|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ryder L.H. Ч Quantum Field Theory |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
  annihilation 20 annihilation 20
action 160
Action, effective 160
Action, principle of least 80
Adiabatic hypothesis 165
Adjoint representation of group 113
Anderson 287
Annihilation experiments 20
Annihilation operator 131
Anomalous dimensions 326
Anomaly ABJ 368
Anomaly chiral (axial, triangle) 366Ч374 384
Anomaly, cancellation of anomaly 373Ч374
Anticommutation relation 139 455
Antiparticles 42Ч46 140
Asymptotic condition 221
asymptotic freedom 328
Asymptotic freedom of Yang Ч Mills theories 353Ч362 389
Auxilliary fields 444 450
Baker Ч Campbell Ч Hausdorff formula 199 222 460
Bare Lagrangian 324
Baryon number 6
BCS theory 297
Becchi Ч Rouet Ч Stora transformation 270Ч272
Bianchi identity 76 121
Bilinear Dirac quantities 46Ч48
Bohm Ч Aharonov effect 98Ч105 125
Boundary operator 70
Brouwer degree 410 418
c-number 159
c-number, anticommuting 210
Cabibbo angle 23
Callan Ч Symanzik equation 329 388
Casimir invariants 60 63
Chain 70
Charm 8
Chiral anomaly 366Ч374 389
Chirality 48
Coleman 288 379
Colour 4 18Ч22 121Ч124
Connected diagram 207
Connected diagram, generating functional for connected diagram 207Ч210
Connection coefficient 116
Connection form 76
Contravariant vector 25
Coset 290
Coulomb potential, modification of Coulomb potential 342
Coulomb scattering 170Ч172
Counter-terms 321Ч324
Covariant derivative 95 115
Covariant derivative in Weinberg-Salam model 300 301
Covariant vector 25
CP invariance, violation of CP invariance 422
CPT theorem 429
Creation operator 131
Delta functional 248
Derivative coupling 238
Differential form 70 78
Differential geometry 69Ч76
Dimensional regularization of 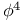 theory 313Ч318 388 theory 313Ч318 388
Dimensional regularization of QED 329Ч37 388
Dirac equation 29Ч42 77
Dirac equation, bilinear expressions 46Ч48
Dirac equation, electron magnetic moment 52Ч55
Dirac equation, negative energy states 44Ч45 138
Dirac equation, non-relativistic limit 52Ч55
Dirac field quantisation 137Ч140
Dirac field, qenerating functional for Dirac field 214
Dirac matrices 46-52
Dirac matrices in d dimensions 333
Dirac matrices, chiral representation 48 430
Dirac matrices, slash notation 52
Dirac matrices, standard representation 48
Dirac monopole 402Ч406 424
Dirac monopole quantisation condition 403
Dirac sea 45
Disconnected graph 207
Divergences in 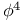 theory 308Ч313 theory 308Ч313
Divergences in QED 329Ч337
Divergences, infrared 308
Divergences, overlapping 321 349
Divergences, primitive 311
Divergences, superticial degree of divergences 309
Divergences, ultraviolet 309
Domain wall 306
Dotted and undotted spinors 39 434
Dual tensor 67
Duality transformation 74
dТAlembertian operator 27 73
effective Lagrangian 250 264
Effective potential 377Ч380 389
Effective potential, loop expansion of effective potential 380Ч382
Einstein 2
Einstein, field equations 26 88
Electromagnetic field quantisation 140Ч150 240Ч245
Electromagnetic field tensor 65 95
Electromagnetic interaction 5 305
Energy-momentum tensor 85 90
Energy-momentum tensor, canonical 88 125
Energy-momentum tensor, symmetric 88
Equal-time commutation relations 128 136
Euclidean group 63
Euclidean space 185
Euler Ч Langrange equation 84
Euler Ч Maseheroni constant 314
Exterior derivative operator 72
Exterior derivative, adjoint 74
Faddeev Ч Popov ghost 250
Faddeev Ч Popov technique 245Ч254 281
Faraday 2-form 75
Fermi 4
Fermi Golden Rule 234
Fermi theory of weak interactions 4 312
Fermion loop 217
ferromagnetism 283Ч284 286
Feynman formula 315
Feynman gauge 146 243 377
Feynman propagator 184Ч186 242 243
Feynman rules for scalar field 189 207 231Ч232
Feynman rules for spinor field 231Ч232
Feynman rules in axial gauge 254
Feynman rules in Lorentz gauge 250Ч253
Feynman rules in non-Abelian gauge theories 252Ч253
Feynman rules in non-relativistic quantum mechanics 166 167 170
Field quantization, canonical 126Ч152
Field quantization, path-integral 182Ч217 240Ч281
Fierz rearrangement formula 444Ч445
Fixed points 327
Flavour 122
Flavour, number of flavours 357
Form factor 16
Four-point function 204Ч206
Four-vector potential 65 94
Functional differentiation 173Ч174
Functional differentiation and fermions 210
Functional integral 159 172
Functional integration 186Ч188
Functional integration and fermions 210Ч217
Fundamental group 103 104
FurryТs theorem 332 350
Gauge fields, geometry of gauge fields 112Ч124
Gauge fields, ghost coupling 252
Gauge fields, masslessness of gauge fields 97 110
Gauge fields, matter coupling 253
Gauge fields, non-Abelian 2 105 118 241 245Ч254
Gauge fields, path-integral quantisation 240ff
Gauge fields, propagator 252 254
Gauge fields, self-coupling vertices 253
Gauge fields, spontaneous symmetry breaking 293ff
Gauge invariance 97
| Gauge principle 79 125
Gauge transformation 66
Gauge transformation of first kind 91 106
Gauge transformation of potential 116
Gauge transformation of second kind 93
Gauge transformation, global 93 284
Gauge transformation, local 93 294
Gauge, Feynman 146 243 377
Gauge, Landau 246 377
Gauge, pure 396 417
Gauge, R 376
Gauge, U 295 377
Gauge, Тt Hooft 375Ч377
Gauge-fixing term 146 242Ч243 250
Gaussian Integrals 179
Gell Ч Mann Ч Nishijima relation 14 15 300
General relativity 88 109 117 119 121
Generating functional 182ff 255
Generating functional for 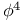 theory 200ff theory 200ff
Generating functional for connected diagrams 207ff
Generating functional for Dirac field 214
Generating functional for interacting fields 196ff
Generating functional, normalised 191 202
Generation problem 374
Generations of leptons 299
Ghost field 241 250 253 281
Ghost field and unitarity 276ff 281
Ghost field propagator 252
Ghost field, gauge field coupling 252
Glashow 4 282
Gluon 4 22 124
Goldstone 282 307
Goldstone boson 286 287 293 294
Goldstone theorem 287Ч93 306
Graded Lie algebra 458
Grand Unified Theory (GUT) 5 6 427
Grassmann algebra 210 214 239
Grassmann quantities 433 454
Gravitation 2
Gravitational field 2
Gravitational radiation 2
Graviton 2
GreenТs function for free scalar particle 189ff 255
GreenТs function for Schrodinger equation 164
GreenТs function, advanced and retarded 219
GreenТs function, connected 255
GreenТs function, generating functional for GreenТs function 189ff
Gupta Ч Bleuler formalism 150 294
Hausdorff formula 199 222 460
Hawking effect 223(f)
Hedgehog solution 407
Helicity 42
Higgs 282
Higgs field 301
Higgs phenomenon 294ff 307 397
High temperature restoration of symmetry 306 307
Hodge star operator 74
Homotopic paths 103
Homotopy group 104 125
Homotopy group, first 104 399
Homotopy group, second 410
Homotopy group, third 414
HuygensТ principle 155
Inelastic scattering 16Ч17
Instanton 414ff 425
Interacting fields, generating functional for interacting fields 196ff
Invariant function 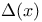 136 136
Isospin 13 105 111
Isospinor 113
Jacobi identity 113
Jets 20 22
Kink, sine-Gordon 391ff
Klein Ч Gordon equation 27ff
Klein Ч Gordon field 126ff
Klein Ч Gordon operator 218
Lamb shift 342
Landau gauge 243 377
Landau singularity 346
Landau-Ginzburg free energy 297 397
Laplacian operator 73
Least action, principle of 80
Left derivative 210
Legendre transformation 258
Legendre transformation, geometrical interpretation 260Ч262
Legendre transformation, thermodynamic analogy 262Ч263 281
Lepton 6
Lepton generations 299
Lepton number 6
Lepton-hadron symmetry 374
Lie algebra 57 63
Lie algebra, graded 458
Lie group 31
Lightlike interval 25
Lightlike particles 63
Little group 61
London equation 297
Longitudinal photons 147
Loop expansion 317Ч318 380Ч382
Loop fermion 217
Loop ghost 280
Lorentz formula 98
Lorentz gauge 66 141
Lorentz gauge quantisation 145ff
Lorentz gauge, Feynman rules in Lorentz gauge 250ff
Lorentz group 36ff 77 427ff
Lorentz group, boost matrix 36Ч37
Lorentz group, generators 37 57Ч59
Lorentz group, inhomogeneous 40 56
Lorentz group, Lie algebra 57Ч59 427Ч428
LSZ condition 221
Magnetic flux 396Ч7
Magnetic moment, anomalous 343Ч345 388
Magnetic moment, electron 1 52Ч55
Magnetic moment, muon 345 388Ч389
Magnetic monopole (charge) 110
Magnetic monopole, Dirac 402ff
Magnetic monopole, Тt Hooft Ч Polyakov 406ff
Majorana condition 435
Majorana condition, spinor 429
Mandelstam variables 316
Mass and Poincare group 56 60
Mass, neutrino 42
Mass, physical (renormalised) 204 257
Mass, zero limit 63Ч64
Maxwell equations 64ff 69ff 96 110 121
Meissner effect 297Ч298
Metric tensor 26
Metric tensor in spinor space 432
Muon, magnetic moment 345 388Ч389
n-point function 191 255
n-point function, irreducible 209
Nambu 282
Negative energy in Dirac equation 45 138
Negative energy in Klein-Gordon equation 29
Neutral current process 305
Neutrino mass 42
Nielsen Ч Olesen flux line 398Ч399
NoetherТs theorem 85Ч87 125
Non-Abelian gauge fields (Yang-Mills fields) 2 105 118 241 245Ч254
Non-Abelian gauge fields, asymptotic freedom of non-Abelian gauge fields 353Ч362 389
Non-Abelian gauge fields, Faddeev Ч Popov method 245Ч254
Non-Abelian gauge fields, renormalisability 276
Non-Abelian gauge fields, renormalisation of non-Abelian gauge fields 302ff 375ff
Normal ordering 132 145
Normalisation of generating functional 191 202
Normalisation, covariant 133
Normalisation, non-covariant 133
Null interval 25
Number operator 130
O(3) 30ff
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



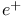
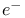 annihilation
annihilation 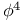 theory
theory