Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Meyer-Ortmanns H., Reisz T. — Principles of phase structures in particle physics
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Principles of phase structures in particle physicsАвторы: Meyer-Ortmanns H., Reisz T. Аннотация: The phase structure of particle physics shows up in matter at extremely high densities and/or temperatures as they were reached in the early universe, shortly after the big bang, or in heavy-ion collisions, as they are performed nowadays in laboratory experiments. In contrast to phase transitions of condensed matter physics, the underlying fundamental theories are better known than their macroscopic manifestations in phase transitions. These theories are quantum chromodynamics for the strong interaction part and the electroweak part of the Standard Model for the electroweak interaction. It is their non-Abelian gauge structure that makes it a big challenge to predict the type of phase conversion between phases of different symmetries and different particle contents. The book is about a variety of analytical and numerical tools that are needed to study the phase structure of particle physics. To these belong convergent and asymptotic expansions in strong and weak couplings, dimensional reduction, renormalization group studies, gap equations, Monte Carlo simulations with and without fermions, finite-size and finite-mass scaling analyses, and the approach of effective actions as supplement to first-principle calculations.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2006Количество страниц: 702Добавлена в каталог: 27.09.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Higgs transition 188 Higgs-boson mass 409 Higgs-field condensate 195 High-temperature expansions 261 Hilbert space 230 233 235 Histogram method 585 Hopping parameter 78 188 255 275 284 Hopping propagator 275 Hopping-parameter expansion 229 502 HTL-action 387 HTL-perturbation theory 387 Hubbard — Stratonovich transformation 483 Hubble time 619 Hybrid Monte Carlo 551 Hydrodynamic equations 626 Hypercubic lattice 206 Hysteresis 124 557 Impact parameter 647 Improved actions 591 Improvement program 321 Incidence matrix 301 Infrared behavior 162 Infrared dimension 110 Infrared problems 244 Instanton coupling 607 instantons 169 Interaction measure 580 Interface tension 554 582 Interference region 645 Intermittency 654 Intermittency analysis 652 Intermittency indices 655 Internal energy 18 42 43 Internal-energy density 124 576 581 IR-artifacts 580 IR-degree 342 345 IR-power counting 339 371 IR-problem 509 IR-singularity 187 Irreducible representation 231 Isentropic expansion 646 Ising ferromagnet 120 Ising model 274 653 Joint probability distribution 122 201 Kirkwood — Salsburg equations 256 Landau gauge 360 375 455 Landau gauge, STALG 350 Landau — Ginzburg model 596 Landau's free energy 21 Landau's mean-field theory 105 Langevin algorithm 552 Large-field domains 88 Large-N expansion 40 477 485 Latent heat 123 147 170 184 201 582 Lattice action 318 Lattice cutoff 206 Lattice gauge theory, SU(2) 264 Lattice gauge theory, SU(N) 277 Lattice gauge theory, Z(2) 264 Lattice-difference operator 26 Lattice-embedding number 292 LCE graphs classification 295 Lebowitz inequality 56 Lee — Yang zeros 201 Legendre transformation 28 50 296 311 389 528 Length scales in QCD 5 Limit cycles 104 Limit distribution 96 Linear hadron collider 621 Linked cluster expansions 33 44 229 Linked cluster expansions as convergent expansions 273 Linked cluster expansions in a finite volume 141 Linked clusters in linked cluster expansions 255 Linked clusters in polymer expansions 255 Liquid/gas system 179 Little bang 6 620 Lorentz boost 626 Lorentz gauge 349 374 Magnetic mass 187 Magnetic screening mass 340 354 Magnetic-mass problem 185 244 247 357 373 377 378 390 414 magnetization 18 Markov process 550 Mass gap 267 346 360 434 558 Mass resummation 397 Mass sensitivity 605 Matching conditions 434 510 Matsubara decomposition 422 Matsubara frequencies 509 Mean-field approximation 25 Mean-field equation 52 Meissner effect 618 Mermin — Wagner theorem 482 Meson, masses 606 Meson, octet 607 Metastability 124 Metastable states 625 Metropolis algorithm 550 Microcanonical algorithm 552 Minimal subtraction scheme 425 Model, O(4) 597 Model, SU(2) Higgs 62 188 390 408 414 Model, Z(2) Higgs 261 Model, Z(3)-Potts 605 Modes, bosonic 509 Modes, fermionic 509 Modes, heavy 509 Modes, light 509 Modes, nonstatic 359 509 Modes, static 359 509 Modes, superheavy 509 Moebius transformation 90 Molecular-mean field approximation 33 Moment of a distribution 140 Momentum cutoff 390 481 Monotony criterion 144 146 Monte Carlo simulations 123 Monte Carlo simulations in QCD 149 Multi-grid approach 91 Multi-histogram technique 197 Multicanonical algorithm 554 Multigrid algorithm 554 Multiplicity fluctuations 574 n-point correlation functions 26 n-point Green functions 27 161 n-point susceptibility 141 No-go theorem 218 Nonabelian gauge theory 214 Nonexceptional momentum 341 Nonstatic modes 418 429 Normalization conditions 365 Nucleosynthesis 3 One-particle irreducible 29 One-particle irreducible, 1PI 297 One-point function 108 Order parameter 18 172 244 449 450 586 Order parameter, parity condensate 482 Order-parameter distribution 124 Order-parameter field 105 Orthogonality relation for characters 262 Osterwalder — Schrader axioms 308 Osterwalder — Schrader positivity 233 267 Osterwalder — Seiler theorem 266 Out-of-equilibrium process 184 Overrelaxation algorithm 554 P4-action 591 Pade approximants 305 Parity condensate 482 Partition function 26 Partition function, 208 Partition function, finite temperature 239 path integral 230 240 Path-integral representation 520 Pauli — Villars cutoff 423 Peierl's — Bogoliubov inequality 42 Percolation 596 Percolation picture 226 Percolation transition 615 Peter — Weyl theorem 236 Phase diagram, SU(2) Higgs 189 Phase structure of QCD 180 Phase transition 17 Phase transition, field driven 18 Phase transition, first order 17 389 Phase transition, mass driven 18 Phase transition, n-th order 19 Phase transition, O(N) model 529 Phase transition, second order 17 279 304 390 521 Phase transition, temperature driven 18 Physical mass point 181 571 Physical singularity 278 Pion gas 622 Pion interferometry 650 Pions 604 636 Planar graphs 482 Planck mass 620 Plasma masses 187 376 Plasma phase 584 632 642 Plasmon mass 414 Pole mass 29 55 106 281 426 Polyakov loop 171 231 560 586 Polyakov-loop correlation 451 Polyakov-pair correlation 560 Polymer activity 253 Polymer expansions 252 Polymer, connected 253 Polymer, disjoint 253 Polymer, partition function 254 Potts model 174 274 Potts model, q-state 147 Power counting in the continuum 330 Power counting on the lattice 329 Power-counting theorem 309 518 545 Power-counting theorem on the lattice 334 Power-counting theorem, statement 323 Pressure, heavy-ion collisions 626 Projection operator 237 Pseudo-critical parameters 116 130 Pseudofermion method 551 Pure gauge theory 154 Pure SU(2) gauge theory 71 QCD, continuum Lagrangian 153 QCD, partition function 153 QCD, sum rules 247 252 Quark condensate 150 Quark masses 596 Quark masses, critical 610 Quark-antiquark potential 450 quark-gluon plasma 449 Quasiparticles 379 387 Quench 657 Quenched limit 170 R-algorithm 562 Radius of convergence 266 278 304 Rapid crossover 626 Rapidity distributions 635 Rapidity range 650 Ratio criterion 306 Real photons 648 Reconstruction theorem 238 Regularization 309 Renormalizability 209 Renormalizability, proof of 544 Renormalization 309 Renormalization constant 29 Renormalization for massless fields 343 Renormalization group 37 356 597 Renormalization group, definition of 93 Renormalization group, exact 526 Renormalization group, flow equations 531 Renormalization group, introduction 80 Renormalization group, rigorous 91 104 Renormalization on the lattice 336 Renormalization procedure at finite T 360 Renormalization procedure, gauge theories 374 Renormalization theory 209 Renormalization-group equations 191 224 518 Renormalization-group equations, exact 86 Renormalization-group transformation linearized 101 Renormalized, action 318 Renormalized, action, in bare parameters 447 Renormalized, Green functions 319 Renormalized, mass 29 Renormalized, moment 299 Renormalized, vertex functions 313 Renormalons 252 Rescattering effect 638 Resummation techniques 358 Root criterion 306 Saddle-point approximation 24 40 Saddle-point expansion 248 Scalar field theory 390 Scalar field theory on the lattice 207 Scalar field theory, 48 Scalar field theory, 344 Scalar field theory, 198 519 Scalar field theory, 26 287 Scalar field theory, N-component 45 Scalar field theory, O(N) 146 158 Scaling fields 120 Scaling relations 87 Scaling relations, connected correlation function 106 Scaling relations, free energy 113 Scaling variable relevant 100 Scaling violation 320 Scaling, shift in 132 Scaling-sum rules 20 105 Scaling-sum rules, violation of 110 Schroedinger formalism 231 Schur's lemma 263 Schwinger functions 230 screening 448 Screening, chromo-electric 194 Screening, chromo-magnetic 194 Screening, color-electric 244 450 Screening, length 55 Screening, mass 244 450 Screening, mass, color-electric 420 Screening, mass, definition 449 Screening, mass, in full QCD 473 Second moment 28 51 Selfsimilar cascades 656 Semiclassical approximation 247 Sigma model, linear 597 Sigma model, linear 596 Sigma model, linear 156 Sigma model, nonlinear 596 Singularity, 123 144 Singularity, algebraic 123 144 Soft-loop momenta 385 Space-time rapidity 627 636 species doubling 218 321 Specific heat 18 Sphaleron rate 184 204 Spin glass 39 78 276 Spinodal decomposition 583 Spontaneous symmetry breaking 21 126 Stability criterion 167 staggered fermions 332 452 572 Static modes 418 429
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



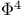 -theory
-theory 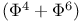
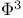
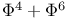
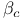
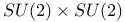
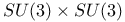
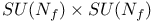
 -function
-function