|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Doi M., See H. Ч Introduction to Polymer Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Affine deformation assumption 48 61 110
Bead-spring model 7 66 71Ч75 106
Bead-spring model, Zimm modification 78 (see also УGaussian chainsФ)
Birefringence, effect of stress 54 55 104
Blends (of polymers) 38Ч40
Block copolymers 40Ч41
Block copolymers, microscopic phase separation in 40 41
Block copolymers, microscopic phase separation in domain size estimation 43Ч44
Bonds, meaning of term 2
Bonds, orientation, in stretched chains 51Ч53
Brownian motion and reptation model 96Ч99
Brownian motion in potential field 67Ч68
Brownian motion of harmonic oscillator 70Ч71
Brownian motion of spherical particles 66Ч67
Brownian motion, bead-spring model used 71Ч73
Brownian motion, Einstein relation 68Ч70
Brownian motion, features of Rouse model 73Ч75
Brownian motion, hydrodynamic interactions accounted for 78
Brownian motion, theory 66Ч71
Centre of mass (of polymer) 9
Centre of mass (of polymer), motion in concentrated solutions 96Ч97
Centre of mass (of polymer), motion in dilute solutions 73Ч74
Chemical gels 45
chemical potential 23Ч24
chi 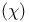 parameter 14 23 parameter 14 23
Co-operative diffusion coefficient 90Ч92
Co-operative diffusion coefficient, concentration dependence 92
Coexistence curves 28 29
Coexistence curves, polymer-polymer mixtures 38Ч39
Coil-globule transition 15 16
Concentration fluctuation correlation function 30
Concentration fluctuation correlation function, block copolymer uniform phase 41Ч43
Concentration fluctuation correlation function, miscible systems 39Ч40
Concentration fluctuations 29Ч38
Concentration fluctuations, dynamics 89Ч93
Configuration changes, in lattice model of reptation 100
Constitutive equation 103
Contractual motion (of polymer in tube) 102
Copolymers, block copolymers 40Ч41
Correlation function see УConcentration fluctuation...; segment pair...; time...; velocity correlation functionФ
correlation length 35
Correlation length, semidilute solutions 37
Critical point 28Ч29
Critical point, polymer-polymer mixtures 39
Critical temperature 28
Crosslinking reaction 46
Cylindrical domains, in block copolymers 40 41
Deformation gradient tensor 47 48
Degree of polymerization 1
Diffusion coefficient, concentrated solutions 90Ч92
Diffusion coefficient, dilute solutions 67 69
Diffusion equation, derivation of 86Ч87
Dilute solution, molecular motion in 65Ч88
Dilute solution, single polymer molecule studied 1
Directional order parameter tensor 51
Directional order parameter tensor and stress tensor 54Ч56
Directional order parameter tensor, calculation of 53
Dynamic light scattering 82Ч86 89
Dynamic scaling law 81Ч82
Dynamic structure factor, concentrated solutions 90 91
Dynamic structure factor, dilute solutions 82Ч83 84
Dynamic structure factor, initial decay rate 92Ч93
Edwards-de Gennes [Сtube'] model 59 94
Effective bond length 6
Einstein relation 68Ч70 71
Elastic free energy, rubber 47Ч48
Elasticity, Kuhn's theory 47Ч48 50
Elasticity, rubber 46Ч50
Elasticity, tube model 61Ч62
End-to-end vector 2
End-to-end vector, probability distribution function 3Ч4 48 97
Energy, Gaussian chain model 7
Energy, polymer-solvent interactions 12Ч13
Entangled polymer systems, molecular motion in 89Ч113
Entanglement effects, and tube model 93Ч94
Entanglement interactions 20 59Ч62 89
Entropy of mixing 38
Entropy, stretched chain 51
Escape time 101 (see also УReptation timeФ)
Excluded volume chain 10
Excluded volume chain, lattice model 12 13
Excluded volume chain, probability distribution function 11
Excluded volume effect 10Ч12 92
Excluded volume interactions 4 56 89
Excluded volume interactions in rubber elasticity 56
Excluded volume interactions, screening of 37
Excluded volume parameter 14 35
Extensional characteristic time 102
Extensional motion [of polymer in tube] 102
First normal stress difference 50
First normal stress difference coefficient, variation with shear rate 104
Flory Ч Huggins theory 21Ч23 38 56 63
Fluctuation-dissipation theorem 69
Fluorescence microscopy 65
Free energy of mixing 23 26Ч28 62Ч63
Free energy, phase-separated system 27
Free energy, rubber elasticity 47Ч48
Free energy, solutions 23 (see also УElastic...; Gibbs...; Helmholtz free energyФ)
Freely jointed chain 51 52
Gaussian chains 6Ч7 (see also УBead-spring modelФ)
Gaussian probability distribution 4 6
Gelation 45 46
Gels 45Ч64
Gels, swelling of 62Ч64
Gibbs free energy 23
Gibbs Ч Duhem relation 24
Harmonic oscillator, Brownian motion of 70Ч71
Harmonic spring 7
Helmholtz free energy 23
Hydrodynamic interactions 75 76Ч82 89
Hydrodynamic radius 16
Hydrodynamic radius, variation with temperature 16
Ideal chain 2Ч7
Ideal chain, meaning of term 5
Ideal chain, tension in 46
Internal motion of polymer chain 74Ч75
Isolated polymer molecule, properties 1Ч19
Kirkwood's equation 85
Kuhn's theory (of rubber elasticity) 47Ч48 50
Lamellar structure 41 43Ч44
Langevin equation 68 70 72 107
Lattice model 2 3
Lattice model, concentrated solutions 21 22 30
Lattice model, elasticity of rubber 46
Lattice model, excluded volume chain 12 13
Lattice model, reptation motion 94Ч96
Light scattering, dynamic effects 82Ч86
Linear viscoelasticity 105
Long-range interactions 6
Mean field approximation 16 21 32
Melts 20Ч21 29
Microscopic phase separation, in block copolymers 40 41
| Miscibility parameter 43
Miscible systems, correlation function 39Ч40
Mixing free energy 23
Mixing free energy and gel swelling 62Ч63
Mixing free energy and phase separation 26Ч28
Mobility matrix 70 76Ч78
Molecular motion in dilute solution 65Ч88
Molecular motion in entangled polymer systems 89Ч113
Monomer unit 1
Nematic interactions 57Ч59
Non-ideal chains 10Ч16
Non-linear viscoelasticity 112Ч113
Normal stress difference, first 50
Normal stress difference, second 50
Normalized coordinates 72 74 79 108
Optical anisotropy 54
Orientational order parameter tensor 51
Orientational order parameter tensor and stress tensor 54Ч56
Ornstein Ч Zernike type distribution function 10
Oseen tensor 77 84
Osmotic pressure 24Ч26
Osmotic pressure anomaly 25
Osmotic pressure, semidilute solutions 36Ч37
Overlap concentration 20 89
Pair correlation function see УSegment pair correlation functionФ
Partial chains 47
Partial chains, interactions between 56Ч62
Partition function 21
Phantom chain models 59
Phase diagrams, polymer solution 28
Phase diagrams, polymer-polymer mixtures 38Ч39
Phase separation (of polymers) 26Ч29
Phase transitions, microscopic, in block copolymers 40 41
Phase transitions, volume change in gel swelling 64
Physical gels 45
Polymer blends 38Ч40
Polymer gels 45Ч64
Polymer melts 20Ч21 29
Polymer melts, stress optical law 56fn. 104 107
Polymer, meaning of term 1
Potential field, Brownian motion in 67Ч68
Preaveraging approximation 78
Radius of gyration 8Ч9
Radius of gyration in semidilute solutions 37Ч38
Random phase approximation 32Ч34
Random walk model 2Ч4
Renormalization theory 16Ч17
Reptation model 89 94Ч96
Reptation model, Brownian motion studied using 96Ч99
Reptation model, fluctuation of tube length 101Ч103
Reptation model, viscoelasticity 109Ч113
Reptation time 99 101
Response function 31
Rotational motion, concentrated solutions 97Ч99
Rotational motion, dilute solutions 74
Rotational relaxation time 74 99
Rouse model 72
Rouse model, comparison with experiments 75
Rouse model, reptation motion 95
Rouse model, viscoelasticity 107Ч109
Rouse theory 71Ч73
Rubber 45
Rubber elasticity 46Ч50
Rubber elasticity, effect of entanglements 59
Rubber elasticity, Kuhn's theory 47Ч48 50
Rubber elasticity, tube model used 61Ч62
Rubber, elastic free energy 47Ч48
Scaling laws 16Ч19
Scaling laws, dynamic scaling law 81Ч82
Scaling laws, examples of application 18 35Ч38
Second normal stress difference 50
Segment pair correlation function 7Ч8 9Ч10 18 84
Segments, distribution in polymer chain 7Ч10
Segments, meaning of term 2
Segments, motion in dilute solution 74Ч75
Self-avoiding walk 10
Self-diffusion constant 91
Self-diffusion constant, calculation for concentrated solutions 93 97
Self-diffusion constant, concentration dependence 92
Self-diffusion constant, factors affecting 97 98
Semidilute solutions 35Ч38
Shape memory function 99Ч101
Shear elastic modulus 49
Shear flow 103 104 108
Shear strain 49
Short-range interactions, effects 4Ч6
Short-range interactions, meaning of term 6
Solutions see УConcentrated...; dilute...; semidilute solutionsФ
Solvent effects 12Ч14
Spherical domains, in block copolymers 40 41
Spherical particles, Brownian motion of 66Ч67
Spinodal line 28
Spinodal point 43
Spring constant (in bead-spring model) 7 47
Static structure factor 92
Stress optical law 51Ч56
Stress optical law coefficient 58
Stress optical law, applications 54Ч55 104
Stress optical law, formula 54
Stress optical law, range of applicability 54 104 107
Stress relaxation experiment, non-linear 112Ч113
Stress relaxation experiment, stress relaxation function 105 111
Stress relaxation experiment, viscoelastic, polymer liquids 110Ч112
Stress tensor and viscoelasticity 105Ч106
Stress tensor in shearing deformation 49
Stress tensor in uniaxial extension 50
Stress-strain relationship, rubber elasticity 48Ч50
Structural unit 1
Structure factor, dynamic 82Ч83 84 90 91
Structure factor, static 92
Thermal motion, and elasticity of rubber 46Ч47
Theta 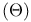 temperature 15 26 temperature 15 26
Time correlation function 87Ч88 89Ч90
Tube model 59Ч60
Tube model, entanglement effects 93Ч94
Tube model, rubber elasticity 61Ч62
Uniaxial extension 49 50
van der Waals forces, interactions due to 13 14
Van't Hoffs law 24Ч25 26
Velocity correlation function 66 67
Velocity correlation time 66
Viscoelasticity 103
Viscoelasticity, linear 105
Viscoelasticity, microscopic model of stress used 105Ч107
Viscoelasticity, non-linear 112Ч113
Viscoelasticity, phenomenological theory 103Ч105
Viscoelasticity, reptation model used 109Ч113
Viscoelasticity, Rouse model used 107Ч109
viscosity 104 105 109
Viscosity, relationship with molecular weight 109 111
Viscosity, variation with shear rate 104
Volume phase transition 64
Zimm theory 78Ч81
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



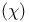 parameter
parameter 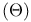 temperature
temperature