|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Curien P.-L. — Categorical Combinators, Sequential Algorithms, and Functional Programming |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
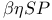 -monoid 1.5.1 -monoid 1.5.1
 -algebra 1.5.1 -algebra 1.5.1
 -calculus, -calculus, 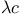 -calculus, partial, with recursion 1.5.13 -calculus, partial, with recursion 1.5.13
 -calculus, -calculus, 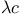 -calculus, typed 1.3.1 -calculus, typed 1.3.1
 -calculus, -calculus, 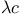 -calculus, untyped 1.2.1 -calculus, untyped 1.2.1
 -calculus, typed 1.3.10.4 -calculus, typed 1.3.10.4
 -calculus, untyped 1.2.27 -calculus, untyped 1.2.27
Abstract algorithm 2.5.4
Abstraction 1.2.1
Accessibility 2.1.1
Accessible 2.1.3
Adequacy Theorem 4.1.4 1.7.4
Algorithm, abstract 2.5.4
Algorithm, sequential 2.5.1
Application,  -calculus 1.2.1 -calculus 1.2.1
Application, algorithm 2.5.1 3.2.2
Application, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
Application, model 1.5.1
Applicative algebra 1.5.5
Applicative algebra, least fixed point 1.5.16
applying 1.2.13
Basic, object 1.3.5
Basic, type 1.3.1
Bicds 4.2.3
Bicds, complete 4.3.1
Boehm tree 1.5.19
Bound, variable 1.2.1
Categorical abstract machine 1.1
Categorical combinatory logic, confluent 1.2.25
Categorical combinatory logic, strong 1.2.12
Categorical combinatory logic, typed 1.3.1
Categorical combinatory logic, universal 1.4.1
Categorical combinatory logic, untyped 1.2.11
Categorical combinatory logic, weak 1.2.14
CdS cf. “concrete data structure”
CDS01, CDS0, expressions 3.5.4
cell 2.1.1 3.1.1
Cell, extensional 4.2.3
Chain 2.2.1
Closure,  1.2.27 1.2.27
Closure, CAM 1.1 1.2.22.3 1.2.22.4 1.3.10
Coherence space 2.4.4.2
Combinatory algebra, combinatory logic 1.2
Combinatory model 1.5.22
Combinatory model, stable 1.5.23
Complete bicds 4.3.1
Complete ideal 2.3.6
Composition, algorithms 2.6.2 3.3.1
Composition, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
Concrete data structure 2.1.1
Concrete data structure, sequential, filiform 2.1.10
Concrete data structure, well founded, stable 2.1.4
Concrete domain 2.2.10
Conditionally multiplicative, function 2.4.1
Conditionally multiplicative, order 2.4.3
Conflict 2.2.1
Consing 1.2.27
Consistence 2.1.1
context 1.5.8
Control, event 4.3.1
Control, value 4.2.3
Couple 1.2.8
Coupling 1.2.13
Covering 2.2.1
Currying, algorithms 2.6.5 3.3.3
Currying, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
dcds 2.1.4
de Bruijn, notation 1.2.2
de Bruijn, translation 1.2.3 1.2.15
Deduction 2.1.1
Definable 4.1.5
Direct approximation 1.5.19
Distributive 2.2.13
Enabled 2.1.3
Enabling, cds 2.1.1
Enabling, event structure 2.2.1
Equivalence theorem, first 1.2.20
Equivalence theorem, fourth 1.4.5
Equivalence theorem, second 1.3.4
Equivalence theorem, third 1.3.9
Equivalence,  - 1.2.3 - 1.2.3
Equivalence, presentation 1.6.6
Equivalence, prime intervals 2.2.1
Evaluation function 3.5.2
| Event domain 2.2.2
event structure 2.2.1
Events, cds 2.1.1 3.1.1
events, control 4.3.1
Events, event structure 2.2.1
Extensional, cell, state 4.2.3
Extensional, model 1.5.1
Filiform 2.1.10
Filled 2.1.3
Free cartesian closed category 1.3.5
Free, variable 1.2.1
Fully abstract 4.1.5
Function, sequential 2.4.5
Function, stable, conditionally multiplicative 2.4.1
Functional  -model 1.5.21 -model 1.5.21
Generate 2.1.1
grafting 3.1.3
Hierarchical coherence theorem 1.3.10
Homomorphism, model 1.5.1
Identity, algorithm 2.6.3
Identity, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
Inclusion, cds 2.3.1
INDEX 2.4.5
Initial, cell 2.1.1
Injection-projection pair: end of 1.4
Input-output function 2.5.1
Interpretation method 1.2.24.2
Inverse sequence of projections 4.1.6
Krivine's abstract machine 1.2
Least fixed point, applicative algebra 1.5.16
Least fixed point, model 1.5.14
Lifting 1.2.7
Mc cf. “conditionally multiplicative”
Model,  -calculus 1.5.1 -calculus 1.5.1
Model, CATAR 1.7.3
Model, least fixed point 1.5.14
Model, PCF 4.1.3
Observably sequential, algorithm 2.6.12
Observably sequential, function 2.6.15
Occurrence 1.2.5
Operational preorder 4.1.5
Order-extensional model 1.5.14
Output value 4.2.3
Pairing, algorithms 2.6.4 3.3.2
Pairing, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
Presentation equivalence 1.6.6
Presentation morphism 1.6.1
Prime interval 2.2.1
Product, cds 2.1.13 3.1.3
Projection, 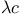 -calculus 1.2.8 -calculus 1.2.8
Projection, algorithms 2.6.4
Projection, categorical combinatory logic 1.2.11
proof 2.1.5
Redex,  - 1.2.6 - 1.2.6
Represent 2.1.1
safety 2.1.1
Semantic function 1.5.1
Sequential data structure 2.1
Sequential, algorithm 2.5.1
Sequential, cds 2.1.10
Sequential, function 2.4.5 2.4.9
session 3.5.6
SIPP cf. “stable injection-projection pair”
Stable injection-projection pair 2.3.5
Stable, cds 2.1.4
Stable, combinatory model 1.5.23
Stable, function 2.4.1
Stable, order 2.4.3
State, cds 2.1.1
State, event structure 2.2.1
State, extensional 4.2.3
Strictly sequential 2.4.5
Strongly algebraic 4.1.6
Strongly sequential 2.4.5
Substitution 1.2.4 1.2.7
Sum, cds 2.3.3 3.1.3
table 3.5.4
Trace 2.4.4.1
Universal type 1.4.1
Value domain 1.5.14
Value, cds 2.1.1
Value, output, control 4.2.3
Weakly extensional 1.5.1
Well founded, cds 2.1.4
Zigzag 2.2.1
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



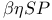 -monoid
-monoid  -algebra
-algebra 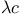 -calculus, partial, with recursion
-calculus, partial, with recursion  -calculus, typed
-calculus, typed  -
-  -
-