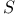|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Raine D.J. — The Isotropic Universe: An Introduction to Cosmology |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
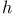 4 41 4 41
 40 40
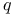 , , 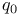 see “Deceleration parameter” see “Deceleration parameter”
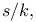 82 219 82 219
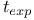 177 185 177 185
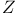 35 35
Abell, G. 8
Absolute space 117
Affine connection 110
Andromeda galaxy 2 66
Angular correlation function 19
Angular diameter 154
Angular diameter, test 156
Anisotropic universes 6 196
Anisotropic universes, classification of 202
Anisotropic universes, expansion of 204
Anthropic principle 221
Antimatter 80—82; see “Matter”
Apparent magnitude test 160
Arrow of time 244
Background radiation 44—7 55;
Background radiation, optical 45
Background radiation, perturbation of 209 210
Background radiation, x-ray 45
Baryon non-conservation 236
Bianchi types 202
Black hole 226 243
Black-body radiation 47 53
Boltzmann formula 71 180
Bulk viscosity 174
Catalogues of galaxies 7
Chaotic cosmology 215
Clusters, rich 3 8 24 31 57 64 243
Coma cluster 3 4 32 69
Compton scattering 57 186—7
Compton scattering, inverse 57
Conservation of mass 214
coordinates 108
Coordinates, Minkowski 96 98 111
Coordinates, normal 108—10 115 128 131
Copernican Principle 125
Correlation function 10 11 14—19 242
Correlation function, cross 28
Correlation function, three-point 28
Cosmic rays 44 46 79—80
Cosmic time 126 199
Cosmological constant 119 137
Cosmological models 153
Cosmological principle 121 124
Cosmological principle, perfect 125
Covariant derivative 114
Critical density 69 141 184
Curvature 99 104 116
Curvature, constant 129
Curvature, Riemannian 116 129
de Sitter, W. 119
de Sitter, W., model 230—2
Deceleration parameter 41 135 141 156 160 184
Deuterium 182—4
Dicke, R.H. 89
Distance classes 9 26
Distance scale 4 39—41
Distribution function 168 172
Doppler effect 35
Dust model 139
E tv tv s, R.V. 89 s, R.V. 89
Einstein field equations 107—8 116 137 147
Einstein field equations, model 120—3
Einstein — de Sitter model 141 157 190 193
Electron scattering 185
entropy 60 175 179 182 219—20 244-6
Equation of state 107 138 151
Equivalence principle 88 118
Equivalence Principle, Galilean 89 90—1
Equivalence Principle, strong form 94
Equivalence Principle, weak form 94
Event horizon 225
Expanding Universe 34 36—8 197
expansion 198
Field equations see “Einstein”
Fragmentation 239 242
Frame of reference 110
Free fall 92 99;
Free fall, divergence of 93
Free-free absorption 184 186
Friedmann, A. 130
Fundamental observers 121 126 132
Galaxies 28—9
Galaxies, active 30
Galaxies, classification of 28
Galaxy 1 3
Galaxy luminosity function 4 69
Galaxy luminosity function, haloes 66 67
Gamma-ray background 81
Geodesic completeness 224
Geodesics 99 102 114 115
Geodesics, deviation of 102 104 116
Grand unified theories 235 241
Gravitational instability 242
Gravitational potential 86
Gravitational waves 46
Gravity 85 90
Gravity, Newtonian theory of 86 91—2
Hagedorn theory 152 235
Helium synthesis 181—3
Hierarchical universe 3 7 27
| Homogeneity 21 26 27 33 36 126
Homogeneous universe 4 6 126
Horizons 192—4 216
Hot Big Bang 43 46 57 83
Hubble classification 29
Hubble constant 40
Hubble flow 67
Hubble parameter 40 135
Hubble, E.P. 4
Hubble’s law 38
Inhomogeneous universe 6 196 208
Intergalactic medium 70 191
Isotropy 6
Isotropy of the Universe 36 49
Jeans mass 239 242
K-correction 38 160
Kasner solution 202—3
Kinetic equation 169 187
Kirchhoff relation 74
Kompaneets equation 210
Last scattering 189 205
Lemaitre, G. 130
Lie derivative 200
Liouville’s theorem 168 172
Local Group 2 3 66 81
Local rotational symmetry 199
Log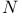 -log -log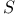 163—4 163—4
Luminosity-volume test 43 163
Mach’s principle 117 207 212—15
Magnitude 5 160
Malmquist effect 205
Mass, conservation of 105
Mass, gravitational 90
Mass, inertial 90
Mass, missing 65
Mass, to light ratio 63 65
Matter-antimatter symmetry 82 83 234—6
Maxwellian distribution and expansion 173
Mean density 69
Metric 97—8 100 108 112
Metric, Minkowski 96
Microwave background 46 47—9 54 71 239
Microwave background, anisotropy of 53—4 205-6
Model universe 118
Neutrinos 45 117 178 217
Neutron-proton ratio 180
Number counts 161—4
Olbers’ Paradox 34
Particle creation 218—19
Perturbations 240—2
Planck distribution 53 59 170
Planck mass 220 241
Planck time 218 241
Poisson equation 86
Power spectrum 10 12 16 17 21—4 33
Quasars 31 43 164 243
Radiation, 21 cm 2 36
Radiation, flux 159
Radiation, transfer 169 189—90
Radiation, universe 147
Radio emission 80
Radio emission, sources 31 33 44
Random distribution 8 11
Reciprocity theorem 158
Recombination 174 188
Redshift 35 59 132—4
Reference frame 110
Reference frame, tetrad 111
Relativistic particles 79
Relativity, general theory of 88
Relativity, principle of 87
Relativity, Special Theory of 87 95—6
Riemannian curvature 129
Robertson — Walker metric 130
Rotation 197 198 206—7
Rubin — Ford effect 204
Scale factor 36 133
Scaling 9 10 21 26 27
Schwarzschild radius 226 227
Shear 197
Singularities 223 226
Singularities, types of 204
Space-time 95
Space-time, curved 97
Spatial homogeneity 126
Spin temperature 72
Steady state theory 42 125 162 219 230—3
Summation convention 96 108
Super clusters 3 9
Superclustering 24
Swiss-cheese model 209 237
Temperature of matter 173 175
Temperature of neutrinos 178
Temperature of radiation 148 170 175 178—80
Tensor 113
Test body 89
Thermal equilibrium 176
Thomson scattering 57 185
Tidal forces 93 116
Tilted Universe 226
Tired light 165
Turbulence 241 243—4
Virgo cluster 2 32
Virial theorem 68
Whimper singularity 230
X-rays 66 78
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



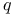 ,
, 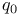
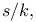
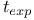
 tv
tv -log
-log