-type methods 109
Laufer, J. 292 293
Launder, B.E. viii; 12 293 294 297 298 300 301 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 316 326 329 334 341 342 343 344 345 346 347
Length scales and see dissipation length scale Kolmogorov Taylor 304 305 344 346 348 349
Leslie, D.C. 125 128 129 130 131 140 247 263 301 319 320 322 327 341 345
Liouville operator 111 130 136
Liouville's equation 38 109 111 112 114 125 129 135 144 157 158 196
Logarithmic flow, logarithmic region 293 295 296 297 302 308 309 342 346 347 348 350 351 352 353
Lumley, J.L. 298
Marked particles see diffusion of particles
Markov process see almost-Markovian process
McComb, W.D. 106 131Ч135 247 263 316 327
Mean field, mean flow, mean velocity (profile) 6Ч10 15 19 28 156Ч158 174 237 285 286 289 309 310 318 319 322 329 349Ч351
Measuring time 189Ч191 194 209
Meecham, W. 150 152
Mellin transform 352 353
Memory time and see correlation time decay response timescales 147
Millionstchtikov, M. 42
Mixing length 10 300 302 303 304
Model equations, model representations 59 60 65 67 80 81 114 119 124 144Ч147 149 150 154 165 177 210
Models, one-point see one-point models
Multi-mode functions, multi-mode operators 113 116 136 137
Navier Ч Stokes equations 2Ч4 5 8 12 16Ч19 34 37 59 67 81 83 88 140 144 145 152 153 158 187 188 190 191 192 268 286 312 313 319 325 346 347 349 350 353 354
Negative production (of turbulent energy) 298
Non-linearity and see inertial transfer 56 59
Normal variables see Gaussian variables
Oboukhov, A.M. 32 33
One-mode functions, one-mode operators, one-mode probability distributions 112 113 114 116 118 135 136 137 138
One-point correlations of the velocity field 9 294 303 305 306 334
One-point equations, one-point models 300 303 304 305 332 334 341 342 .343 346 350 353
Operator and see Fokker Ч Planck operator Liouville 111Ч115 128 130 135 136
Orszag, S.A. 13 47 86 119 153 264 327 352
Oscillator model see collective model model
Pair correlations of the velocity field 20Ч23 29 34 35 37 303 315 319 334
Pao, Y-h. 26Ч28 161 162 171 172
Paquin and Pond 160 270
Particle diffusion see diffusion of particles
Phase space 109Ч111 125 126
Phythian's method 109 140Ч144 154 257
Phythian, R. 109 140Ч145 154 157
Prandtl number 162 165 272
Prandtl, L. 302Ч304
Pressure 2 4 8 9 13 15 28 162 255Ч258 267 313 319 336 347
Pressure drop 9 28 285 287 288
Probability distributions 30 39 40 51 109 111 118 125 126 129 130 132 135Ч137 172 176 277
Production length scale see dissipation length scale
Production of turbulent energy 11 12 25 29 30 95 96 292 295 297 298 306 307 318 322 333 345 349 350
Production range 25 96 238 242 251 296 324 326 327 335 345 347 351
Projection of an operator 136
Quasi-normahty 41 -45 47 59 62 109 122 123 153 163 188 273 306 345
Random coupling model 80Ч83 86 144 145 154
Random walk 113 174 176
Real flows 16 285 286 Chapter 318 325 354
Realisation averaging (definition of) 6
Redistribution term 305 307
Reducible diagrams 76 77
Representative points 109Ч111
Response equation 50Ч52 59 91 92 94Ч96 123Ч124 129 130 134 140 142Ч145 149 150 154 163 209 228 259 261 312 343 344 349 351 354
Response function 54Ч57 60 95 106 107 117 121 122 126 128 130Ч135 139Ч142 145 148 149 176 193 196 198 227 230 233 260 263 273 360 361
Response function method (in FP theory) 124Ч129 131 140
Response function, definition of 48Ч50
Response function, divergence of 95Ч98 103Ч108 124 128 129 133Ч135 150 160 177 186 209 227 229 230 262 263 316 317 346
Response functions for real flows 312 320 323 325 329 332 334 343 348
Response integral, response tensor see response function
Response time 66 92 93 95 121 128 129 227 230 233 321 331 343
Retarded Green's function see Green's function
Reynolds stress 1 9 10 12 19 287 288 291 293 300 302 304 306 309 318 321 322 323 324 330 342 343
Reynolds' equation 8 9 10 287 300 301 304 314
Reynolds, O. 1
Richardson, L.F. xvi; 179 184 250 280 281 283
Roberts, P.H. xvi; 174 177 179Ч181 184 250 277 280 281
Rotta, J.C 304 341
Rough walls 286Ч288 290 297
Saffman, P.G. 171 173 296
Scalar and see diffusion fluctuations 3 56 57 156 157 193 196 204 209 210 267
Scalar variance 159 161 264 270 271 272 273 275 283
Scir-consislcnt field 109 135 140 144 264 265 346
Series method 38 39 59 61 62 109 188
Shear flows 15 19 312 317 346
Shear stress (turbulent) see Reynolds stress diffusion
Similarity solution 280
Single-mode operators see one-mode operators
Solenoidal (definition of) 44
Spalding, D.B. 303 304
Spectral representation (of functions) see eigenfunction expansions
Spectral shape and see energy spectrum 326Ч328 335 340 342 347 353
Spectrum functions (of turbulent field) see energy spectrum response spectral temperature
Square-exponential lime-dependence 92 93 95 103 230 233 235
Stability theory 8
Stationary, slationarily 7 15 19 23 24 26 47 50 51 55 56 88 98 121 129 148 149 229 230 278 286 319
Statistics, elementary introduction to 5Ч8
Stirring force 16 19 24 25 42 47 52 111 125 147 148 319 323
Straining motion 166 168 171
Stress see Reynolds stress viscous
Structure functions 249 256
Taylor microscale 29
Taylor, G.I. 1 29 156
Temperature fluctuations 156 158 160 167 169 267
Temperature spectrum 156 159 268
Tensors 1Ч3 16 20Ч22 34 35 49 50 250
Test field model 257 259 261 262 263 264 265 282Ч283 284 312 316 322 346 349
Thermal energy equation 286 302
Timescales 30 47 230 249 251 272
Townsend, A.A. 9 10 30 31 166 298 302 318
Transfer funclion 105 229 235Ч236 269
Transport power and see energy flow 100 102 233 235 269
Triangle relation 18 19 42 89 90 97 100Ч102 158 159 242 337 356 360
Triple correlations of the velocity field 37 303 305 316 323 324 334
Turbulence, homogeneous isotropic see homogeneous isotropic turbulence
Turbulent dissipation see dissipation of
Turbulent energy, intermittency turbulent energy and see energy spectrum E(k) transport 8 10 12 15 23Ч25 27 37 96 98 100 132 234 236 292 295 297 298 304 307 309 323 324 327 343
Turbulent Reynolds number 13 16 30 32 33 92 264 265
Turbulent velocity see velocity fluctuations
Universality 289 290 293 294 296
Velocity fluctuations 32 33 47 52 98
Viscous range 161 283
Viscous response funclion 49 50 55 95 96
Viscous stress 9 10 287
Viscous-conduction range 162 272
Viscous-convection range 165 167 169 170 171 173 274 275 277 283
von Karman constant 290 302 348 353 354
von Karman, T. 289
Wall layer, wall region 96 289Ч291 293 294 302 326
Wall roughening 291
Wiener Ч Hermile function 150 151
Wiener Ч Hermite method 109 150Ч153 154 347
УKraichnanianФ fluid mechanics 189Ч193 257
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте