|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hickman M. (Ed), Mirchandani P. (Ed) — Computer-Aided Systems in Public Transport |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
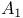 transformation 100 transformation 100
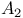 transformation 91 transformation 91
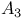 and and 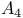 transformations 91 transformations 91
Allotropy 90
Alloy, irreversible 107
Alloy, reversible 107
Alloys, cobalt-nickel 116—118
Alloys, Heusler's 118—121
Alloys, iron-cobalt 113—115
Alloys, iron-nickel 105—112
Alloys, manganese-antimony 120
Ashworth 39
Atomic rays 240
Austenite 99
Austin 119
Bain 91
Ballistic galvanometer 7
Ballistic method 22—24
Barrett 79
Barus 64
Bauer, C. 36
Bauer, E. 137
Beck, K. 150 153
Beck, N. 192
Beetz 35
Benedicks 38
Bidwell 54
Bloch 116 117 136
Bohr 231 239
Boltzmann 176
Borel 29
Bound electron 167
Broadway 223
Bruins 231
Burgess 95 187
Cabrera 231 238
Cailletet 139
Cantone 67
Cementite 99
Change of length by magnetization 53—59 83—87 108—109 115 117—118 160—161
Change of volume by magnetization 62—63 109—110
Charpy 97
Coercive force 35
Compensating coil 17
Corresponding states, equation of 191
Coulomb 200
Critical temperature 79
Curie 81 92 131 133 134 136 141 178
Curie's laws 132
Curve of magnetization 7
de Haas 140
Debye 183
Deflection 21
Demagnetizing factor 9 16
Demagnetizing force 7 9—10
Deslandres 27
Devaud 140
Dewar 84
Diamagnetic substance 2 183—189
Dieckmann 120 122
Dilatometer 62
Directions of easy and difficult magnetizations 164
Drapier 140
du Bois 26 34 137
du Jassoneix, Binet 122
Dumat 106
Dumont 106
Effective field 16
Electric current 1
Electric resistance at high temperatures 95—96 104
electromagnetic field 1
Electromagnets 25—28
Electromagnets, H. Deslandres et A. Perrots' 27
Electromagnets, H. du Bois' 26
Electromagnets, P. Weiss' 26
Electromagnets, Rumkorf's 25
Electron 167
Elementary complex 199
Elementary magnet, nature of 167—168
Elias 231
Endo 132
Equilibrium diagram of cobalt-nickel alloys 116
Equilibrium diagram of iron-carbon alloys 99—101
Equilibrium diagram of iron-cobalt alloys 113
Equilibrium diagram of iron-nickel alloys 105
Equivalent area 30
Eutectoid mixture 100
Ewing 37 40 53 54 198 199 200 212
Faraday 1 123 145 146
Faraday's law 1
Ferrite 99
Ferromagnetic compounds 121—122
Ferromagnetic substance 3—4
Ferromagnetism, origin of 173—175
Feytis 140 236
Finke 146 148
Foeex 92 136 149
Frankamp 231
Free electron 167
Free magnetism, distribution of, on a magnetized substance 37—39
Frenkel 186
GANs 49 182 183 199
General theory of magnetostriction 43—44
Gerlach 154 240
Geuther 122
Goldschmidt 153
Gore 79
graphite 99
Gravitational potential 10
Grenet 97
Grondahl 119
Guertler 113
Guillaume 105 119
Gumlich 36 229
Hadfield 39
Harrison 95
Haupt 119
Hector 130 139
Hennig 137
Heusler 119 188
Heydweiller 49 52
Hilpert 120 121 122
History of thermomagnetism 79—80
Hoejendahl 186
Hog 118
Holborn 36
Homma 37
Honda 33 34 49 51 52 53 54 55 57 58 59 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 73 74 75 76 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 91 94 95 96 97 101 102 103 104 106 107 108 109 110 111 113 114 115 120 124 129 130 131 132 134 135 136 137 140 141 142 143 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 166 178 191 193 200 212 214 215 240
Hopkinson 79 81 95 105
Hysteresis-loop 35 40 214
Iitaka 104
Imai 104
Induced current 1
Induced electromotive force 1
Intensity of magnetic field 1
Intensity of magnetization 5 33—34
Ishiwara 92 119 122 141 142 143 144 240
Isihara 104
Jackson 141 149
Jantsch 140
Jimeno 231
K.S. magnet steel 115
Kadooka 38
Kaneko 113 116
Kase 105
Kaufmann 36
Kaya 154 155 156 157 158 159 222
Keesom 183
Kelberg 95 187
Kido 108 114 115
| Kinoshita 146
Kirchhoff 67 70 77 89
Kirchhoff's constants 67—70
Kohlrausch 79
Kolacek 49
Kunz 150 164 165
Kusakabe 81
Langevin 176 178 180 182 183 184 185 189 190 229 238
Larmor 175 183
Larmor precession 170
Le Chatelier 80 95
Lenard 29
Line of magnetic force 3
Line of magnetic induction 3
Loschmidt 229 235
Loschmidt number 235
Magnetic field 1
Magnetic flux 1
Magnetic Hysteresis 3 34—36
Magnetic hysteresis in ferromagnetic crystals 223—227
Magnetic induction 3
magnetic moment 6 229—231
Magnetic permeability 3
magnetic susceptibility 5
Magnetic susceptibility at high temperatures 131—137
Magnetic susceptibility of different gases 137—140
Magnetic susceptibility of elements 128—131
Magnetic susceptibility of ferromagnetic elements above their critical points 135—137
Magnetic susceptibility of inorganic compounds 140—143
Magnetic susceptibility of organic compounds 143—144
Magnetic susceptibility of oxygen at different temperatures 134
Magnetic susceptibility of para- and diamagnetic crystals 145 148—149
Magnetic susceptibility of tin at different temperatures 134—135
Magnetic susceptibility of water 140
Magnetic viscosity 37
Magnetization and concentration in cobalt-nickel alloys 117
Magnetization and concentration in iron-cobalt alloys 114
Magnetization and concentration in iron-nickel alloys 106—107
Magnetization at different temperatures in iron-nickel alloys 110—112
Magnetization at high temperatures in ferromagnetic metals 80—82
Magnetization due to revolving electrons 168—173
Magnetization in iron crystal 153—159 216—221
Magnetization in magnetite 161—163
Magnetization in nickel crystal 33—34
Magnetization in pyrrhotite 164—166
Magnetization in very weak fields 36—37
Magnetization of ferromagnetic substances 33—34 207—212
Magnetization of iron at high temperatures 81
Magnetization of steel at high temperatures 102
Magnetization, circular, effect of twist on 71 74—75
Magnetization, effect of hydrostatic pressure on 61—62
Magnetization, effect of hydrostatic tension or pressure on 48
Magnetization, effect of temperature on 102 214—216
Magnetization, effect of tension or pressure, on 49—53
Magnetization, effect of twist on 63—64
Magnetization, effect of vibration on 39—40
Magnetization, longitudinal, effect of twist on 70—71 74—75
Magnetization, spontaneous 190—191
Magnetizing coil 17
Magnetometer 17
Magneton 233
Magnetostriction 59
Magnetostriction at high and low temperatures 83—89
Magnetostriction in cobalt-nickel alloys 117—118
Magnetostriction in iron crystal 160—161
Magnetostriction in iron-cobalt alloys 115
Magnetostriction in iron-nickel alloys 108—110
Mann 16
Marquina 231
Mashiyama 154 160 161
Masumoto 93 99 113 116 117 118
Matsuda 104
Maurain 35 36
Maxwell 10 123 176 198 215
Meier 36
Mendeleff 130
Method of measuring magnetization in ferromagnetic crystals 150—153
Method of measuring magnetization in strong fields 30—33
Method, ballistic, of measuring magnetization 22—24
Method, differential, of measuring magnetostriction 55—56
Method, magnetometric, of measuring magnetization 17—22
Method, of measuring strong magnetic field, Bismuth spiral 28—29
Method, of measuring strong magnetic field, Exploring coil 30
Method, of measuring strong magnetic field, Plane-polarised light 29—30
Method, of measuring the magnetic susceptibility, cylinder 127—128
Method, of measuring the magnetic susceptibility, Faraday's torsion balance 123—125
Method, of measuring the magnetic susceptibility, Hydrostatic 126—127
Method, of measuring the magnetic susceptibility, Weiss' electromagnetic 125—126
Method, yoke, of measuring magnetization 24—25
Meyer 95 140
Modulus of elasticity, change of, by magnetization 56—57 59
Molecular field 189
Moles 231
Morris 81
Nagaoka 21 33 34 54 55 58 61 62 63 67 68 69 73 74 75 76 81 106 107 108 109 110 121
Nature of elementary magnet 167—168
Normal curve of magnetization 8
Nucleus 167
Ogura 95 96 104
Okubo 166 178 200 212 214 215
Onnes 134 141 183 234 238
Oosterhuis 141 182 183
Optical lever 54
Osawa 105
Osmond 105
Owen 129 130 132 133
Oxley 144
Paramagnetic substance 2
Paramagnetism, origin of 173—175
Pascal 140 141 143 188 235 236
Pascal's addition-law 143
Pearlite 100
Peddie 199
Permalloy 112
Perrier 134 141 183
Perrot 27
Phase change 90
Piccard 137 140
Pierce 36
PINA 231
Planck 239
poisson 10 68 196
Potter 223
Preuss 113 229
Principal axes of magnetization 145
Principal susceptibility 145
Proton 167
Quartarolli 231
Quittner 150 161 162 164
Rabi 150
Ragowski 36
Rayleigh 36 209
Recalescence 80
Reciprocal relation 49
Reiche 183
Relation, between para- and ferromagnetic substances 194—196
Relation, between susceptibility and temperature above critical point 191—192
Residual magnetism 35 212—214
Richarz 119
Rigidity 48 65—66
Rigidity, change of, due to magnetization 64—67
Robert-Austin 93
Roessler 19
Roop 137
Rotszajn 183
Ruer 113 116
Rumkorf 25
Rutherford 174
Sato 98
Saturated magnetization 7
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



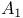 transformation
transformation 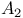 transformation
transformation 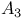 and
and 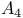 transformations
transformations