  222 222
  118 118
  , copolyesters 139 , copolyesters 139
  , rearing 222 , rearing 222
  , active site determinations 284Ч285 , active site determinations 284Ч285
  , mutation studies 279 , mutation studies 279
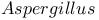 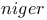 , phytase isolation 278Ч279 , phytase isolation 278Ч279
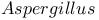 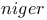 , phytase production with 266Ч268 , phytase production with 266Ч268
  , sequence studies 281Ч284 , sequence studies 281Ч284
  243Ч246 243Ч246
  246Ч248 246Ч248
 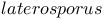 248Ч250 248Ч250
  115Ч116 115Ч116
 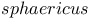 257 257
 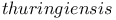 257 257
  , application 4Ч6 , application 4Ч6
  , as biological insecticide 16Ч17 , as biological insecticide 16Ч17
  , description 1Ч4 , description 1Ч4
 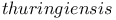 , genes see " , genes see " genes" genes"
  , novel strains, construction 17Ч18 , novel strains, construction 17Ч18
  , protein structure 10Ч14 , protein structure 10Ч14
 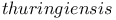 , recombinant strains, construction 18Ч19 , recombinant strains, construction 18Ч19
  , resistance 25Ч27 , resistance 25Ч27
 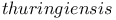 , resistance management via refuges 28Ч29 , resistance management via refuges 28Ч29
 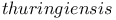 , resistance management via rotations 27Ч28 , resistance management via rotations 27Ч28
  , resistance management via toxin mixtures 28 , resistance management via toxin mixtures 28
  , toxins, classification 6Ч10 , toxins, classification 6Ч10
  , toxins, delivery systems 21Ч26 , toxins, delivery systems 21Ч26
 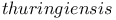 , toxins, dosage 29Ч30 , toxins, dosage 29Ч30
 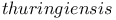 , toxins, mechanisms of action 14Ч16 , toxins, mechanisms of action 14Ч16
 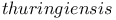 , vectors, baculoviruses as 21 , vectors, baculoviruses as 21
  231Ч233 231Ч233
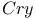 genes 8Ч10 genes 8Ч10
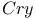 genes in Bt strain construction 18Ч19 genes in Bt strain construction 18Ч19
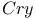 genes in transgenic microbe construction 19Ч20 genes in transgenic microbe construction 19Ч20
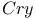 genes, expression in plants 22Ч25 genes, expression in plants 22Ч25
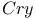 genes, insect-tolerance and 31Ч33 genes, insect-tolerance and 31Ч33
 genes, screening 12Ч14 genes, screening 12Ч14
 genes, structure 10Ч12 genes, structure 10Ч12
  , ,  222 222
  233Ч236 233Ч236
  229Ч231 229Ч231
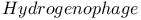  118 118
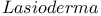  227Ч228 227Ч228
  228 228
  158 158
  see " see " 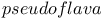 " "
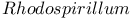  118 158Ч159 118 158Ч159
  224Ч226 224Ч226
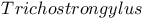  228Ч229 228Ч229
 -Butyrolactone polymerization 114Ч115 -Butyrolactone polymerization 114Ч115
 -Ketothiolases 140 -Ketothiolases 140
 -Lactone, polymerization 111Ч113 -Lactone, polymerization 111Ч113
 -Endotoxins 30 -Endotoxins 30
Acetoacyl-CoA reductase 140Ч142
Acid phosphatase, active site determinations 284Ч285
Acid phosphatase, characterization 279Ч281
Acid phosphatase, cloning 288Ч291
Acid phosphatase, enzyme engineering studies 285Ч288
Acid phosphatase, immobilization studies 291Ч292
Acid phosphatase, sequence studies 281Ч284
Acidification 82
Activated sludge 164Ч165
Aeration 63
Agitation 63
Archaebacteria, carbohydrate-utilizing halophilic 125
Bacillus spp., Bacillus alvei systematics 241Ч243
Bacillus spp., biology 256
Bacillus spp., candidate cultures 252
Bacillus spp., fermentation 252Ч253
Bacillus spp., general considerations 221Ч222
Bacillus spp., Indian meal moths and 228
Bacillus spp., products from 255Ч256
Bacillus spp., sources 221Ч222
Bacillus spp., strain comparison techniques 236Ч241
Bacillus spp., targets 222
Bacillus spp., toxins 253Ч256
bacteria see also "Archaehacteria"
Bacteria in lactic acid production 50Ч54
Bacteria nitrogen-fixing 122Ч125
Bacteria PHAs, biosynthesis 128Ч135
Bacteria, phytase sources 272
Baculoviruses, as Bt vectors 21
batch processes 65Ч66
Beetles see "Cigarette beetles"
Biodegradable polyesters 169Ч173
Biodegradable polyesters, application 169Ч173
Biodegradable polyesters, classification 98Ч100
Biodegradable polyesters, granules 146Ч151
Biodegradable polyesters, microbial production 158Ч164
Biodegradable polyesters, natural 100
Biodegradable polyesters, synthetic 100Ч104
Biodegradable polyesters, terminology 107
Biodegradation 173Ч176
Biodegradation, approaches 176Ч179
Biodegradation, bacterial 176Ч179
Biodegradation, Biopol 181Ч182
Biodegradation, enzymatic 179Ч180
Biodegradation, extracellular 176
Biodegradation, factors effects 182Ч187
Biodegradation, hydrolytic 179Ч180
Biodegradation, in natural environments 181
Biodegradation, methanogenic 176
Biodegradation, PHA depolymerases in 187Ч194
Biodegradation, polymer composition and 187
Biodegradation, synthetic polyesters 194Ч198
Biodegradation, temperature and 183Ч184
Biodegradation, under aerobic conditions 185
Biological controls 257Ч258
Biological insecticides,   as 16Ч17 as 16Ч17
Biopolymers, description 97Ч98
Biting blackfly larvae 224Ч226
Bt see " 
Centrifugation 82Ч83
Cigarette beetles 227Ч228
Clean Water Act 45
Conjugation, in Bt strains construction 17Ч18
Continuous membrane cell recycle systems 68Ч71
Continuous stirred tank reactor systems 66Ч68
Copolymer P(HB-co-HV), polymerization 113Ч114
Cornstarch, phytase synthesis and 274Ч278
Cutin 100
Dialysis systems 77Ч79
Distillation, lactic acid 83
Dutch cloning studies 290
Feed studies 292Ч295
Fermentations   242 242
Fermentations   244Ч246 244Ч246
Fermentations   246Ч247 246Ч247
Fermentations   250 250
Fermentations  spp. 252Ч253 spp. 252Ч253
Fermentations, extractive 84Ч85
Fermentations, lactic acid, acidification 82
Fermentations, lactic acid, adsorption 83Ч84
Fermentations, lactic acid, aeration 63Ч64
Fermentations, lactic acid, agitation 63Ч64
Fermentations, lactic acid, bacteria 50Ч54
Fermentations, lactic acid, batch processes 65Ч66
Fermentations, lactic acid, centrifugation 82Ч83
Fermentations, lactic acid, continuous membrane cell recycle systems 68Ч71
Fermentations, lactic acid, continuous stirred tank reactor systems 66Ч68
Fermentations, lactic acid, dialysis systems 77Ч79
Fermentations, lactic acid, economics 87Ч88
Fermentations, lactic acid, equipment 63
Fermentations, lactic acid, history 45Ч47
Fermentations, lactic acid, HPLC 86Ч87
Fermentations, lactic acid, immobilized cell systems 71Ч77
Fermentations, lactic acid, inoculum development 64Ч65
Fermentations, lactic acid, ion exchange 83Ч84
Fermentations, lactic acid, microfiltration 82Ч83
| Fermentations, lactic acid, modeling studies 79Ч81
Fermentations, lactic acid, molds 54
Fermentations, lactic acid, on-line control systems 87
Fermentations, lactic acid, pH control 86
Fermentations, lactic acid, process control 85Ч86
Fermentations, lactic acid, process kinetics 79Ч81
Fermentations, lactic acid, process systems 58Ч64
Fermentations, lactic acid, purification 82
Fermentations, lactic acid, raw materials 54Ч58
Fermentations, lactic acid, reverse osmosis 84
Fermentations, lactic acid, solvent extraction 84Ч85
Fermentations, lactic acid, sterilization 63
Fermentations, lactic acid, temperature control 63Ч64
Fermentations, lactic acid, tubular bioreactors 71
Fermentations, lactic acid, ultrafiltration 82Ч83
Fermentations, PHAs 159Ч161
Fungi see also "  " "
Fungi, phytase sources 272Ч273
Granules 146Ч151
High-performance liquid chromatography 86Ч87
HPLC see "High-performance liquid chromatography"
Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase 140Ч142
Immobilization 291Ч292
Immobilized cell systems 71Ч77
Indian meal moths 228
Inoculum development 64Ч65
Insect tolerance in plants 21Ч26
Insect tolerance, Cry genes and 31Ч33
Insecticides see "Biological insecticides"
Ion exchange 83Ч84
Lactic acid, commercial uses 48Ч50
Lactic acid, distillation 83
Lactic acid, fermentation, acidification 82
Lactic acid, fermentation, adsorption 83Ч84
Lactic acid, fermentation, aeration 63Ч64
Lactic acid, fermentation, agitation 63Ч64
Lactic acid, fermentation, bacteria 50Ч54
Lactic acid, fermentation, batch processes 65Ч66
Lactic acid, fermentation, centrifugation 82Ч83
Lactic acid, fermentation, continuous membrane cell recycle systems 68Ч71
Lactic acid, fermentation, continuous stirred tank reactor systems 66Ч68
Lactic acid, fermentation, dialysis systems 77Ч-79
Lactic acid, fermentation, economics 87Ч88
Lactic acid, fermentation, equipment 63
Lactic acid, fermentation, history 45Ч47
Lactic acid, fermentation, HPLC 86Ч87
Lactic acid, fermentation, immobilized cell systems 71Ч77
Lactic acid, fermentation, inoculum development 64Ч65
Lactic acid, fermentation, ion exchange 83Ч84
Lactic acid, fermentation, microfiltration 82Ч83
Lactic acid, fermentation, microorganisms 50Ч54
Lactic acid, fermentation, modeling studies 79Ч81
Lactic acid, fermentation, molds 54
Lactic acid, fermentation, on-line control systems 87
Lactic acid, fermentation, pH control 86
Lactic acid, fermentation, precipitation 82
Lactic acid, fermentation, process control 85Ч86
Lactic acid, fermentation, process kinetics 79Ч81
Lactic acid, fermentation, process systems 58Ч64
Lactic acid, fermentation, purification 82
Lactic acid, fermentation, raw materials 54Ч58
Lactic acid, fermentation, reverse osmosis 84
Lactic acid, fermentation, solvent extraction 84Ч85
Lactic acid, fermentation, sterilization 63
Lactic acid, fermentation, temperature control 63Ч64
Lactic acid, fermentation, tubular bioreactors 71
Lactic acid, fermentation, ultrafiltration 82Ч83
Lactic acid, properties 47Ч48
Microbes see "Transgenic microbe construction"
Microfiltration 82Ч83
Microorganisms, in phytase production 266Ч268
Molds, in lactic acid production 54
Mosquito larvae 222
Moths see "Indian meal moths"
Mussels see "Zebra mussels"
Nematodes, phytoparasitic 229Ч231
Nematodes, zooparasitic 228Ч229
Nitrogen, PHB synthesis and 154Ч155
Nutrition, phytic acid in 270Ч271
Osmosis see "Reverse osmosis"
Pan Labs cloning studies 290Ч291
Pellet formation, in phytase synthesis 278Ч279
pH control 86
PHA synthase (polymerase) 143Ч146
PHAs see "Poly(hydroxyalkanoates)""
PHB see "Poly( -hydroxybutyrate)" -hydroxybutyrate)"
Phosphorous, phytase synthesis and 274Ч278
Phototrophs 116Ч118
Phytase,  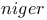 producing 266Ч268 272Ч273 producing 266Ч268 272Ч273
Phytase, active site determinations 284Ч285
Phytase, bacterial sources 272
Phytase, characterization 279Ч281
Phytase, cloning 288Ч291
Phytase, enzyme engineering studies 285Ч288
Phytase, feed studies 292Ч295
Phytase, fungal sources 272Ч273
Phytase, immobilization studies 291Ч292
Phytase, microorganisms producing 266Ч268
Phytase, plant sources 271
Phytase, pollution abatement and 295Ч296
Phytase, product development 263Ч269
Phytase, sequence studies 281Ч284
Phytase, synthesis, cornstarch source effects 274Ч278
Phytase, synthesis, medium ingredient effects 278Ч279
Phytase, synthesis, pellet formation effects 278Ч279
Phytase, synthesis, phosphorous effects 274Ч278
Phytase, synthesis, yields 278Ч279
Phytic acid in nutrition, role 270Ч271
Phytic acid in plants, role 269Ч270
Plants see also "Transgenic plants"
Plants, phytase sources 271Ч274
Plants, phytic acid in, role 269Ч270
Pollution abatement 295Ч296
Poly( -hydroxyalkanoates) 146 -hydroxyalkanoates) 146
Poly( -hydroxyalkanoates), granules 149-151 -hydroxyalkanoates), granules 149-151
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in -hydroxybutyrate) in 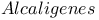 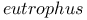 118 118
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in -hydroxybutyrate) in  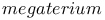 115Ч116 115Ч116
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in -hydroxybutyrate) in  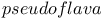 118 118
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in -hydroxybutyrate) in 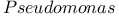  158 158
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in -hydroxybutyrate) in 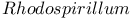 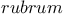 118 158Ч159 118 158Ч159
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in activated sludge 164Ч165 -hydroxybutyrate) in activated sludge 164Ч165
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in natural environments 164Ч165 -hydroxybutyrate) in natural environments 164Ч165
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in nitrogen-fixing bacteria 122Ч125 -hydroxybutyrate) in nitrogen-fixing bacteria 122Ч125
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in phototrophs 116Ч118 -hydroxybutyrate) in phototrophs 116Ч118
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) in transgenic plants 125Ч126 -hydroxybutyrate) in transgenic plants 125Ч126
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate) physical properties 165Ч169 -hydroxybutyrate) physical properties 165Ч169
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, approaches 176Ч179 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, approaches 176Ч179
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, bacterial 176Ч179 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, bacterial 176Ч179
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, Biopol 181Ч182 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, Biopol 181Ч182
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, enzymatic 179Ч180 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, enzymatic 179Ч180
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, extracellular 176 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, extracellular 176
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, factors effects 182Ч187 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, factors effects 182Ч187
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, hydrolytic 179Ч180 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, hydrolytic 179Ч180
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, methanogenic 176 176Ч179 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, methanogenic 176 176Ч179
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, PHA depolymerases in 187Ч194 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, PHA depolymerases in 187Ч194
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, polymer composition 187 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, polymer composition 187
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, temperature and 183Ч184 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, temperature and 183Ч184
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, under aerobic conditions 185 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, under aerobic conditions 185
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, under natural environments 181 -hydroxybutyrate), biodegradation, under natural environments 181
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis 128Ч135 135Ч138 -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis 128Ч135 135Ч138
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with 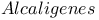 copolyesters 139 copolyesters 139
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with  -ketothiolases 140 -ketothiolases 140
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with acetoacyl-CoA reductase 140Ч142 -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with acetoacyl-CoA reductase 140Ч142
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase 140Ч142 -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis with hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase 140Ч142
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis, PHA synthase (polymerase) 143Ч146 -hydroxybutyrate), biosynthesis, PHA synthase (polymerase) 143Ч146
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), carbohydrate-utilizing halophilic archaebacteria 125 -hydroxybutyrate), carbohydrate-utilizing halophilic archaebacteria 125
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), characterization 128 -hydroxybutyrate), characterization 128
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), chemical synthesis 107Ч115 -hydroxybutyrate), chemical synthesis 107Ч115
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), chemotrophs 118Ч125 -hydroxybutyrate), chemotrophs 118Ч125
Poly( -hydroxybutyrate), descriptions 104Ч107 -hydroxybutyrate), descriptions 104Ч107
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



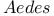
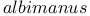 , rearing
, rearing 
 , active site determinations
, active site determinations 
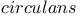
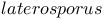
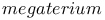
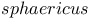
 genes"
genes"
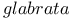
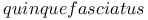 ,
, 
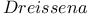
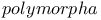
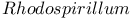
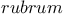
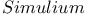
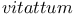
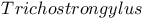
 -Butyrolactone polymerization
-Butyrolactone polymerization  -Endotoxins
-Endotoxins 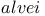
 "
"