|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Born M. Ч Natural philosophy of cause and chance (The Waynflete lectures) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -pomt 117Ч118 -pomt 117Ч118
Absolute temperature 38 42 48 53 149 157
Absorption 82 86
Accessibility 144Ч146
Ackermann 169
Adiabatics 34Ч39 147 149Ч151
Adrian, A.D. 125
Advanced potential 26
Antecedence 9 12 15 17 25Ч26 30Ч32 44 71Ч73 102 120 124
Astronomy 10Ч16
atom 17 84
Atomic physics 187
Atomistics 46
AvogadroТs number 63 176
Balmer 85 87
Bernoulli, D. 47
Binary encounters 68
Biot 138
Boer, de 169
Bohr 82 85Ч87 105 127 191 208
Boitzmann 53 55 56 58Ч60 62 76 140 163 167 182Ч183
BoltzmannТs constant 53 158 176
BoltzmannТs constant, equation 55 68 71 165 172 174 181
BoltzmannТs constant, H-theorem 57Ч59 113
Born 65 169 186 188Ч189 195 207
Boscovich 46
Bose 112 197
Bose Ч Einstein statistics 113 199Ч202
Boyle Ч Charles law 48
BoyleТs law 47 54 59 149 152 159
Broglie, de 89Ч92
Brownian motion 62Ч65 73 99 170 196
Buchner 74
Bueherer 27
Caloric 31
Calorimeter 31
Canonical distribution 60 72 112 113 175Д 197
Canonical form 18 49 96
CaratheodbryТs principle 39 41 42
Caratheodory 38Ч39 143 146 149
Carnot cycle 143
Casirnir, H.B.G. 151
Cassirer, E. 208
Cauchy 19 21 26 44 114 134 140
CauchyТs equation 20 58 70 141
CauchyТs Theorem 160
Causality 3 5Ч9 17 72 76 95 101Ч103 120 124 126 129
Cause 47 92 101 109 120 129
Cause-effect relation 5 15 46Ч47 71
Cavendish 23
Chance 3 46Ч73 83 84 92 101 103 109 120 123
Chapman 56
Chapman and Cowling 56 58
Charge 104
Chemical equilibrium 146
Cheng, Kai Chia 207
Clausius 38
Collision cross-section 55 101 109 163
Collision cross-section, integral 56 59 68 72 163 180 183
Colloids 65
Commutation law 89 91 189
Commutator 94Ч97 190 193 203
Conduction of heat 54 58 65 70 114
Conservation of energy 19 119 164 182
Conservation of mass 20
Conservation of momentum 164 182
Constants of motion 112
Contact forces 21
Contiguity 9 12 16 17Ч30 74 103 120 124 140 141
Continuity equation 20 24 31 49 57 134 137 139 205
Continuous media 19Ч22 134
Convective derivative 21 49 137 206
Copernicus 12
Corpuscular theory of light 22
Correspondence principle 87 191 203
Cosmology 10 11
Coulomb forces 23Ч24 103 180
CoulombТs law 25 85 138
Cowling see УChapmanФ
Critical temperature 117
Curvature of space 28
Darwin, C.O. 54 155 160
Debye 65
Decay, law of 84
Degeneration of gases 197
Degeneration of gases, temperature 118
Demokritos 46
density 20 34 170 204
Density, function 113
Density, matrix (of operator) 106 111 193 199 204
Dependence 6 8 76 102 124
Descartes 11 16
Determinism 3 5Ч9 17 30 92 101 108 110 120 122Ч124 126
Dewar vessel 35
Diffraction 22 106
Diffusion 54 58 175
Dirac 91 92 95 113 141 189 191
DiracТs  -function 60 96 195 -function 60 96 195
Displacement current 25
Distribution function 50 71 96 106 176Ч180
Distribution function, law of Bose Ч Einstein 81
Distribution function, law of Maxwell Ч Boltzmann 51Ч54 57 60 78 82 112 167 181
Eckhart 151
Economy of thinking 207
Eddington 141
Ehrenfest 59 86
Eigenfunction 93Ч94 98 102 105Ч106 198Ч199
Eigenvalue 91 93Ч94 98 100 111Ч112 195
Einstein 15 27Ч30 62Ч65 75 78 80Ч83 88Ч90 92 100 101 112 116 122Ч124 141Ч143 151 170 172 173 175 197 202
EinsteinТsТlaw 75Ч76
electromagnetic field 22Ч26 138
Electromagnetic field, wave 25
Electron 84Ч92 95 103Ч105 116Ч118 141 199 207 208
Electron, spin 87 95 104 113
emission 82 86
Energy and mass 75
Energy and mass, and relativity 90
Energy in perturbation method 100 111
energy levels 82Ч85 87 91 198 199
Energy of atom 159
Energy of oscillator 77Ч79
Energy of system 36 47Ч48 53 147Ч148 171Ч173
Energy surface 62 170
Energy, density of 29
Energy, dissipation of 113
Enskog 56
Enthalpy 148
Entropy and probability 53 57 151 162 172
Entropy and temperature 116
Entropy from CaratheodoryТs theory 149Ч150
Entropy in chemical equilibria 148
Entropy of atom 159
Entropy, change of 43Ч44 71Ч72 183 186
Entropy, definition of 42 113Ч114 165
Entropy, establishment of 38
Equations of motion 18 21 49 57 95Ч96 103 116 137 182 203Ч206
Equations of state 36 48
Equipartition law 77 188
Erlanger Programm 104
Ether 19 22 74
EulerТs theorem 147Ч148
Excluded Middle 107
Exclusion principle 87
Faraday 23Ч24 140
Fermi 113 197
Fermi Ч Dirac statistics 113 199Ч1203
Field equations 28Ч29
Field of force 17
Field vector 140
Fitzgerald 27
| Fluctuation law 79 81
Fluctuations 151 170Ч176 196
Fock, V.A. 29 143
FOURIER 31
Fowler, R.H. 39 54 155 160
Franck 86
Free energy 44 61 148 159 167 186
Free energy, will 3 126Ч127
Frenkel, J. 65
frequency 88Ч90
Fresnel 22
Fuchs, K. 169
Functional equation of quantum statistics 112 197
Galileo 10Ч13 129
Gamma-function 155
Gas constant 48
Gauss 18 46 48 133
GaussТs theorem 134 165
Geodesic 29
Gerlach 87
Gestalten theory 209
Gibbs 58 60Ч62 65 66 112 149 167
Godel 108
Goeppert-Mayer 169
Goudsmit 87
Gravitation 13 17 26Ч30 124 133 134 141 142
Green, H.S. 65 68 100 115 120 169 181 183 185Ч186 195
Groot, de 151
Hamilton 18 91 191
Hamiltonian as matrix 89
Hamiltonian as operator 95
Hamiltonian in equations of motion 49Ч51 59 66 103 115
Hamiltonian in perturbation method 99 110 112
Hamiltonian in statistical mechanics 167
Hamiltonian of a particle 102 165 176 182
Hamiltonian of oscillator 77 188
Hamiltonian, definition of 18
Heat 31 34 36Ч37 119 147 157
Heisenberg 86 88Ч89 92 94 188Ч189 191 206Ч207
Helium 116Ч118
Helmholtz 61
Hermitian operator 93
Hertz, G., and Franck, J. 86
Hertz, H. 25
hilbert 56 108
Hoffmann, B. 29 143
HookeТs law 21
Huygens 22
Hydrogen atom 86
Hydrothermal equations 115 118 119 203
Ideal gas 47 50 54 112 149 159 171 197
Indeterminacy 101Ч109 119 208
Induction 6 7 14 46 64 84
Infeld, L. 29 143
Initial state 48
Integral of motion 98 100 110 112
Integral of motion, operator 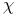 66 177 181 203Ч204 66 177 181 203Ч204
Integrating denominator 40Ч41 143Ч144
Inter-phenomena 107
Interference 22 106
Irreversibility 17 32 55 57Ч59 72 109 151 165 183
Isotherms 36 47 149
Jeans 77 81
Jordan, P. 188Ч189
Joule 33Ч36
Kahn, B. 169
Kelvin 38 46
Kepler 10 12 129 132
KeplerТs laws 12Ч13 129Ч132
kinetic energy 18 50 61 80 116 117 206
Kinetic theory, general 64Ч70 202
Kinetic theory, of gases 46Ч58 69 151Ч153 174
Kinetic theory, quantum 109Ч121
Kirkwood 69 176
Klein, F. 104
Kohlrausch 25 140
Lagrange 18
Lagrangian factor 156
Landau 120
Laplace 18 30
Laplace, differential operator 22
Laue, M.v. 206
Levi-Civita 28 142
Light quantum 82
LiouvilleТs theorem 49 52 58 60 66 68 159 181
Logic, three-valued 107Ч108
London, F. 206
Lorentz 27 80
Lorentz transformation 27
Lorentz, force 141
Loschmidt 58
Mach, E. 207
MacMillan 169
Magnetic field 138
Margenau, H. 143
Mass, gravitational 15 142
Mass, inertial 14 15 28 75 104 142
Matrix 83 88Ч89 91 97Ч98 100Ч101 115
Matrix, mechanics 90Ч91 188Ч189
Matter 74 83
Maxwell 24Ч27 50 51 54 56 62 112 124 138Ч141
MaxwellТs equations 24Ч26 75 124 138Ч141
MaxwellТs functional equation 153
MaxwellТs tensions 141
Mayer, B. 32
Mayer, J. 169
Mean free path 55
Mechanical equivalent of heat 32Ч33
Meixner 151
Mendelssohn 120
Meson 96 141 199
Method of ignorance 68
Michels 169
Michelson and Morley experiment 27
Minkowski 28 142
Molecular chaos 47 48 50 152
Moll 88
Momentum 18 29 75 86 90 91 116 136 152 184
Montroll 169
Multinomial theorem 160
Multiplet 88
Murphy, G.M. 143
Neumann, J.V. 109
Neutrino 199
Neutron 199
Newton 10Ч30 74 80 95 103 124 126 129 132 133 141
Non-commuting quantities 92Ч96
Non-Euclidean geometry 28
Non-linear transformation 27 142
Nucleon 199
Nucleus 84 103 199
Number density 97Ч98
Objectivity 124Ч125
Observational invariant 125 209
Oersted 25
Onsager, L. 151
Operator 91 93Ч95 97Ч98 100 188Ч189
Ornstein 88
Oscillator 77Ч79 85Ч86 116
Partition function 54 60 61 72 158Ч159 162 167 171 199
Pauli 87 141
PauliТs exclusion principle 199
Periodic system of elements 87
Perrin 63 176
Perturbation 99 110 193Ч196
Pfaffian equation 38Ч41 143Ч144 147
Phase rule 149
Phase space 49 51
phase velocity 22 90
Photo-electric effect 80Ч81
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -pomt
-pomt  -function
-function