|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rubinoff M., Yovits M. Ч Advances in Computers, Volume 14 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Mode behavior, user-defined 67Ч69
Mode-behavior definition facility, in programming 74
Modularization, "tuning" process and 47
MRAM 34 see
MRAM, differentiated from RAM 31Ч32 39
MRAM, simulation of Turing machines by 38
Multiplexing, in pulse code modulation 219
Munro, I. 2 42 141 142 166 185
Myhill, J. 27 43
N-TAPE languages 4
National Bureau of Standards 233
National Computer Conference 234
National Science Foundation 233
Natural languages, advances in study of 77Ч79
Naval Ship Research and Development Center 233
Nee, C.J. 257 272
Neumann, P.G. 239 271
Neurophysiology, TSP applications in 227
Nonarithmetic objects, aids for 72
Nonassociative products, binary trees and 149Ч158
Nondeterministic lba 28
Nondeterministic tape computations 27Ч30
Nonexpert programmer, aids for 69Ч72
Nonterminal set, left or right recursive 95
NP, problem in 2Ч3
NP-complete language 13Ч16
NP-complete language, defined 10
NP-complete language, universal 10
NP-TAPE language 17Ч18 27
NP-TIME language 8Ч9
Off-line algorithm, in parsing of general context-free languages 111
Off-line computation, for Turing machine 104
Office of Naval Research 233
Ohio State University 233
Olaravria, J.M. 229
On-line algorithm, in parsing of general context-free languages 111
On-line computation, for Turing machine 104
On-line recognition algorithm, Earley's algorithm as 127
Oppen, D.C. 26 43
Optical bundles, in bundle processing 227
Organick, E.I. 232 239 272
P = NP? problem 3 9 41
Pager, D. 139 185
Papoulis, A. 229
Parsing algorithm for context-free languages 112Ч115
Parsing algorithm in Earley's algorithm 136Ч139
Parsing of general context-free languages 77Ч184
Parsing, Cocke Ч Kasami Ч Younger algorithm in 107Ч122
Parsing, Earley's algorithm in 122Ч129
Parsing, hardest context-free language and 176Ч180
Parsing, linear context-free language and 110Ч121
Parsing, recognition algorithm in 107Ч112
Parsing, rules in 83
Parsing, time and space bounds in 181Ч184
Parsing, upper bound for 176
Parsing, Valiant's algorithm in 140Ч176
Parsing, Valiant's lemma and 149Ч166
PCM see "Pulse code modulation"
PENDING variable, in Earley's algorithm 133Ч136
Pennsylvania, University of 233
Peterson, W.W. 188 229
Petrovic, R. 191 229
Photocell, random pulses in 226
Physical protection mechanisms, in information security 236
Pirotte, A. 139 184
PL/1 programs in information security 232
PL/1 programs in information security in large-scale programs 52 54
Poigjaner, L. 228
Poppelbaum, W.J. 187 190 199 202 216 229
POSTCOMP (portable stochastic computer), examples of 197Ч198
PPL system, vs APL system 54Ч55
Pratt, V. 6 31 39 43
PREDICT function, in Earley's algorithm 123 128 130 133Ч134
Pressburger arithmetic, decision procedures for 25Ч26
Pressburger, M. 25 26 43
Privacy protection, in information security 236Ч238
Probability theory, arithmetic operations and 191
Probert, R.L. 140 145 184
Procedure protection, in information security 236
Program reduction 70Ч72
Programmer for medium-scale programs 50Ч51
Programmer, aids for nonexpert type of 69Ч72
Programming 45Ч75
Programming and production of complex programs 72Ч75
Programming languages, spectrum of 45
Programming system, formation of 72Ч75
Programming, aids in 69Ч72
Programming, basic language in 58Ч63
Programming, BREAK procedure in 65
Programming, case statement in 65Ч66
Programming, changes in 73
Programming, classes of programs in 48Ч53
Programming, closure in 70Ч72
Programming, constraints in 74
Programming, ECL procedures in 63Ч65
Programming, extended modes in 66Ч69
Programming, extensible languages in 53Ч54
Programming, facilities for small-scale programs in 53Ч55
Programming, mode in 58Ч59
Programming, mode-behavior definition facility in 74
Programming, mode-valued expression in 62
Programming, program reduction in 70Ч72
Programming, rewrite facility in 75
Programming, software tailoring and packaging in 69Ч70
Programming, testing aids in 75
Programming, user-defined mode behavior in 66Ч69
Programming, variables in 58
Programs, classes of 48Ч52
Programs, complex 72Ч75
Programs, large-scale 51Ч53
Programs, medium-scale 50Ч51
Programs, small-scale 49Ч50
Protection thresholds, in information security 255
PTAPE languages 3Ч4 17 27
PTAPE languages and first-order propositional calculus 21
PTIME language family 5Ч8
PTIME language family vs PTAPE, for Turing machines 30Ч31
PTIME language family, MRAM and 40
Pulse code modulation, multiplexing in 219
Pulse code modulation, statistical representation in 188Ч190
Pulse code modulation, time stochastic and burst processing systems in 188Ч190
Pulse, appearance of in time stochastic processing 190
Quantized quasi-random analog signal 196
Quasi-noise, in phototransistor output encoding 200
Quasi-random number generator 196
Quasi-random number sequence, defined 196
Quasi-random number sequence, generation of 195Ч197
Rabin, M.O. 6 26 31 39 42 43
RAM model 34Ч35 see
Rand Corporation 233
Random access machines vs Turing machine 103 105Ч106 115Ч116
Random access machines, complexity measures for 32
Random access machines, feasible computations with 30Ч39
Random access machines, FIND function in 33Ч35
Random pulses, examples of 226Ч227
Random pulses, examples of, generation of 195Ч197
Rangel, J.L. 24 43
RASCEL (regular array of stochastic computing elements), as time stochastic machine 198Ч199
Recognition algorithm, Chomsky normal form of grammar and 107Ч108
Recognition, as transitive closure problem 141
Reed, S.K. 234 272
Resource Secure System 232
Ribeiro, S.T. 190 229
Right recursive nonterminal set 95
Ring mechanism, in information security 234 237
Ring, D. 187 205 211 229
Roberts, G.T. 196 228
| Rogers, J., Jr. 6 10 27 43
RSS see "Resource Secure System"
Ruzzo, W.L. 181 184
Ryan, L.D. 194 199 229
SABUMA (safe bundle machine) 212Ч214
Saltzer, J.H. 237 272
Saviteh, W.J. 4 27 43
Scherr, A.L. 233 272
Schroeder, M.D. 237 272
Schugurensky, C.M. 229
Second-order logical theory 26
Security-atoms, in information secure systems 260Ч261
Semantic connection, in logical access control mechanisms 242
Shank, H. 10 16 42
Siljak, D. 191 229
Simon, J. 6 30 31 42 43
Single-attribute data protection 250Ч252
Single-attribute data protection, information secure systems with 257Ч262
Small-scale programs, facilities for 53Ч55
Snelling, M. 139 184
Software, tailoring and packaging of 69Ч70
Solovay, R. 39 41
Southern California, University of 233
Space complexity, Turing machine and 103Ч104
Spring Joint Computer Conference 231
SRPS see "Synchronous random pulse sequence"
Standish, T.A. 53 76
Statistical processing, outlook for 226Ч228
Statistical processors 187Ч228
Statistical processors, bundle processing and 205Ч211
Statistical processors, ergodic processing of 205Ч211
Statistical processors, fluctuations and precision of stochastic sequences in 194Ч195
Statistical processors, generation of random and quasi-random sequences in 195Ч197
Statistical processors, time stochastic machines and 197Ч205
Statistical representation 187Ч190
Statistical representation, autonomous processing element system in 202Ч205
Statistical representation, block sum register in 218
Statistical representation, burst processing in 188 216Ч226
Statistical representation, defined 187
Statistical representation, pros and cons of 187Ч190
Statistical representation, time averaging in 187
Statistical representation, time stochastic processing in 188
Statistical representation, transducer problem in 189Ч190
Statistical representation, weighted vs unweighted systems in 187
Stearns, R.E. 22 43 183 185
Stochastic processing, bundle processing and 205
Stochastic sequences, fluctuations and precision of 194Ч195
Stochastics, "fundamental trick" of 191
Stockmeyer, L.J. 2 4 6 8 21 31 39 42 43
Strassen's algorithm, boolean matrix multiplication and 145Ч149
Strassen, V. 140 145 185
Structural programming, clear programs and 72
Structural programming, defined 46Ч47
Structural programming, modularization in 46Ч47
Structurally ambiguous grammar 82
Submatrices, central 158Ч160
Supervisory calls, in information security 237
Synchronous random pulse sequences in time stochastic processing 190Ч194
Synchronous random pulse sequences, generation of 195Ч197
Synchronous random pulse sequences, mask and complementary mask in 227
Synchronous random pulse sequences, subtraction and division of 192Ч193
Szymanski, T. 8 42
Taft, E.A. 53 55 76
Tape computations, nondeterministic 27Ч30
Tape-complete language 18
Tape-complete language, construction of 20
Tape-complete problem, Kleene star in 19Ч20
Tarjan, R.E. 20 42
Tausworthe, R.C. 196 229
Time and space bounds for Earley's algorithm 128Ч136
Time and space bounds in parsing of general context-free languages 181Ч184
Time slip cascade multiplier 223
Time slip register 223
Time stochastic machines, examples of 197Ч205
Time stochastic processing for numerical and communication purposes 189
Time stochastic processing in neurophysiology 227
Time stochastic processing in statistical representation 188
Time stochastic processing, arithmetic in 188
Time stochastic processing, hydrodynamic simulation and 227
Time stochastic processing, overview of 190Ч194
Time stochastic processing, pulse in 190
Time stochastic processing, synchronous random pulse sequence in 190Ч194
Time-averaging, in statistical representation 187
Time-Sharing Option 232
TM see "Turing machine"
Tompa, F.W. 76
Torii, K. 107 185
Townley, J.A. 75 128 185
TRANS(A) procedure 167Ч168
Transducer problem, in statistical representation 189Ч190
TRANSFORMATRIX, as time stochastic machine or parallel processor 199Ч202
Transitive closure problem, recognition as 141Ч145
TRW, Inc. 232Ч233
TSO see "Time-Sharing Option"
TSP see "Time stochastic processing"
Turing machine and hardest context-free language 176
Turing machine and P=NP? problem 41
Turing machine for NP-complete language 10
Turing machine in parsing of general context-free languages 115Ч119
Turing machine in polynomial tape or time 17
Turing machine vs random access computer 115Ч116 176
Turing machine, 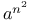 input for 104 input for 104
Turing machine, accepting states and 103
Turing machine, algorithmic analysis and 104
Turing machine, deterministic vs.nondeterministic 5 12 20
Turing machine, effectively computable function and 6Ч7
Turing machine, finite state control for 103
Turing machine, implementation of in Earley's algorithm 139
Turing machine, instantaneous description in 13
Turing machine, linearly bounded automaton and 27Ч30
Turing machine, MRAM languages and 34Ч35
Turing machine, NP problem and 2Ч3
Turing machine, off-line computation in 104
Turing machine, PTIME vs PTAPE for 30Ч31
Turing machine, simulation of by MRAM's 38
Turing machine, space complexity of 103
Turing machine, tape length in 24Ч25
Turing machine, valid and nonvalid computations for 13Ч15 19 22
Ullman, J.D. 2 5 8 9 13 22 28 32 41 42 82 83 103 106 116 127 132 166 177 182 183 184 185
Unambiguous grammar 82
Universal NP language 10
Unweighted systems, in statistical representation 187
Uriivac, Inc. 233
User-row approach, in information security 239
Valiant's algorithm 140Ч176 181
Valiant's algorithm and recognition as transitive closure problem 141Ч145
Valiant's algorithm in computing 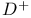 in less than O(n^{3}) time 161Ч176 in less than O(n^{3}) time 161Ч176
Valiant's algorithm, Strassen's algorithm and 145Ч149
Valiant's lemma 149Ч166 170Ч172
Valiant's lemma, statement and proof of 161Ч166
Valiant, L.G. 79 140 141 185
Van Horn, E.C. 234 271
Vernier divider, principle of 224
Vernier encoding and addition, in burst processing 225
von Neumann, J. 187 230
Warshall, S. 52 76
Watergate affair, information security and 231
Wegbreit, B. 56 71 75 76
Weighted systems in statistical representation 187
Wimbrow, J.H. 233 272
Winograd, T. 76
Wirth, N. 76
Wo, Y.K. 199 202 230
Wong, E. 259 272
World-Wide Military Command and Control System 232
Yamada, H. 19 43
Younger, D.H. 79 107 185
Zirphile, J. 229
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



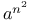 input for
input for 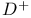 in less than O(n^{3}) time
in less than O(n^{3}) time