|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Pathria P.K. Ч Statistical Mechanics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
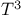 -law of specific heats 177Ч178 -law of specific heats 177Ч178
 -expansion 436Ч439 -expansion 436Ч439
Adiabatic processes 17 21 28 153 259
Adiabats of a Bose gas 167
Adiabats of a Fermi gas 229
Adiabats of black-body radiation 172
Adsorption 103
Anharmonic oscillators 86 87
Antiferromagnetism 316 320 361
Autocorrelation functions 466Ч467 474Ч479 481Ч484 491Ч492
Barometric formula 153
beta function 499
Beth Ч Uhlenbeck formalism 249Ч253 260
Bethe approximation to the Ising lattice 328Ч334 362 369 383 386Ч387 408 410
Binary alloys 321 361Ч362
Binary collision method 258Ч259 276 293 303 304
Binding energy of a Thomas Ч Fermi atom 226Ч227 231
Black-body radiation 168Ч172 190Ч191
Bloch's 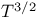 -law 360 -law 360
Block-spin transformation 415
Bogoliubov transformation 274Ч275
Bohr Ч van Leeuwen theorem 88 208
Boltzmann factor 2 61Ч62 87 135 153
Boltzmannian systems, classical 16 30 56 129Ч132 135 137 232Ч245
Boltzmannian systems, quantum-mechanical 258 260
Bose gas, imperfect 270Ч277 299Ч300
Bose liquids, energy spectrum of 277Ч280 300
Bose Ч Einstein condensation 160Ч168 187 188Ч190 193 400Ч403
Bose Ч Einstein condensation, with interactions 270Ч273 278 299Ч300
Bose Ч Einstein functions 159 506Ч508
Bose Ч Einstein statistics 5 6 119 127Ч137 148Ч149
Bose Ч Einstein systems 120Ч124 127Ч137 157Ч194 249Ч260 490
Bose Ч Einstein systems, multi-dimensional 190 192 398Ч404
Bose Ч Einstein systems, nonuniform 283Ч285
boundary conditions 449 495Ч497
Bragg Ч Williams approximation to the Ising lattice 321Ч327 332 333 360Ч362 383 386Ч387 410
Brillouin function 75Ч76
Broken symmetry 324 365
Brownian motion 452 459Ч469 470Ч474 490Ч492
Brownian motion of a suspended mirror 472Ч474 490
Brownian motion, observation of 462 480 490
Canonical distribution 34 45 51 53 55
canonical ensemble 34 43Ч56 60Ч63 83 85 109Ч110 131Ч133
Canonical transformations 40 64
Chandrasekhar limit 222
chemical potential 14 54 90Ч92 see
Chemical potential of a Bose gas 272Ч273
Chemical potential of a classical gas 24Ч25
Chemical potential of a Fermi gas 200 204Ч205 214 227Ч230
Chemical potential of a Fermi liquid 297 302
Chemical potential of a gas of phonons 193
Chemical potential of a gas of photons 193
Circulation, quantized 280Ч288 300Ч301 303
Classical limit 26 122 135 140 160 193 196Ч197
Classical systems 15Ч25 30Ч34 56Ч60
Classical systems in the canonical ensemble 56Ч60 132
Classical systems in the grand canonical ensemble 132Ч133
Classical systems in the microcanonical ensemble 131
Classical systems, interacting 63Ч6 232Ч245
Cluster expansions, classical 232Ч239
Cluster expansions, general 245Ч249
Cluster expansions, quantum-mechanical 254Ч258
Cluster functions 256Ч257 260
Cluster integrals 235Ч236 239 246 248 257 260
Cluster integrals, irreducible 239 248 261 359
Complexions see "Microstates"
Compressibility, adiabatic 189 228 412
Compressibility, isothermal 101 189 228 412 454 458
Condensation 306Ч310 see
Condensation of a van der Waals gas 310Ч314
Condensation, scaling hypothesis for 363
Condensation, Yang Ч Lee theory of 310
Conductivity, electrical 209 212 484
Conductivity, thermal 209 212
Configuration integral 233Ч237 245Ч246 254Ч255
Configurational distribution functions 456Ч458
Conformal transformation 440Ч441
Cooperative phenomena see "Phase transitions"
Coordination number 318 365
Correlation function 349Ч351 354Ч355 364 418
Correlation function in the mean-field approximation 351Ч353 358 363
Correlation function in the scaled form 354 446
Correlation function of a Bose gas 402Ч403 411
Correlation function of a fluid 457Ч459
Correlation function of an n-vector model 373Ч375
Correlation function of the Ising model 371 387Ч388 410
Correlation function of the spherical model 395Ч397 411
Correlation function of the X-Y model 405
correlation length 353 355 364 406 414 417
Correlation length in the mean-field approximation 352Ч353 359
Correlation length of a Bose gas 403 411
Correlation length of an n-vector model 374Ч376 409
Correlation length of the Ising model 371Ч372 387Ч388 408 409
Correlation length of the spherical model 396Ч397 411
Correlation length of the X-Y model 404Ч405
Correlations, spatial 123Ч124 452 456Ч459
Correlations, spin-spin 289 331
Correlations, statistical 123Ч124 137 490 494
Corresponding states, law of 312
Covariance matrix 489 494
Critical behavior of a Bose gas 161Ч165 400Ч402 412Ч413
Critical behavior of a fluid 363
Critical behavior of a magnetic system 342Ч343 346Ч347 351Ч353 363
Critical behavior of a van der Waals gas 311Ч314 359
Critical behavior of the Ising model 324Ч326 329Ч333 370Ч372 383 385Ч388 410 432 434Ч436 450
Critical behavior of the spherical model 392Ч395 411 433
Critical behavior of the X-Y model 404Ч405
Critical curve 435 437 451
Critical dimension, lower 404 441 445 448
Critical dimension, upper 357 398 441 448
Critical exponents 334Ч338 353Ч356 362 363 364 451
Critical exponents of a Bose gas 401Ч404
Critical exponents of an n-vector model 375 407 437 438Ч439 451
Critical exponents of polymers 407
Critical exponents of the Ising model 370 372 388 407 432 434
Critical exponents of the spherical model 395Ч397 407 411Ч412 433
Critical exponents, experimental values of 336
Critical exponents, hyperscaling relation among 355Ч357 406
Critical exponents, mean-field values of 335 342Ч343 353Ч355 407 430Ч431
Critical exponents, scaling relations among 346Ч347 355Ч356 364 406
Critical exponents, theoretical values of 406Ч407
Critical exponents, thermodynamic inequalities for 338Ч341 355Ч356 362
Critical opalescence 101 452 459
Critical surface 427Ч429 451
Critical trajectories 428
Critical velocity of superflow 180 187Ч188 194 285Ч258 301
Crossover phenomena 440
Curie temperature 324 329Ч330 360
Curie Ч Weiss law 326 343 353 360
Curie's law 73 75 203 205 208
Darwin Ч Fowler method 47Ч52
Debye function 176 191
Debye temperature 176Ч178 191 211
Debye's theory of specific heats 175Ч178 191Ч192
Decimation transformation 415Ч418 418Ч426 426Ч431 449
Degeneracy criterion 122Ч123 140 157 193 see
Delta function 501Ч503 505
Density fluctuations 100Ч101 455Ч456 458 490
Density fluctuations, in the critical region 459
Density function in phase space 4 31Ч34
Density matrix 6 104Ч110 124Ч125 126
Density matrix of a free particle 111Ч113 255
Density matrix of a linear harmonic oscillator 113Ч115
Density matrix of a system of free particles 119Ч124
Density matrix of a system of interacting particles 254Ч256
Density matrix of an electron 111 124
Density of states 20 56 59Ч60 230 250Ч252
Density of states for a free particle 37 230 495Ч497
Density of states for a system of harmonic oscillators 68 70
Detailed balancing 106
| Diamagnetism, Landau 202 206Ч209
diatomic molecules 87Ч88 103 142Ч150 154Ч156
Dietrici equation of state 359
Diffusion coefficient 463 465 471 481Ч483
Diffusion equation 463 471
Diffusion, Brownian motion in terms of 463Ч464
Dipole-dipole interaction 88
Dirac delta function 501Ч503 505
Dissipative phenomena 452 464 481Ч484
Distribution functions, configurational 456Ч458
Doppler broadening 153
Duality transformation 381Ч382
Dulong Ч Petit law 175
Edge effects 496
effective mass 187 192 208 210 231 296Ч297 299 302 304
Effusion 139 154
Effusion of electrons from metals 213Ч216 216Ч218
Effusion of photons from a radiation cavity 171
Einstein function 174
Einstein Ч Smoluchowski theory of the Brownian motion 459Ч462
Einstein's relations 452 465Ч466
Electron gas in metals 5Ч6 209Ч218
Electrons in a magnetic field 111 206Ч209
Elementary excitations in a Bose liquid 277Ч280 280Ч285 285Ч288 300Ч301
Elementary excitations in a Fermi liquid 293Ч299 302
Elementary excitations in an imperfect Bose gas 273Ч277 300
Elementary excitations in liquid helium II 182Ч188 192 279Ч280 285 287
Energy cells 127Ч130
Energy fluctuations 60Ч3 85 101Ч102 455Ч456
Ensemble average 31 35 105 107
Ensemble of Brownian particles 463 470Ч472 482
Ensemble theory 3Ч4 6 30Ч36 43Ч55 60Ч63 90Ч95 100Ч102 104Ч110
Enthalpy 15
entropy 12Ч13 20 22Ч4 27 36 54Ч55 71 95 166 196
Entropy in nonequilibrium states 453Ч455 485Ч487
Entropy of an Ising ferromagnet 326 361 362 410
Entropy of mixing 22Ч24
Entropy, statistical interpretation of 13 54Ч55 102 108
Equation of state see also "van der Waals equation of state"
Equation of state of a Bose gas 159Ч160 253 272
Equation of state of a Fermi gas 197 253
Equation of state of a lattice gas 360 409 410
Equation of state of classical systems 16 21 65Ч66 238Ч245 247Ч249 359
Equation of state of quantum-mechanical systems 247Ч249 258 299 301
Equation of state, reduced 312
Equilibrium constant 85 154 331
Equilibrium, approach to 11Ч12 13Ч14 452 469Ч472 485
Equilibrium, deviations from 453Ч456 489Ч490
Equilibrium, persistence of 468
Equipartition theorem 63Ч65 86 151 153 465 468 472 473 479
Equipartition theorem, failure of 65 143 145Ч146 149 151 165 174Ч175 200Ч201 209
Ergodic hypothesis 41
exchange interaction 315Ч316
Exclusion principle 5 29 118 128 198 231 267 268 493
Extensive variables 9Ч10 22 24 28
Factorial function 497Ч501
Fermi energy 198 200 202 205 210 214Ч215 219 229Ч230
Fermi gas, imperfect 289Ч293 297Ч299 301Ч302
Fermi liquids, energy spectrum of 293Ч299 302
Fermi momentum 198 219 220 224 231 294 302
Fermi oscillators 87
Fermi temperature 200 210 219 227 229
Fermi velocity 229 295
Fermi Ч Dirac functions 195 508Ч510
Fermi Ч Dirac statistics 5 6 118Ч119 127Ч137 148Ч149
Fermi Ч Dirac systems 120Ч124 127Ч137 195Ч231 249Ч260 490
Fermi Ч Dirac systems, n-dimensional 229
ferromagnetism 314Ч316 320 323Ч326 329Ч330 see
Feynman's circulation theorem 281
Feynman's theory of a Bose liquid 278Ч282 285 300
Fick's law of diffusion 463
Field-theoretic approach 262Ч270
Finite-size effects 18Ч19 190 397 411 412 413 441Ч449 495Ч497
Finite-size scaling 441Ч449
Fixed point 406 427Ч428 432Ч433 435 450
Fixed point, Gaussian 436Ч437
Fixed point, non-Gaussian 436Ч437
Fluctuation-dissipation theorem 350 354 356 409 447 452 481Ч484 487
Fluctuations 452Ч494 see "Phase
Fluctuations in a multiphase system 364
Fluctuations in an (L,R)-circuit 480Ч481
Fluctuations in an electrical resistor 483Ч484
Fluctuations in the canonical ensemble 51Ч2 60Ч63 85
Fluctuations in the grand canonical ensemble 100Ч102 103
Fluctuations of occupation numbers 7 136Ч137 155
Fluctuations thermodynamic 453Ч456 489Ч490
Fluctuations, critical 101 459 492
Fluctuations, frequency spectrum of 474Ч481
Flux quantization in superconductors 303
Fokker Ч Planck equation 469Ч472 491
Fourier analysis of fluctuations 474Ч481 491Ч492
Fowler plot 218
Free volume 84Ч85
Fugacity 94 98Ч99 110 213 238Ч239 247Ч248 see
Fugacity of a Bose gas 161Ч162 273 299
Fugacity of a Fermi gas 200 227 292 301
Fugacity of a gas of phonons 193
Fugacity of a gas of photons 193
Fugacity of a lattice gas 319Ч320 409
Fugacity of a two-phase system 98Ч99
Gamma function 497Ч501
Gaussian model 389
Gibbs free energy 15 24Ч25 54
Gibbs paradox 22Ч25 25Ч26
Ginzburg criterion 357
Goldstone modes 376
grand canonical ensemble 90Ч95 100Ч103 110
Grand partition function 94Ч95 110
Grand partition function of a lattice gas 319
Grand partition function of a multiphase system 308Ч310
Grand partition function of an ideal gas 133Ч134 158 195
Grand partition function of an imperfect gas 238 245 299 301
Ground-state properties of a Bose gas 270Ч272 273Ч277 300
Ground-state properties of a Fermi gas 197Ч199 202Ч203 205 209 220Ч221 226Ч227 230 231 292Ч293 297Ч299 301Ч302
H-Theorem 3
Hard sphere gas 1 27 86 243Ч245 252Ч253 303
Harmonic approximation 173
Harmonic oscillators 27 37Ч38 41 66Ч71 86 97Ч98 168Ч169 173Ч178
Heisenberg model 316 360
Helicity modulus 365
Helmholtz free energy 15 25 53 95
Hyperscaling relation 355Ч357 430Ч431
Ideal gas of bosons 158Ч168 398Ч404 412Ч413
Ideal gas of fermions 195Ч209
Ideal gas, classical 15Ч25 36Ч37 57Ч60 62Ч63 65 96Ч97
Ideal gas, quantum-mechanical 115Ч124 127Ч139
Indistinguishability of particles 5 25Ч26 96 117Ч119 127Ч129
Indistinguishability of photons 5 169
Inertial density of excitations 179Ч182 186 192
Integrating factor for heat 94
Intensive variables 10 28
Internal molecular field 323 328 360 see
Internal motions of molecules 140Ч152 154Ч155 190
Irrelevant variables 429 434 437 451
Irrelevant variables, dangerously 430Ч431 437
Irreversible phenomena 3 452 459 463Ч465 469 484Ч489 493
Ising model 316 319 321Ч334 360 362
Ising model in one dimension 366Ч372 407Ч409 418Ч421 432
Ising model in three dimensions 405Ч407
Ising model in two dimensions 377Ч388 410 423Ч426 433Ч436
Isothermal processes 21 see
Isotherms of a Bose gas 166
Isotherms of a multiphase system 307Ч308 310
Isotherms of a van der Waals gas 311
Joule Ч Thomson coefficient 260
Kinetic coefficients 484
Kinetic pressure 1Ч2 138Ч139 192
Kirkwood approximation 362
Kramers' q-potential 93 103 see
Kubo's theorem 484 487
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



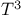 -law of specific heats
-law of specific heats  -expansion
-expansion 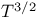 -law
-law