|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rees M.J. Ч Just Six Numbers: The Deep Forces That Shape the Universe |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 (lambda) 2 100 (lambda) 2 100
 (lambda), control of expansion (cosmic repulsion) 2 100 (lambda), control of expansion (cosmic repulsion) 2 100
 (lambda), cosmological constant 96Ч97 (lambda), cosmological constant 96Ч97
 (lambda), decay 154Ч155 (lambda), decay 154Ч155
 (lambda), effects of different values 3 99 101Ч102 155 (lambda), effects of different values 3 99 101Ч102 155
 (lambda), latent energy of space vacuum 97Ч98 130 151 153 154Ч155 (lambda), latent energy of space vacuum 97Ч98 130 151 153 154Ч155
 (lambda), non-zero value 97Ч99 101Ч102 114 156 (lambda), non-zero value 97Ч99 101Ч102 114 156
 (spatial dimensions) 3 134Ч136 143Ч145 (spatial dimensions) 3 134Ч136 143Ч145
 (spatial dimensions), black holes 78 81 82 (spatial dimensions), black holes 78 81 82
 (spatial dimensions), brown dwarfs 77Ч78 82 105 (spatial dimensions), brown dwarfs 77Ч78 82 105
 (spatial dimensions), composition 76Ч83 (spatial dimensions), composition 76Ч83
 (spatial dimensions), Dark matter 70 73Ч83 93 114Ч115 (spatial dimensions), Dark matter 70 73Ч83 93 114Ч115
 (spatial dimensions), deflection of light 75Ч76 (spatial dimensions), deflection of light 75Ч76
 (spatial dimensions), detected in clusters of galaxies 76 (spatial dimensions), detected in clusters of galaxies 76
 (spatial dimensions), exotic particles 79Ч81 82 (spatial dimensions), exotic particles 79Ч81 82
 (spatial dimensions), gravitational pull of 74Ч75 96 (spatial dimensions), gravitational pull of 74Ч75 96
 (spatial dimensions), inverse-cube law implied by four dimensions 135 see "Space-time" "Superstring "Time" (spatial dimensions), inverse-cube law implied by four dimensions 135 see "Space-time" "Superstring "Time"
 (spatial dimensions), main contributor to (spatial dimensions), main contributor to  73 79 126 73 79 126
 (spatial dimensions), major constituent of universe 83 91 109 (spatial dimensions), major constituent of universe 83 91 109
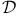 (spatial dimensions), neutrinos 79Ч80 (spatial dimensions), neutrinos 79Ч80
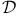 (spatial dimensions), non-radiating 76 (spatial dimensions), non-radiating 76
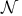 (gravitational ratio) 2 27Ч28 30Ч31 39 89 130 141 142 153 (gravitational ratio) 2 27Ч28 30Ч31 39 89 130 141 142 153
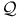 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy) 3 56 113Ч114 153 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy) 3 56 113Ч114 153
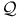 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), critical value 106 108 115Ч116 118 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), critical value 106 108 115Ч116 118
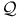 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), determinant of 'ripple' amplitude 107 114Ч115 127 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), determinant of 'ripple' amplitude 107 114Ч115 127
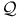 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), effects of deviation from critical value 114Ч116 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), effects of deviation from critical value 114Ч116
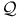 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), input to computer models of virtual universes 109 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), input to computer models of virtual universes 109
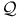 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), measure of gravity weakness in major structures 106 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy), measure of gravity weakness in major structures 106
 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe) 73 87 124 126 153 156 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe) 73 87 124 126 153 156
 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), effects of deviation from value of unity 2 86Ч90 100 114 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), effects of deviation from value of unity 2 86Ч90 100 114
 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), exotic particles 79Ч80 83 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), exotic particles 79Ч80 83
 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), supernova cosmology project 94Ч95 (omega, ratio of actual to critical density of matter in universe), supernova cosmology project 94Ч95
 (nuclear fusion efficiency) 47Ч51 52 81 84 89 153 (nuclear fusion efficiency) 47Ч51 52 81 84 89 153
 (nuclear fusion efficiency), effects of differing values 48Ч51 153 (nuclear fusion efficiency), effects of differing values 48Ч51 153
 (nuclear fusion efficiency), strength of nuclear forces 2 125 126 (nuclear fusion efficiency), strength of nuclear forces 2 125 126
Andromeda galaxy 53 61
Andromeda galaxy, collision with Milky Way galaxy 71 100
Angels and Devils (Escher) 60
Antimatter 47 83Ч86
Antimatter, energy released on annihilation 84
Antimatter, matter-antimatter asymmetry 84Ч86 123 139
Arrow of time see "Time"
Asteroids 15 18
Atomic structure 5 21 27Ч28 43Ч44 49
Atomic structure, electrons 5 21 27Ч28 47
Atomic structure, isotopes 44
Atomic structure, neutrons 44 47Ч50
Atomic structure, nuclei 5 43Ч44 48 50
Atomic structure, protons 21 27Ч28 43Ч44 47Ч50
Atomic structure, strong (nuclear) interaction 48 49 52 121 122 143
Atoms, contribution to  73 78Ч79 122 130 73 78Ч79 122 130
Atoms, created in early Big Bang 66
Atoms, created in supernovae explosions 43 45
Atoms, decay rate 86 101
Atoms, heavier elements less abundant in older stars 46
Atoms, minority constituent of universe 83 109
Atoms, Periodic table 43Ч45 50
Atoms, quantum effects 5
Atoms, stellar transmutation to heavier elements 8Ч9 44Ч45
Atoms, uniform throughout universe 10Ч11 21 42
Axions 81
Bekenstein, Jacob 145Ч146
Beryllium 50
big bang 9 78
Big bang theory 10Ч11 67Ч68 117 123 see
Big Bang, 'ripples' in early stages 56 106 107 114Ч115 127Ч128 151
Big Bang, conversion of photons to neutrinos 79
Big Bang, cosmic repulsion in early stages 124Ч125
Big Bang, deuterium 69Ч70 78 119Ч120
Big Bang, first stars 117
Big Bang, helium created from hydrogen 69Ч70 127 139
Big Bang, matter-antimatter asymmetry 84Ч86 139
Big Bang, non-uniform densities 107
Big Bang, primordial radiation shifts into infrared 121
Big Bang, temperature drop 66Ч67 70 107
Big Bang, timescale 2 8Ч9 30Ч31
Biological evolution 17 115
Biosphere 16 22Ч23
Biosphere, development of intelligence 18Ч19
Biosphere, elements formed in supernovae 43
Biosphere, evolution of 10 18Ч19
Black body radiation 65
Black holes 3 35Ч39 115 139
Black holes at atomic scale (primordial) 39 81 101 130 146 154
Black holes at galactic centres 36 38 53
Black holes entropy 146
Black holes in quasars 112Ч13
Black holes radiation 101 146
Black holes, binary systems with ordinary stars 35
Black holes, collision and coalescence 132
Black holes, constituent of dark matter 78 81
Black holes, decay rate 101
Black holes, developed from superstars 112
Black holes, Einstein's hostility to 98Ч99
Black holes, enveloped by surface 37
Black holes, gamma-ray bursts 35Ч36
Black holes, size proportional to mass 36
Black holes, spinning 36 37 112
Black holes, standardized objects 36 150
Black holes, temperature 146
Black holes, time dilation 37
Bruno, Giordano 19
Carbon 9 44Ч45 46
Carbon, isotopes of 44
Carbon, transmutation to oxygen 50
Cosmic Background Explorer Satellite (—ќ¬≈) 65Ч66 107Ч108 117
Cosmic environment, microwave background 65Ч67 80 98
Cosmic environment, sensitivity to cosmic numbers 22Ч23 48Ч51
Cosmic environment, uniformity of 10Ч11 21 42
Cosmic numbers (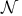 , ,  , ,  , ,  , , 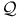 , , 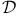 ) 2Ч4 ) 2Ч4
Cosmic numbers (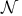 , ,  , ,  , ,  , , 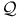 , , 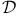 ) fine tuning 4 22Ч23 48Ч51 86Ч90 114Ч116 124 148Ч161 see ) fine tuning 4 22Ч23 48Ч51 86Ч90 114Ч116 124 148Ч161 see
Cosmic rays 80
Cronin, James 85
Cubic Space Division (Escher) 57 58
Deuterium (heavy hydrogen) 49 82
Deuterium (heavy hydrogen), abundance 112 118 123
Deuterium (heavy hydrogen), atomic structure 69
Deuterium (heavy hydrogen), created in Big Bang 69Ч70 78
Deuterium (heavy hydrogen), detected in distant galaxies 78Ч79 112
Dinosaurs, exterminated by asteroid impact 15 18
Doppler effect 14 15 57 59
Doppler effect, gas orbiting black holes 113
Doppler effect, stars orbiting barycentre 14
Earth, age of 40
Earth, asteroid impacts 15 18
Earth, atmosphere 16
Earth, destruction by expanding Sun 41 71Ч72
Eddington, Arthur 29Ч30
Einstein, Albert, 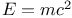 (rest-mass energy) 34 47 83 (rest-mass energy) 34 47 83
Einstein, Albert, cosmological constant ( ) 96 ) 96
Einstein, Albert, hostile to concept of black holes 99
Einstein, Albert, search for unification of gravity and electromagnetism 121
Einstein, Albert, Special Theory of Relativity 62
Einstein, Albert, theory of general relativity 31Ч32 35 36 38 96 98 101 112 145
entropy 104 146
Faraday, Michael 120 121 129 135
Feynman, Richard 22 146 159
Fitch, Val 85
Fractals 54Ч55
Friedman, Jerome 122
Galactic and stellar spectra, red-shifted 14 15 57Ч59 62
Galaxies, Andromeda 53 61
Galaxies, black holes at centre of 36 38 53
Galaxies, cannibalism 92 112
Galaxies, clusters and superclusters 53 55 75Ч76 106 110 122
Galaxies, clusters seeded by 'ripples' in early Big Bang 56 114Ч115 151
Galaxies, collisions 53Ч54 71
Galaxies, dark matter 74Ч75
Galaxies, disc shaped 53
Galaxies, distant galaxies viewed in early evolutionary stages 60Ч62 92 99 107 112
| Galaxies, Elliptical 53 54
Galaxies, evolution 60Ч63 64 92 110Ч111
Galaxies, gravitational lenses 76
Galaxies, local group 53 54 100
Galaxies, Virgo Cluster 54 see "Stars" "Stellar
Galileo 26Ч27 160
Gamma-ray bursts 35Ч36
Gamow, George 69 96
Gell-Mann, Murray 124
Glashow, Sheldon 121
Gravitational lensing, brown dwarfs revealed by 77Ч78 82
Gravitational lensing, dark matter in galactic clusters 75Ч76
Gravity 24Ч39 121
Gravity and black holes 34Ч39
Gravity and neutron stars 34Ч35
Gravity in virtual universes (computer simulations) 109 110 112 113Ч114
Gravity, amplification of small primordial density differences 105Ч106 138
Gravity, balanced by internal pressure of stellar cores 25 41 104
Gravity, effect on light 32Ч34 35 37
Gravity, effects of differing values of 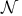 2 30Ч31 154 2 30Ч31 154
Gravity, effects on animal sizes 26Ч27 30
Gravity, escape velocities 34
Gravity, gravitational potential energy 131
Gravity, gravitational radiation 101
Gravity, indistinguishable from accelerated motion 38
Gravity, Newton's inverse-square law 10 24Ч25 75 106 135
Gravity, pull exerted by dark matter 74Ч75 96
Gravity, ratio to atomic electric charges 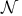 2 27Ч28 30Ч31 89 2 27Ч28 30Ч31 89
Gravity, self-gravity 29
Gravity, singularities 37 38
Gravity, strength of 27 30Ч31 89 106 130 142 153
Gravity, tidal forces in black holes 38
Gravity, time dilation near large masses 34 37
Guth, Alan 124 129
Hawking, Stephen 143 146
Helium, atomic structure 49
Helium, produced from hydrogen in Big Bang 69Ч70 139
Helium, product of hydrogen fusion 41 44 46 47Ч48
Helium, transmutation to heavier elements 47 50
Helium, uniform abundance in primordial objects 69 117
Hoyle, Fred 50 67Ч68 69
Hubble Space Telescope (HST) 61 63 76
Hubble, Edwin 57 65
Hydrogen, atomic structure 21 27Ч28
Hydrogen, conversion to heavier elements 2 9 41 44Ч45 68Ч69
Hydrogen, sensitivity to value of  49 49
Hydrogen, stellar fuel 44Ч45 47Ч48
Hydrogen, transmutation to helium 41
Inflationary universe theory 123Ч133 150Ч151
Inflationary universe theory, cosmic repulsion in very early Big Bang 124Ч125
Inflationary universe theory, exponential expansion 125
Inflationary universe theory, flat universe 126 150Ч151
Inflationary universe theory, gravitational waves 128
Inflationary universe theory, new inflationary episodes within black holes 130 133
Inflationary universe theory, size of universe 132Ч133
Inflationary universe theory, tests of theory 126Ч128
Intelligence, extraterrestial, assumed rarity of 18Ч19
Intelligence, extraterrestial, common culture 22
Intelligence, extraterrestial, communications based on ratios of physical constants 21Ч23
Intelligence, extraterrestial, methods of detection 20
Intelligence, extraterrestial, search for (SETI) 20Ч21
Iron 44Ч46 68
Jupiter, composition 46
Jupiter, effects of self-gravity 29
Jupiter, possibility of life on moons 17Ч18
Jupiter, Sun-Jupiter system rotation about barycentre 13Ч14
Kaluza, Theodor 143Ч144
Kelvin, William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin 40
Kendall, Henry 122
Kerr, Roy 36
Kirschner, Robert 55
Klein, Oscar 143Ч144
Large Hadron Collider 120
Linde, Andrei 124 133 151
LISA project (Laser Interferometric Space Array) 128
Lowell, Percival 19Ч20
Magnetic monopoles 129
Mandelbrot set 148 149
Mars, canals 19Ч20
Mars, canals, search for life 17
Maxwell, James Clark 120 121 129
Mayor, Michel 14
Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) 108 127
Microwave background radiation 65Ч67 80 139
Microwave background radiation, black body spectrum 65 108 117
Microwave background radiation, non-repetitive distribution 140
Microwave background radiation, non-uniform distribution 98 107Ч108 119
Microwave background radiation, residue of Big Bang 65 98
Milky Way 53 71 100
Multiverses 11 23 133 150Ч161
Neutrinos 48 79 118 121
Neutrinos, Kamiokande experiment 80
Neutrinos, non-zero mass 80 82 118
Neutrinos, possible dark matter component 79Ч80 82
Neutrinos, ratio to atoms 79
Neutron stars 34
Newton, Sir Isaac 10 31Ч32
Newton, Sir Isaac, inverse-square law of gravity 24Ч25 34 42 75 106 156
Nuclear fusion 41 44 46 47Ч48
Nuclear fusion, efficiency ( ) 47Ч48 ) 47Ч48
Nuclear fusion, rest-mass energy 47
Ouraborus 7Ч8 161
Oxygen 9 17 44Ч46 50
Paley, William 135Ч136 149
Particle physics, antiparticles 83Ч84
Particle physics, asymmetric particle decay(neutral kaon 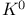 ) 85 ) 85
Particle physics, electromagnetism, linked to weak force 121 122 143
Particle physics, electrons 5 21 27Ч28 47
Particle physics, gluons 122 143
Particle physics, grand unified theories (GUT) 89 97 122Ч123
Particle physics, laws applicable throughout universe 10Ч11 21 42 158
Particle physics, neutrinos see "Neutrinos"
Particle physics, neutrons 44 47Ч50 121
Particle physics, nuclei 43Ч44 48 50 121
Particle physics, protons 21 27Ч28 43Ч44 47Ч50 121 123
Particle physics, protons and antiprotons 83
Particle physics, quarks 122 143
Particle physics, quarks and antiquarks 83 85
Particle Physics, Standard Model 122
Particle physics, strong (nuclear) interaction 47Ч48 49 52 121 122 143
Particle physics, super-symmetry 81
Particle physics, weak force 85 121 143 see "Atoms" "Superstring
Periodic table 43Ч45
Periodic table, effect of different values for  50Ч51 50Ч51
Perlmutter, Saul 94Ч95
Photons (quanta of radiation), density in universe 66 79 85
Photons (quanta of radiation), insignificant gravitational effects 80
Planck's constant 141
Planck, Max 141
Planck-Surveyor spacecraft 108 127Ч128
Planetary systems, detection 13Ч16
Planetary systems, formation 12Ч13
Planetary systems, search for 16
Planetary systems, unstable among close-packed stars 115
Planetary systems, unstable if gravity followed inverse-cube law 135Ч136
Principia (Newton) 25
Quantum 'foam' 6 142 154
Quantum gravity 140Ч143
Quantum gravity in black hole singularities 142Ч143
Quantum gravity in early Big Bang 142
Quantum theory, Planck length 141 142 143Ч144
Quantum theory, Planck time 141 142
Quantum theory, Planck's constant 141
Quasars 39 92 110 112Ч113
Queloz, Didier 14
Quintessence 42
Radio transmissions 20
Relativity, general theory of 31Ч32 35 36 38 96 98 101 112 145
Relativity, general theory of, built into superstring theory 145 see Albert"
Sakharov, Andrei 84Ч85 139
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 (lambda)
(lambda) 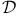 (spatial dimensions)
(spatial dimensions) 
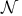 (gravitational ratio)
(gravitational ratio) 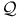 (ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy)
(ratio of gravitational binding force to rest-mass energy)  (nuclear fusion efficiency)
(nuclear fusion efficiency) 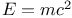 (rest-mass energy)
(rest-mass energy) 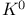 )
)