|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gavrila M. (ed.) Ч Atoms in intense laser fields |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) 2 11Ч25 43Ч45 50Ч54 61Ч65 see
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) and harmonic generation 175Ч177 276Ч277 313
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) in long pulse regime 50Ч51
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) in nonperturbative theories 17Ч23 267Ч271 311Ч312 489Ч499
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) in numerical experiments 311Ч312
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) in perturbation theory 11Ч17 490Ч491 494
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) in short pulse regime 52Ч54 61 62
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), hydrogen atom, Floquet results 396Ч405 407Ч411 488Ч499
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), hydrogen atom, TDSE results 267Ч271
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), microwave 99Ч105
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), photoelectron energy spectra 12 14 33 51Ч52 54 60 254Ч256 267Ч271 311Ч312 355 356 360 367
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), resonance structures in 52Ч54
Above-threshold ionization (ATI), role of angular momentum 23Ч25
Absorbing boundaries, for TDSE approach 256
Ac Stark shifts 16 26 29Ч34 44 52 58 59 61 77Ч98 264 269 291 294 307Ч308 see
Adiabatic evolution of resonance (Floquet) states 376Ч377 385Ч387 405Ч406 444Ч445 493Ч494 498Ч499
Adiabatic stabilization 439
Adiabatic stabilization of ground state of H 492Ч494 496
Adiabatic stabilization of Rydberg states 498Ч499
Alkaline-earth atoms, MPI studies of 8 35Ч36
Argon, ATI photoelectron spectra 54 60
Argon, harmonic generation, experiment 148Ч155
Argon, phase mismatch 187
Argon, single-atom harmonic generation spectrum 172
ATI see "Above-threshold ionization"
Autoionization 98Ч99
Autoionizing states 385
Avoided level crossings 77 82Ч85 91 238Ч239 385Ч387 399 413 472 480 482
Beam focusing 55 146 406
Beam focusing, influence on harmonic generation 157Ч160 183Ч184
Beam focusing, influence on photoionization yields 54Ч61 405Ч407
Boundary conditions, stationary approach, laboratory frame 442Ч444
Boundary conditions, stationary approach, oscillating frame 446Ч450
Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) 6
Classical field versus photon descriptions of microwave ionization 80Ч91
Coherence length 194
Coincidence measurements, electron 36
Collision-free ionization 211Ч225 see
Complex coordinate dilatation 424
Complex electric field plane 387Ч391
Continuity equation 440 446 450
Continuum generation 7
Correlation diagrams, atomic 472 480Ч482
Coulomb explosion, molecular 219
Diabatic evolution of Floquet (resonance) states 385Ч387 396 398 405Ч406 445
Dichotomy, atomic 277Ч287 474Ч476 484Ч486 see
Dipole approximation 440 500
Dipole, radiatively induced atomic 162Ч163 170 257
Dominant and shadow states 376 382Ч385 388 417Ч419
Doubly charged ions 35 36
Doubly excited states 290
Dressed potential Hamiltonian 325 456 463
Dynamic stabilization 502Ч504
Energy level crossings (avoided crossings) see "Quasi-energies and level crossings"
Energy level shifts 307Ч308 411Ч413 462 465 467Ч468 473Ч474 see "Perturbation "Stark in
Excess-photon ionization (EPI) 2 see
Faisal Ч Reiss theory 63Ч64 405 see "Keldysh
Field ionization 2 23 37 67Ч69 see
Field-induced bound states 384Ч385 417Ч419 500Ч501
Floquet states 87 169 375Ч376 381 see
Floquet states, adiabatic evolution 376Ч377 385Ч387 405Ч406 444Ч445 493Ч494 498Ч499
Floquet states, boundary conditions 381Ч383 424
Floquet states, diabatic evolution 385Ч387 396 398 405Ч406 445
Floquet states, dominant and shadow states 376 382Ч385 388 417Ч419
Floquet states, normalization 392Ч393 453
Floquet theory (laboratory frame) 375Ч379 380Ч382 see
Floquet theory (laboratory frame) for Rydberg states 85Ч89 92Ч93
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), boundary conditions 381Ч383 424 442Ч444
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), eigenvalue problem 380Ч385
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), high frequency regime 411Ч419 501
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), low frequency regime 419Ч423
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), normalization of states 392Ч393 453
Floquet theory (laboratory frame), system of coupled equations 170 381 423Ч429
Fluorescence following laser irradiation from atomic ions 225Ч229
Fluorescence following laser irradiation from ionic molecules 229Ч233
Free-free transitions (FFT) see also "Scattering laser
Free-free transitions (FFT) and ionization 442 448 463
Free-free transitions (FFT) in numerical experiments 315Ч317
Gordon Ч Volkov wave function 329 441 445 see
Green's functions 456Ч459
Harmonic generation 7 119Ч127 139Ч201 257Ч258 271Ч276 286Ч288 378 379
Harmonic generation and ATI 175Ч176 276Ч277
Harmonic generation from 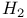 274Ч276 274Ч276
Harmonic generation from Ar 148Ч155
Harmonic generation from H 169Ч170 272Ч276
Harmonic generation from He 149 154
Harmonic generation from Kr 148 149 154
Harmonic generation from models 173Ч177 274Ч276
Harmonic generation from Ne 149Ч155 295Ч297
Harmonic generation from stabilized states 286Ч288
Harmonic generation from Xe 147Ч154 199 295
Harmonic generation in large ponderomotive potentials 119Ч127 130Ч131
Harmonic generation, experimental methods 143Ч147
Harmonic generation, experimental results 126Ч127 147Ч161
Harmonic generation, fifth harmonic 155 156 158 159
Harmonic generation, phase matching effects 119Ч127 178Ч196 258 271Ч276
Harmonic generation, single atom spectra 162Ч177 271Ч273
Harmonic generation, theoretical description 161Ч199
Harmonic generation, third harmonic 154 199
Helium, harmonic generation 149 154
Helium, single active electron model 291Ч294
Helium, threshold ionization intensity 213 216
Helium, time-dependent 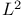 -basis theory 365 -basis theory 365
Helium, time-dependent Hartree Ч Fock method for 260 288Ч291
High-frequency Floquet theory 455Ч499
High-frequency Floquet theory, analytical results for H 471Ч479 488Ч496
High-frequency Floquet theory, convergence of iteration scheme 468Ч470
High-frequency Floquet theory, high-frequency condition 469
High-frequency Floquet theory, iteration scheme 459Ч463
High-frequency Floquet theory, lowest approximations 463Ч468
High-frequency Floquet theory, relativistic generalization 500
High-frequency Floquet theory, two-electron case 499Ч500
High-frequency regime 411Ч419 455Ч500
Hydrogen atom, experiments 8 25Ч27
Hydrogen atom, experiments, Bielefeld experiment compared to theory 407Ч411
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, Bielefeld experiment, comparison with 26 407Ч411
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, harmonic generation 169Ч171 378 379
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, high-frequency regime 411Ч419
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, multiphoton ionization (MPI) 396Ч405
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, stabilization 414Ч417
Hydrogen atom, full Floquet theory results, two-color ionization 394Ч395
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, adiabatic stabilization 492Ч494 496 498Ч499 504
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, in circularly polarized fields 472Ч474 476Ч479 486Ч487 489Ч494
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, in linearly polarized fields 472Ч476 479Ч486 494Ч499
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, ionization 488Ч499
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, large-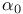 474Ч479 492Ч494 495Ч496 500 474Ч479 492Ч494 495Ч496 500
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, low-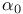 472Ч474 490Ч491 494 472Ч474 490Ч491 494
Hydrogen atom, high-frequency Floquet theory results, structure 470Ч487
Hydrogen atom, TDSE results, ATI photoelectron spectra 267Ч271
Hydrogen atom, TDSE results, harmonic generation 170Ч173 175 271Ч277 295Ч297
Hydrogen atom, TDSE results, ionization rates 261Ч267
Hydrogen atom, TDSE results, stabilization and trapping 277Ч287
Hydrogen molecule, harmonics spectra 274
Hydrogen negative ion 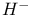 9Ч10 403Ч405 499Ч500 9Ч10 403Ч405 499Ч500
Intensity, time-dependent, and stationary approach 405Ч407 444Ч445 493Ч494 498Ч499
Intensity, time-dependent, in TDSE approach 267Ч271 305Ч306
Inverse Bremsstrahlung 110 115 see
Inverse Faraday effect 134
Ionization see also "Multiphoton ionization (MPI)"
Ionization, channels 381Ч384 448Ч449
Ionization, rates see "Rates of ionization"
Ionization, regimes 317Ч323
Ionization, resonant 34 35 52Ч54 256 268 269 335Ч370 385Ч387
Kapitza Ч Dirac effect 101
Keldysh parameter 212 264 289 380 419
Keldysh theory 215Ч218 405 see "Faisal
Keldysh Ч Faisal Ч Reiss (KFR) theory 18 24 27 63Ч64 see "Faisal
Kramers Ч Henneberger frame 323Ч324 394 see
Kramers Ч Henneberger frame, ionization physics in 277 323Ч331
Krypton, harmonic generation, experiment 148 149Ч151 154
| Krypton, phase mismatch for 187
Krypton, single-atom harmonic generation spectrum 172
Krypton, threshold ionization intensity 213
Landau Ч Zener theory 55Ч56 77 79 80 82Ч85 89 91 239 377
Lasers, 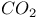 , picosecond 7 112 , picosecond 7 112
Lasers, amplifiers for short pulses 5Ч7
Lasers, dye 6
Lasers, excimer 6Ч7
Lasers, frequency conversion 7Ч8
Lasers, Kr F*, subpicosecond 208Ч210
Lasers, Nd:YAG 5
Lasers, oscillators for short pulses 4Ч5
Lifetime, atomic 450Ч455 see
Lifetime, atomic, of hydrogen 488Ч499
Line of charges 464 471 486 487
localization 276Ч287 322Ч323 see atomic"
Low-frequency regime 419Ч423
Lowest order perturbation theory (LOPT), limitations of 11Ч17 310 435Ч436 490Ч492 494
Mask function 256
Microwave cavity 70Ч76
Microwave excitation of Rydberg states 80Ч82
Microwave ionization of Rydberg states, circular polarization 94Ч99
Microwave ionization of Rydberg states, linear polarization 77Ч80 91Ч94
Molecular MPI 218Ч225
Molecular MPI, atomic ion production 219Ч221
Molecular MPI, diatomic ion yields 224Ч225
Molecular MPI, site-specific energy deposition 221Ч224
MPI see "Multiphoton ionization (MPI)"
Multiphoton ionization (MPI) 1Ч37 see "Collision-free
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), in nonperturbative theories 17Ч23
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), in perturbation theory 11Ч17
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), of atoms 212Ч218
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), of molecules 218Ч225
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), quasistatic model of 111Ч116 see
Multiphoton ionization (MPI), role of angular momentum 23Ч25
Multiphoton multiple ionization 3 35Ч37
Multiphoton multiple ionization and collective electron response 3 36
Multiphoton multiple ionization, direct 35Ч37
Multiphoton multiple ionization, sequential 35
Negative ions, as targets for MPI experiments 8Ч10
Neon, harmonic generation, experiment 149Ч156
Neon, single-atom harmonic generation spectra 295Ч297
Neon, threshold ionization 213
Normalization of Floquet (resonance) states 392Ч393 453
Numerical experiments 301Ч303
Oscillating, Kramers Ч Henneberger frame 445Ч446 see
Pade approximants method 390Ч391 393
Peaceman Ч Rachford propagator 249 252 289
Perturbation theory expansion for level shifts 14Ч17 390Ч391 421
Perturbation theory, lowest order results for energy level shifts 472Ч474
Perturbation theory, lowest order results for harmonic generation 273
Perturbation theory, lowest order results for ionization rates 263 403Ч405 414 490Ч491 494
Phase matching in harmonic generation 183Ч195 271Ч273
Phase matching in harmonic generation, geometrical 184
Phase matching in harmonic generation, model, for strong fields 193Ч195
Phase matching in harmonic generation, neutral atoms 181 186 187
Phase matching in harmonic generation, strong fields 188Ч193
Phase matching in harmonic generation, weak fields 183Ч188
Phase mismatch in harmonic generation, free electrons 187 198
Photoelectric yield (signal) 339Ч340 405Ч411
Photoelectric yield (signal), spatial structure in 54Ч61
Photoelectron energy spectra (ATI) 50Ч61 254Ч256 267Ч271 355 356 367
Photon versus classical field descriptions of microwave ionization 80Ч91
Plasmas, electron temperature 133
Plasmas, enhanced collision frequency 134
Plasmas, magnetic field effects 133Ч134
Plasmas, MPI effects in 131Ч134 240
Polarizability, atomic 30 186 258
Ponderomotive forces 44Ч52 101 410Ч411 442
Ponderomotive potential energy 45Ч52 99Ч105 117Ч119 262 267 339 374 377 379 396
Potential (energy), dressed 324Ч325 463 464
Potential (energy), dressed Coulomb 471
Potential (energy), effective, one-electron 249 260Ч261
Potential (energy), end-point 474 475
Potential (energy), short range 444 457 500Ч501
Potential (energy), soft core Coulomb 303Ч306 502 503
Potential (energy), zero-range 20 24 378
Propagation of radiation in ionized medium 119Ч127 196Ч198
Propagation of radiation in ionized medium, channeled propagation 240
Propagation of radiation in neutral medium, integral formalism for 180Ч187
Propagation of radiation in neutral medium, phase matching, strong fields 188Ч195
Propagation of radiation in neutral medium, phase matching, weak fields 183Ч187
Propagation of radiation in neutral medium, theoretical background 178Ч180
Quasi-energies 376 379 382 448 see
Quasi-energies and level crossings (avoided crossings) 77 82Ч85 377 385Ч390 396Ч403
Quasi-energies for hydrogen 396Ч405
Quasi-energies, analytic structure in complex electric field plane 387Ч391
Quasi-energies, location in complex energy plane 381Ч385
Quasi-energies, numerical computation 379 423Ч429
Quasi-energies, series expansion in electric field 390Ч391 420Ч421
Quasi-energies, series expansion in frequency 420Ч423
Quasi-static model of MPI 111Ч116
Quasi-static model of MPI and conservation laws 116Ч117
Quasi-static model of MPI, relativistic generalization 127Ч130
Quiver energy see "Ponderomotive potential energy"
Quiver motion 15 22 28 127 250 256 441 see
Quiver motion, relativistic 127Ч129
Rates of ionization 256 376 381Ч382 391Ч394 450Ч453 see
Rates of ionization in Keldysh and Faisal Ч Reiss approximation 405
Rates of ionization in LOPT 263 403Ч405 414 490Ч491 494
Rates of ionization, Born approximation for 488Ч489
Rates of ionization, continuity equation approach 450Ч451
Rates of ionization, high-frequency expressions 465Ч467
Rates of ionization, partial 391Ч394 450Ч453
Refractive index, nonlinear 156 179
REMPI (resonantly enhanced multiphoton ionization) 335 see resonant"
REMPI (resonantly enhanced multiphoton ionization), density matrix description of 337Ч343
REMPI (resonantly enhanced multiphoton ionization), type A 343Ч353
REMPI (resonantly enhanced multiphoton ionization), type B 353Ч358
REMPI (resonantly enhanced multiphoton ionization), type C 358Ч360
Resonance energies 448Ч449 461Ч462 see
Resonance energies, in high-frequency Floquet theory 461Ч462 465Ч468
Resonance states 436Ч438 446Ч450 see
Resonance states in high-frequency Floquet theory 459Ч468
Resonant ionization see "REMPI"
Rydberg atoms (states) 68Ч69
Rydberg atoms (states) in strong microwave fields 67Ч106
Rydberg atoms (states), adiabatic stabilization 496Ч499
Rydberg atoms (states), stark shift in 77Ч98
Saturation (intensity) 3 152 199 340
Scattering, laser assisted 378 383 see
Shadow poles see "Dominant and shadow states"
Short-wavelength generation 207Ч241
Simple-man's theory 22 24 28 102Ч105 see Quasi-static
Space charge 10
Space-time dependence of laser pulse 254 305Ч306 314Ч315 349 405Ч407 see time-dependent"
Space-time dependence of laser pulse, and photoelectric yields 267Ч271 405Ч407
Space-time dependence of laser pulse, effects of 345Ч346 349Ч352 354Ч357 369Ч370 409Ч410
Space-translated Schroedinger equation 445
Spectrometers (electron) for MPI/ATI experiments 10Ч11
Stabilization see also "Adiabatic stabilization" "Dynamic "Localization"
Stabilization and ponderomotive shift of Rydberg levels 118Ч119
Stabilization in full Floquet theory 414Ч417
Stabilization in high-frequency Floquet theory 439 492Ч494 496 498Ч499
Stabilization in numerical experiments 317Ч332
Stabilization in TDSE approach 277Ч287 367Ч369
Stabilization, comparison of Adiabatic and Dynamic stabilizations 504
Stark shifts in Rydberg atoms 77Ч98
Stationary approach 436Ч454 see "Floquet "Resonance
Stationary approach and wave packet approach 454Ч455 502Ч504
Stationary approach for oscillating frame 446Ч454
Stationary approach for oscillating frame, boundary conditions 446Ч450
Stationary approach for oscillating frame, high-frequency Floquet theory 455Ч499
Stationary approach for oscillating frame, limitations of 452 454Ч455
Stationary approach for oscillating frame, regularization procedure 450 462Ч463
Stationary approach for oscillating frame, resonance states 436Ч438 446Ч450 454Ч455
Stationary approach, connection with wave packet approach 454Ч455 502Ч504
Stationary approach, laboratory frame 439Ч444
Stationary approach, oscillating frame 446Ч454
Stimulated photon scattering 46 50
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



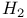
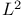 -basis theory
-basis theory 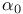
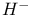
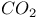 , picosecond
, picosecond